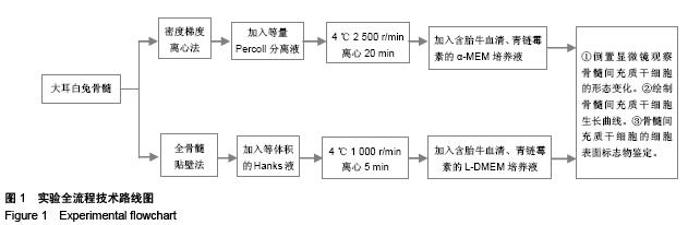
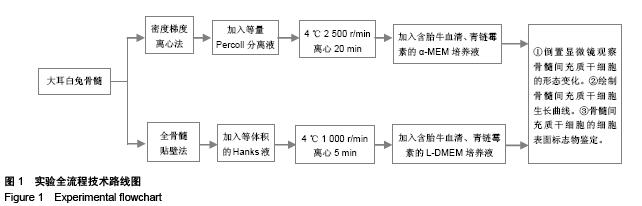
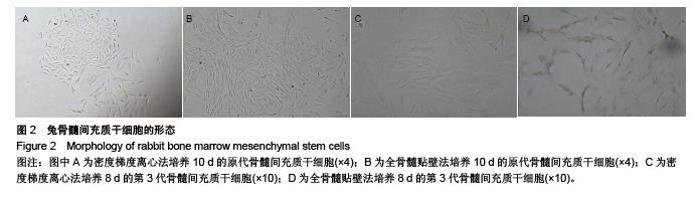
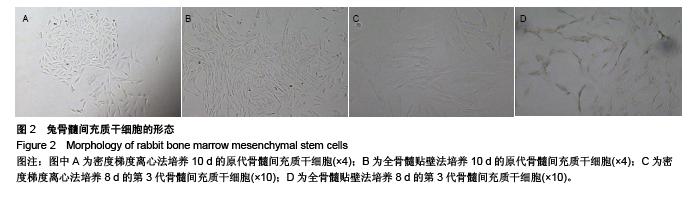
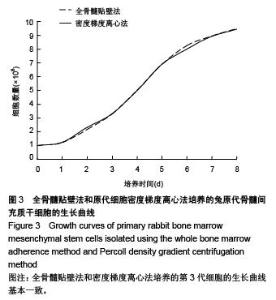
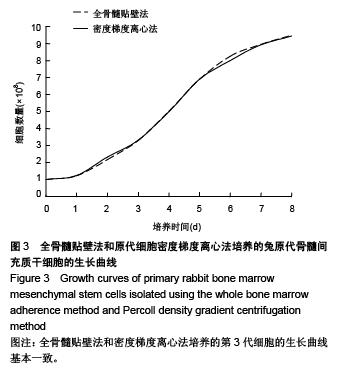
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (50): 8043-8047.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.50.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Primary culture and biological characteristics of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from a rabbit
Yang Jun-li1, Han Xia2, Sun Ming-qi3, Li Yun-xia1
- 1Health Centre, 2Laboratory of Stem Cells, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2015-10-18Online:2015-12-03Published:2015-12-03 -
Contact:Li Yun-xia, Professor, Health Centre, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yang Jun-li, Master, Physician, Health Centre, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Mesenchymal Stem Cells; Cell Separation; Cell Culture Techniques; Tissue Engineering
Funding: the Youth Innovation Fund of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2014QNCX014
CLC Number:
Cite this article
share this article
| [1] Wislet-Gendebien S, Hans G, Leprince P, et al. Plasticity of cultured mesenchymal stem cells: switch from nestin-positive to excitable neuron-like phenotype. Stem Cells. 2005;23(3): 392-402. [2] Oshima Y, Watanabe N, Matsuda K, et al. Behavior of transplanted bone marrow-derived GFP mesenchymal cells in osteochondral defect as a simulation of autologous transplantation. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005;53(2):207-216. [3] Silva GV, Litovsky S, Assad JA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into an endothelial phenotype, enhance vascular density, and improve heart function in a canine chronic ischemia model. Circulation. 2005;111(2):150-156. [4] 中华人民共和国科学技术部. 关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-9-30. [5] 王英慧,郑瑞,陈莉.密度梯度离心及贴壁分离筛选相结合分离培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(28): 4463-4468. [6] 闫峰,张越林,刘宁,等.全骨髓贴壁法分离骨髓间充质干细胞并诱导其定向神经元样细胞的分化[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2014, 30(11):1162-1165. [7] Wulf GG, Jackson KA, Goodell MA. Somatic stem cell plasticity: current evidence and emerging concepts. Exp Hematol. 2001;29(12):1361-1370. [8] 张超,王涛.兔骨髓间充质干细胞的体外分离、培养及诱导分化[J].重庆医科大学学报,2012,37(8):694-697. [9] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [10] 刘伟,陈剑,宋佳,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞的分离、培养及鉴定[J].中国实验诊断学,2013,17(8):1366-1369. [11] 刘小珍,郑智国,凌志强.肿瘤细胞原代培养与保存[J].中国肿瘤, 2015,24(4):276-283. [12] 施明,刘振文,张政,等.干细胞治疗终末期肝病的进展与挑战[J].解放军医学杂志,2013,38(8):685-692. [13] Guo-ping W, Xiao-chuan H, Zhi-hui Y, et al. Influence on the osteogenic activity of the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfected by liposome-mediated recombinant plasmid pIRES-hBMP2-hVEGF165 in vitro. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;65(1):80-84. [14] 张焱如,刘宗正,韦林盖,等.蒙古马骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及多向分化潜能的研究[J].畜牧兽医学报,2011,42(10):1357-1361. |
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||