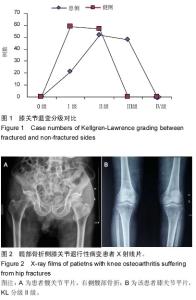
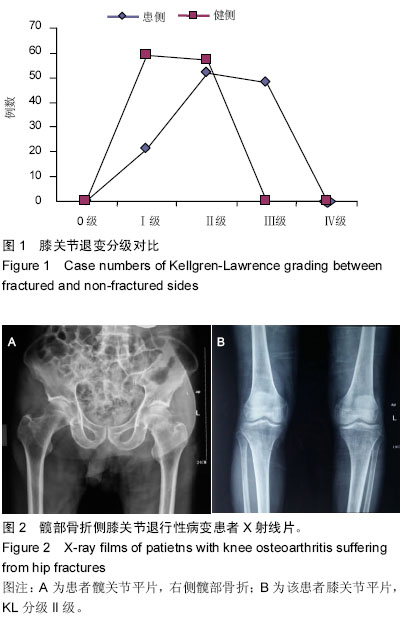
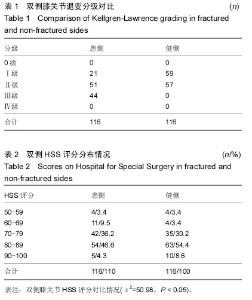
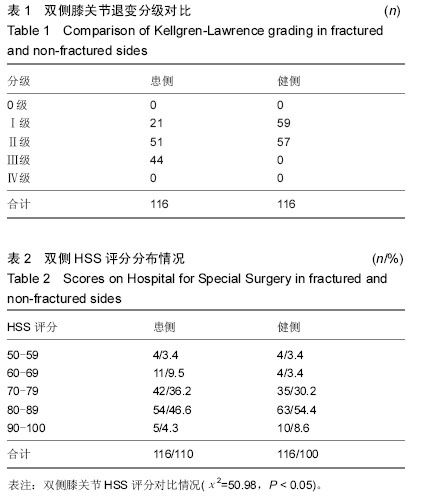
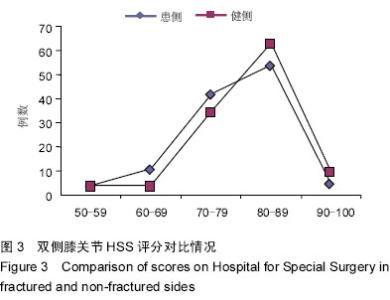
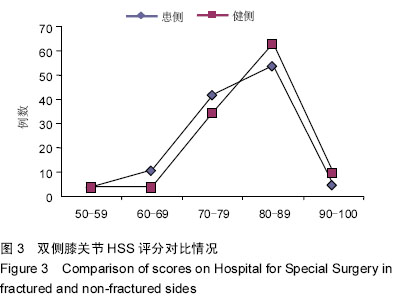
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (37): 5938-5942.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.37.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between low-energy hip fracture and knee osteoarthritis
Zhao Wen-jie, Zhang Bin, Gao Song, Zhou Song, Wang Qiang, Dai Min
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China