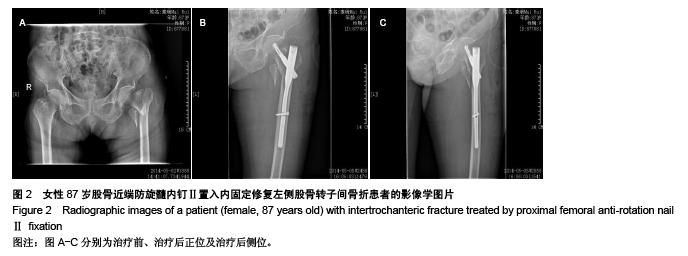
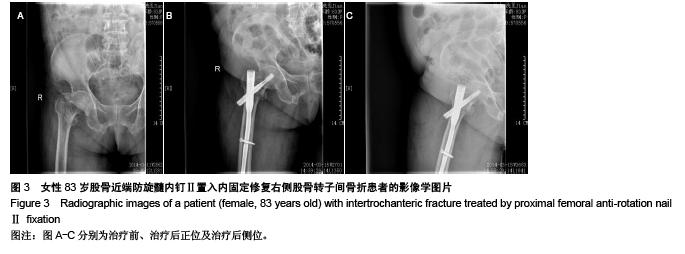
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (48): 7784-7789.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.48.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Proximal femoral anti-rotation nail Ⅱ fixation repairs intertrochanteric fracture: the importance of unarmed guided needle placement
Dou Qing-yin, Hu Hong-yong, Liang Xu-qiang
- Department of Orthopedics, Shenzhen Songgang People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518105, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-13Online:2015-11-26Published:2015-11-26 -
About author:Dou Qing-yin, Master, Department of Orthopedics, Shenzhen Songgang People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518105, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dou Qing-yin, Hu Hong-yong, Liang Xu-qiang. Proximal femoral anti-rotation nail Ⅱ fixation repairs intertrochanteric fracture: the importance of unarmed guided needle placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(48): 7784-7789.
share this article
| [1] Strauss E, Frank J, Lee J, et al. Helieal blade versus sliding hip seew for treatment of unstable Intcrtrochanteric hip fractures abiomeehanical evaluation. Injury. 2006;37(5): 984-989.[2] Wemer-Tutschku W, Lajatai G, Schmiedhube G, et al. Intra and perioPerrative complocation in the stabilization of per and subtrochanteric femoral fractures by means of PFN. Unfallehirurg. 2002;105(10):881-885.[3] 唐佩福,姚琦,黄鹏,等.股骨近端髓内钉-螺旋刀片治疗高龄骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(7): 622-624.[4] Chan KC,Gill GS. Cemented hemiarthroplasties for elderly patients with intertrochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(371): 206-215.[5] Watanabe M,Toyama Y,Fujimura Y.Atlantoaxial instability in os odontoideum with myelopathy. Spine. 1996;21(12):1435-1439.[6] Friedl W,Colombo Benkmann M.Gamma nail osteosynthesis of per and subtrochanteric femoral fractures.4 years experiences and their consequences for further implant development.Chirurg. 1994;65(11):953-963. [7] Ahrengart L,Tornkvist H,Fornander P,et al.A ran-domized study of the compression hip screw and Gamma nail in 426 fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(401):209-222.[8] Gool SG, Khoo EH, Benny E, et al. Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation of Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur: A Comparison of Outcome With and Without Using Traction Table. Malays Orthop J. 2011;5(1):21-25.[9] Nikolaou VS,Papathanasopoulos A,Giannoudis PV.What’s new in the management of proximal femoral fractures? Injury. 2008;39(12):1309-1318.[10] Haynes RC,Poll RG,Miles AW,et al.Failure of femoral head fixation:a cadaveric analysis of lag screw cutout with the gamma locking nail and AO dynamic hip screw. Injury. 1997; 28(56):337-341.[11] Haidukewych GJ,Berry DJ.Salvage of failed internal fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (412):184-188.[12] 董爱军.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与股骨近端锁定板治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的比较研究[J].中外医学研究,2014,12(23):42-43.[13] 苏宝霞,王志强,谢鹏.应用PFNA治疗高龄不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折45例分析[J].武警后勤学院学报(医学版),2013,22(6):527-528.[14] 单倚绅.不同手术方式治疗老年粗隆间不稳定型骨折疗效比较[J].中国医学工程,2013,21(3):88-89.[15] 张庆猛,李明,刘培来,等.人工关节置换和PFNA内固定治疗老年人股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].山东医药,2013,53(1):69-71.[16] Lenich A,Bachmeier S,Dendorfer S,et al.Development of a test system to analyze different hip fracture osteosyntheses under simulated walking. Biomed Tech(Berl). 2012;57(2): 113-119.[17] Macheras GA,Koutsostathis SD,Galanakos S,et al.Does PFNAⅡ avoid lateral corteximpingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470 (11): 3067-3076 .[18] 姚刚.Gamma钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 中国医药,2013,8(3): 374-375.[19] Simmermacher RK,Bosch AM,van der Werken C.The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail(PFN):a new device for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 1999; 30(5):327-332.[20] Domingo LJ,Cecilia D,Herrera A,et al.Trochanteric fractures treated with a proximal femoral nail. Int Orthop. 2001;25(5): 298-301.[21] Banan H,Al Sabti A,Jimulia T,et al.The treatment of unstable,extracapsular hip fractures with the AO/ASIF proximal fermoral nail(PFN)our first 60 cases. Injury.2002; 33(5):401-405.[22] Albareda J,Laderiga A,Palanca D,et al.Complications and technical problems with the gamma nail. Int Orthop. 1996; 20(1):47-50.[23] 王海.股骨近端髓内钉内固定术治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效观察[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(14):97-98.[24] 王登峰,华俊,杨侃.老年股骨粗隆间骨折应用股骨近端髓内钉固定的临床分析[J].中国医药指南,2014,12(28):189-190.[25] 张文奎,温建伟.经皮行股骨粗隆间骨折闭合复位空心钉内固定术[J].北方药学,2014,11(2):110-111.[26] 梁雨田,唐佩福.老年髋部骨折[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2009.[27] 屈峥嵘,周敬滨,马进仓,等.动力髋螺钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折失效分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2008,14(8):470-472. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||