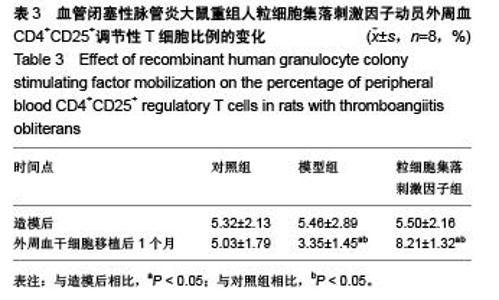
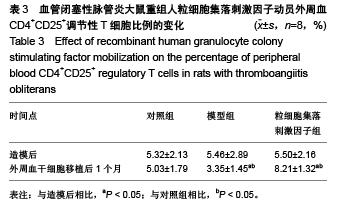
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (50): 8102-8107.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.50.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
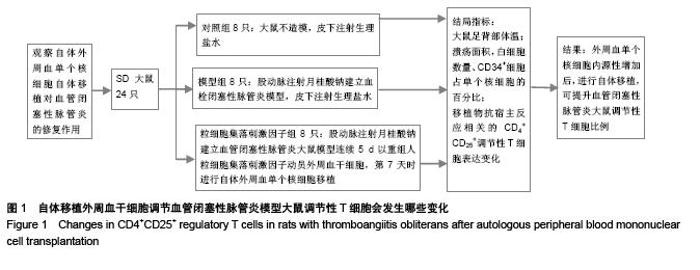
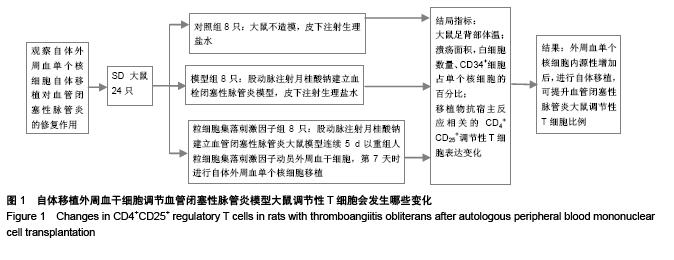
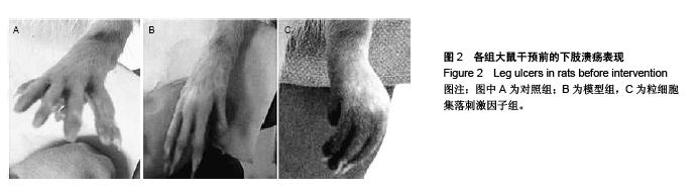
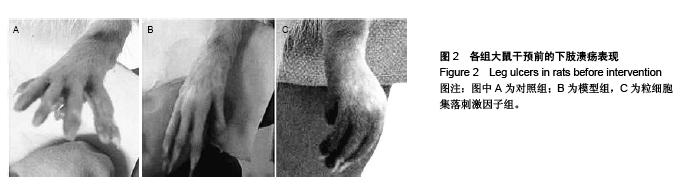
Autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cell transplantation following cell mobilization increases CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in rats with thromboangiitis obliterans
Zhao Feng1, Deng Mo2
- 1Department of Interventional Radiology, 2Department of Anesthesiology, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-21Online:2015-12-03Published:2015-12-03 -
Contact:Deng Mo, Master, Attending physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhao Feng, Master, Attending physician, Department of Interventional Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical Science Project of Hebei Province, No. 20110515
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Feng1, Deng Mo2. Autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cell transplantation following cell mobilization increases CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in rats with thromboangiitis obliterans[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(50): 8102-8107.
share this article
| [1] 王会梅,高荣芳,吕金波.中西医结合治疗下肢动脉硬化性闭塞症65例[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2007,13(4):398. [2] Latza U, Stang A, Bergmann M, et al. The problem of response in epidemiological studies in Germany (part I). Gesundheitswesen. 2004;66(5):326-336. [3] Ruiz-Salmeron R, de la Cuesta-Diaz A, Constantino-Bermejo M, et al. Angiographic demonstration of neoangiogenesis after intra-arterial infusion of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(10):1629-1639. [4] Lasala GP, Minguell JJ. Vascular disease and stem cell therapies. Br Med Bull. 2011;98:187-197. [5] Idei N, Soga J, Hata T, et al. Autologous bone-marrow mononuclear cell implantation reduces long-term major amputation risk in patients with critical limb ischemia: a comparison of atherosclerotic peripheral arterial disease and Buerger disease. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4(1):15-25. [6] Matsumura G, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Shin'oka T, et al. First evidence that bone marrow cells contribute to the construction of tissue-engineered vascular autografts in vivo. Circulation. 2003;108(14):1729-1734. [7] Simper D, Stalboerger PG, Panetta CJ, et al. Smooth muscle progenitor cells in human blood. Circulation. 2002;106(10): 1199-1204. [8] Lin Y, Weisdorf DJ, Solovey A, et al. Origins of circulating endothelial cells and endothelial outgrowth from blood. J Clin Invest. 2000;105(1):71-77. [9] Yoon YS, Wecker A, Heyd L, et al. Clonally expanded novel multipotent stem cells from human bone marrow regenerate myocardium after myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115(2):326-338. [10] Yamashita J, Itoh H, Hirashima M, et al. Flk1-positive cells derived from embryonic stem cells serve as vascular progenitors. Nature. 2000;408(6808):92-96. [11] Miranville A, Heeschen C, Sengenès C, et al. Improvement of postnatal neovascularization by human adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Circulation. 2004;110(3):349-355. [12] 宫立众,夏顺中.外周血干细胞移植研究进展[J].重庆医学,2002, 31(5):430-432. [13] 李施施,刘忠,严庆丰.外周血细胞重编程为诱导性多潜能干细胞的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2011,(8):930-935. [14] 吴德沛,唐晓文,夏学鸣.自体外周血干细胞移植并发Ⅳ度移植物抗宿主病一例[J].中华血液学杂志,2000,21(8):423-424. [15] Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995;155(3):1151-1164. [16] Shevach EM. Certified professionals: CD4(+)CD25(+) suppressor T cells. J Exp Med. 2001;193(11):F41-46. [17] Annacker O, Pimenta-Araujo R, Burlen-Defranoux O, et al. CD25+CD4+ T cells regulate the expansion of peripheral CD4 T cells through the production of IL-10. J Immunol. 2001; 166(5):3008-3018. [18] Field EH, Matesic D, Rigby S, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells in acquired MHC tolerance. Immunol Rev. 2001;182: 99-112. [19] Cohen JL, Trenado A, Vasey D, et al. CD4(+)CD25(+) immunoregulatory T Cells: new therapeutics for graft-versus-host disease. J Exp Med. 2002;196(3):401-406. [20] Hoffmann P, Ermann J, Edinger M, et al. Donor-type CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells suppress lethal acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Exp Med. 2002;196(3):389-399. [21] Edinger M, Hoffmann P, Ermann J, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells preserve graft-versus-tumor activity while inhibiting graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation. Nat Med. 2003;9(9):1144-1150. [22] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30. [23] 孙晓春,蔡花,吴乐乐,等.G-CSF动员大鼠外周血间质干细胞的初步实验研究[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2010,(5):762-765. [24] 杨镛,杨国凯,何晓明,等.经皮透光负压旋切术治疗下肢静脉性皮肤溃疡的疗效与评价[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2009, 16(12): 996-999. [25] 李学锋,沈振亚,谷涌泉,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗血栓闭塞性脉管炎[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2010,17(7):656-659. [26] 李国剑,杨镛,杨国凯,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗血栓闭塞性脉管炎的临床应用[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2012,19(11): 1187-1190. [27] 虞希祥,朱国庆,郝伟远.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗下肢严重缺血的临床研究[J].医学影像学杂志,2010,20(8):1165-1167. [28] 孙文,郁涂巍,梁健.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗下肢动脉硬化闭塞症11例报告[J].中国医师进修杂志,2006,29(32):62,68. [29] Tateishi-Yuyama E, Matsubara H, Murohara T, et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis for patients with limb ischaemia by autologous transplantation of bone-marrow cells: a pilot study and a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360(9331):427-435. [30] 杨镛,陆平,何晓明,等.人自体干细胞移植在重症肢体缺血血流重建中的疗效与评价[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2009,16(2): 115-118. [31] 缪健航,师天雄,胡锡祥,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗下肢动脉缺血性疾病的临床应用[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2008, 15(2):106-108. [32] Matoba S, Tatsumi T, Murohara T, et al. Long-term clinical outcome after intramuscular implantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells (Therapeutic Angiogenesis by Cell Transplantation [TACT] trial) in patients with chronic limb ischemia. Am Heart J. 2008;156(5):1010-1018. [33] 杨继武,周业庭,刘伟平,等.重组人肝细胞生长因子联合粒细胞集落刺激因子对血管新生的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010, 27(6): 842. [34] Yamamoto K, Kondo T, Suzuki S, et al. Molecular evaluation of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with ischemic limbs: therapeutic effect by stem cell transplantation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(12):e192-196. [35] Lee HC, An SG, Lee HW, et al. Safety and effect of adipose tissue-derived stem cell implantation in patients with critical limb ischemia: a pilot study. Circ J. 2012;76(7):1750-1760. [36] Bura A, Planat-Benard V, Bourin P, et al. Phase I trial: the use of autologous cultured adipose-derived stroma/stem cells to treat patients with non-revascularizable critical limb ischemia. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(2):245-257. [37] Zhi K, Gao Z, Bai J, et al. Application of adipose-derived stem cells in critical limb ischemia. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014;19:768-776. [38] Cai A, Qiu R, Li L, et al. Atorvastatin treatment of rats with ischemia-reperfusion injury improves adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell migration and survival via the SDF-1α/CXCR-4 axis. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e79100. [39] Acosta L, Hmadcha A, Escacena N, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stromal cells isolated from type 2 diabetic patients display reduced fibrinolytic activity. Diabetes. 2013; 62(12):4266-4269. [40] Moazzami K, Majdzadeh R, Nedjat S. Local intramuscular transplantation of autologous mononuclear cells for critical lower limb ischaemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (12):CD008347. [41] Benoit E, O'Donnell TF, Patel AN. Safety and efficacy of autologous cell therapy in critical limb ischemia: a systematic review. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(3):545-562. [42] Teraa M, Sprengers RW, van der Graaf Y, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived cell therapy in patients with critical limb ischemia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Ann Surg. 2013;258(6):922-929. [43] von Boehmer H. Mechanisms of suppression by suppressor T cells. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(4):338-344. [44] Taylor PA, Lees CJ, Blazar BR. The infusion of ex vivo activated and expanded CD4(+)CD25(+) immune regulatory cells inhibits graft-versus-host disease lethality. Blood. 2002; 99(10):3493-3499. [45] Xia G, Kovochich M, Truitt RL, et al. Tracking ex vivo-expanded CD4+CD25+ and CD8+CD25+ regulatory T cells after infusion to prevent donor lymphocyte infusion-induced lethal acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004;10(11):748-760. [46] Joffre O, Gorsse N, Romagnoli P, et al. Induction of antigen-specific tolerance to bone marrow allografts with CD4+CD25+ T lymphocytes. Blood. 2004;103(11):4216-4221. [47] Hanash AM, Levy RB. Donor CD4+CD25+ T cells promote engraftment and tolerance following MHC-mismatched hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2005;105(4): 1828-1836. [48] Edinger M, Hoffmann P, Ermann J, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells preserve graft-versus-tumor activity while inhibiting graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation. Nat Med. 2003;9(9):1144-1150. [49] Trenado A, Charlotte F, Fisson S, et al. Recipient-type specific CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells favor immune reconstitution and control graft-versus-host disease while maintaining graft-versus-leukemia. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(11):1688-1696. [50] Zorn E, Kim HT, Lee SJ, et al. Reduced frequency of FOXP3+ CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2005;106(8):2903-2911. [51] Gehrie EA, Booth GS. Stem cell collection considerations for AL amyloidosis. Conn Med. 2014;78(10):587-590. [52] Flommersfeld S, Sohlbach K, Jaques G, et al. Collection of peripheral blood progenitor cells on Day 4 is feasible and effective while reducing granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor exposure to healthy donors. Transfusion. 2015;55(6): 1269-1274. [53] Zhang WX, Zhao QY, Huang HQ. Febrile neutropenic infection occurred in cancer patients undergoing autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2015;47(2):523-527. [54] Pulsipher MA, Chitphakdithai P, Logan BR, et al. Lower risk for serious adverse events and no increased risk for cancer after PBSC vs BM donation. Blood. 2014;123(23):3655-3663. [55] Eapen M, Logan BR, Horowitz MM, et al. Bone marrow or peripheral blood for reduced-intensity conditioning unrelated donor transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(4):364-369. [56] Hatsuse M, Fuchida S, Okano A, et al. Secondary MGUS following by adenovirus-induced hemorrhagic cystitis after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in a patient with multiple myeloma. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2014;55(11): 2277-2282. |
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||