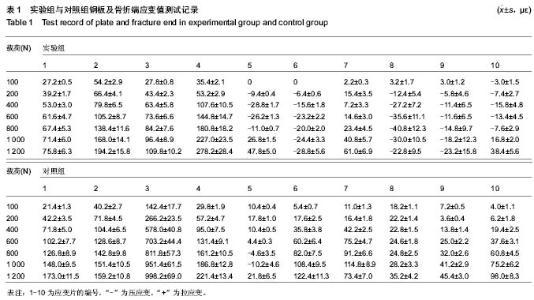
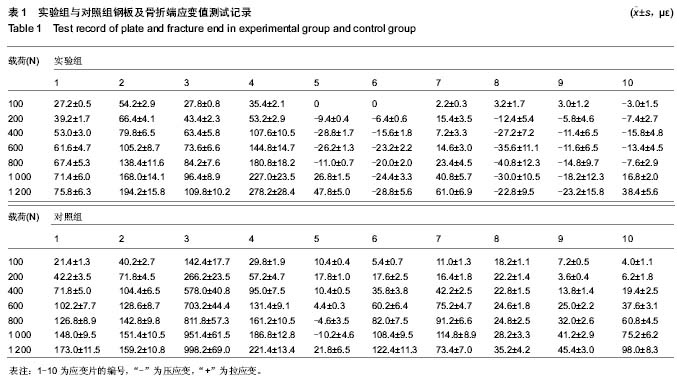
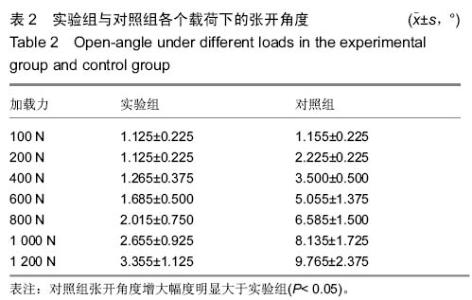
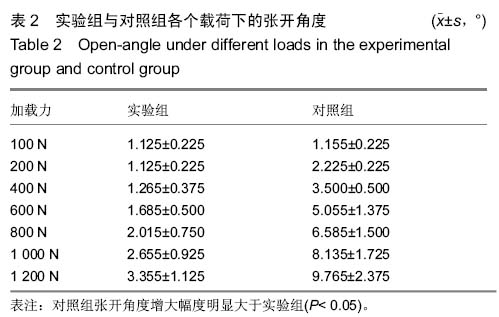
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Intertrochanteric fracture: design and biomechanical evaluation of triangle truss locking plate
Miao Xu-man, Zuo Hao, Yao Shu-zhi
- Department of Orthopedics, the 208 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Changchun 130062, Jilin Province, China
-
Online:2015-09-24Published:2015-09-24 -
About author:Miao Xu-man, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the 208 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Changchun 130062, Jilin Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Miao Xu-man, Zuo Hao, Yao Shu-zhi. Intertrochanteric fracture: design and biomechanical evaluation of triangle truss locking plate[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.39.025.
share this article
| [1] Biber R,Bail HJ,Stedtfeld HW.Lateral cortical notching in specific cases of delayed unions or nonunions after intertrochantericand reversed fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2013;133(4):495-501. [2] Gunadham U,Jampa J,Suntornsup S,et al.The outcome in early cases of treatment of subtrochanteric fractures with proximal femur locking compression plate.Malays Orthop J.2014;8(2):22-28. [3] Kumar N,Kataria H,Yadav C,et al.Evaluation of proximal femoral locking plate in unstable extracapsular proximal femoral fractures: Surgical technique & mid term follow up results.Clin Orthop Trauma.2014;5(3):137-145. [4] Lee WT,Murphy D,Kagda FH,et al.Proximal femoral locking compression plate for proximal femoral fractures.Orthop Surg (Hong Kong).2014;22(3):287-293. [5] Wieser K,Babst R.Fixation failure of the LCP proximal femoral plate 4.5/5.0 in patients with missing posteromedial support in unstable per-, inter-, and subtrochanteric fractures of the proximal femur.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2010;130(10): 1281-1287. [6] Wang Y,Yang YY,Yu ZH,et al.Comparative study of intertrochanteric fractures treated with proximal femur locking compress plate in aged.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011;24(5): 370-373. [7] Ziebarth K,Slongo T.Proximal Femoral Osteotomies with the Paediatric Hip Plate (LCP): Valgus osteotomy.Oper Orthop Traumatol.2015;27(3):210-220. [8] Weiser L,Ruppel AA,Nüchtern JV,et al.Extra- vs. intramedullary treatment of pertrochanteric fractures: a biomechanical in vitro study comparing dynamic hip screw and intramedullary nail.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015; 135(8): 1101-1106. [9] Glassner PJ,Tejwani NC.Failure of proximal femoral locking compression plate: a case series.Orthop Trauma.2011;25(2): 76-83. [10] Gunadham U,Jampa J,Suntornsup S,et al.The outcome in early cases of treatment of subtrochanteric fractures with proximal femur locking compression plate.Malays Orthop J.2014;8(2):22-28. [11] Chen Y,Liu S,Lin P,et al.Comparative biomechanical study of reversed less invasive stabilization system and proximal femoral nail antirotation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures.Chin Med J (Engl).2014;127(23):4124-4129. [12] Bonnaire F,Lein T,Bula P.Trochanteric femoral fractures: anatomy, biomechanics and choice of implants.Unfallchirurg. 2011;114(6):491-500. [13] Werner BC,Fashandi AH,Gwathmey FW,et al.Trends in the management of intertrochanteric femur fractures in the United States 2005-2011.Hip Int.2015;25(3):270-276. [14] Bartoní?ek J,Bartoška R.Rozhl Chir.Trochanteric fractures- anatomy and classification.et al.2013;92(10):581-588. [15] Langford J,Pillai G,Ugliailoro AD,Rozhl Chir.Perioperative lateral trochanteric wall fractures: sliding hip screw versus percutaneous compression plate for intertrochanteric hip fractures.Orthop Trauma.2011;25(4):191-195. [16] Gotfried Y.The lateral trochanteric wall: a key element in the reconstruction of unstable pertrochanteric hip fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2004;(425):82-86. [17] Palm H,Jacobsen S,Sonne-Holm S,et al.Integrity of the lateral femoral wall in intertrochanteric hip fractures: an important predictor of a reoperation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(3): 470-475. [18] 陈雁西,梅炯,毕刚,等.PFNA治疗股骨转子间伴或不伴外侧壁骨折的疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(7):614-620. [19] Wateon TJ,Wiss DA.Fracture of the proximaltibia and fibula.Philadelphia:Lippin cott,Wilhamsang Wilkins, Philadelphia. 2001:1801-1842. [20] Haidukewych GJ.Intertrochanteric fractures: ten tips to improve results.Instr Course Lect.2010;59:503-509. [21] Saini P,Kumar R,Shekhawat V,et al.Biological fixation of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures with proximal femur locking compression plate.Injury.2013;44(2):226-231. [22] 仲飙,张弛,罗从风.股骨近端锁定钢板:失败原因分析及其适应症探讨[Z].中华医学会第十四届全国骨科学术会议暨第七届国际学术大会(Chinese Orthopaedic Association, COA),2012. [23] Wirtz C,Abbassi F,Evangelopoulos DS,et al.High failure rate of trochanteric fracture osteosynthesis with proximal femoral locking compression plate.Injury.2013;44(6):751-756. [24] Märdian S,Schmölz W,Schaser KD,et al.Interfragmentary lag screw fixation in locking plate constructs increases stiffness in simple fracture patterns.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2015.pii: S0268-0033(15)00172-2. 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2015.06.008. [Epub ahead of print] [25] Biber R,Bail HJ,Stedtfeld HW.Lateral cortical notching in specific cases of delayed unions or nonunions after intertrochanteric and reversed fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2013;133(4):495-501. [26] Zhen P,Liu XY,Gao MX,et al.Application of the anatomic plate and trapezoid plate in comminuted intertrochanteric fracture combined with trochanteric coronal position fracture: a controlled clinical trial.Zhongguo Gu Shang.2010;23(5): 332-335. [27] Ozkan K,Türkmen I,Sahin A,et al.A biomechanical comparison of proximal femoral nails and locking proximal anatomic femoral platesin femoral fracture fixation: A study on synthetic bones.Indian J Orthop.2015;49(3):347-351. [28] Lu W,Zhu W,Peng L,et al.Femoral footprint variation of the posterolateral bundle of the anterior cruciate ligament and double-bundle reconstruction.Knee.2015;22(3):169-173. [29] Vidyadhara S,Rao SK,Pandian S,et al.Closing lateral wedge valgus osteotomy with dynamic hip screw for the treatment of varus nonunion of pertrochanteric fracture: can restoration of biomechanics and stabilization alone heal?Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2009;129(6):827-832. [30] Arai T,Yamamoto M,Iwatsuki K,et al.Mechanical advantages of a truss-structure-based fracture fixation system--a novel fracture fixation device "PinFix".Nagoya J Med Sci.2013; 75(3-4):181-192. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [5] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [6] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [7] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [8] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [9] | Tan Jiachang, Yuan Zhenchao, Wu Zhenjie, Liu Bin, Zhao Jinmin. Biomechanical analysis of elastic nail combined with end caps and wire fixation for long oblique femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 334-338. |
| [10] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [11] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of multiple implants in treatment of traumatic dislocation of sternoclavicular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 443-448. |
| [12] | Li Kun, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Gao Shang, Sun Hao, Yang Xi, Wang Xing, Dai Lina . A 4-year-old child model of occipito-atlanto-axial joints established by finite element dynamic simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3773-3778. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| [15] | Liu Jinyu, Ding Yiwei, Lu Zhengcao, Gao Tianjun, Cui Hongpeng, Li Wen, Du Wei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical study of full endoscopic fenestration decompression for cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3850-3854. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||