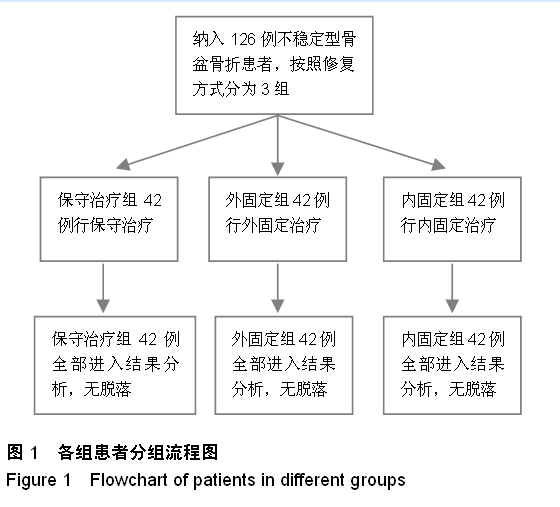
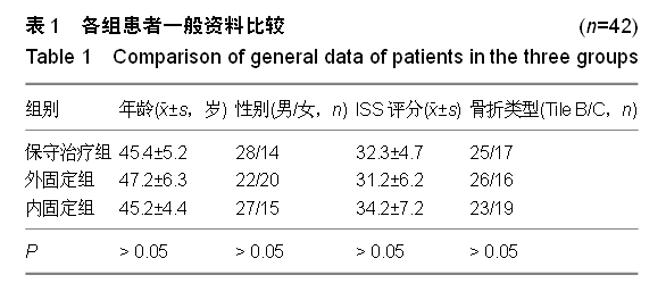
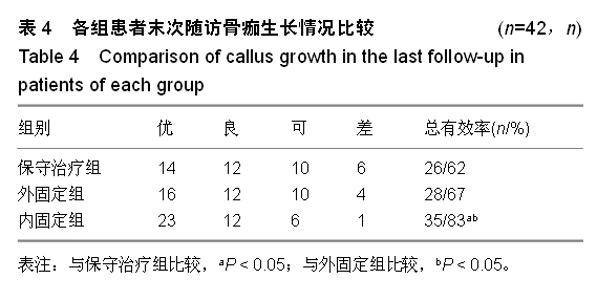
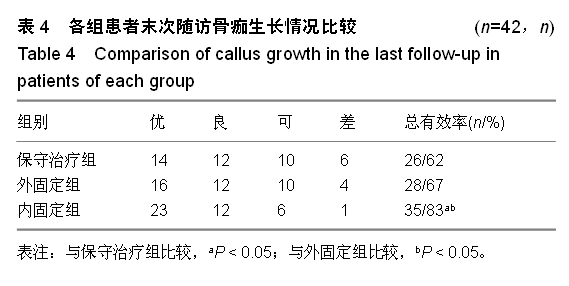
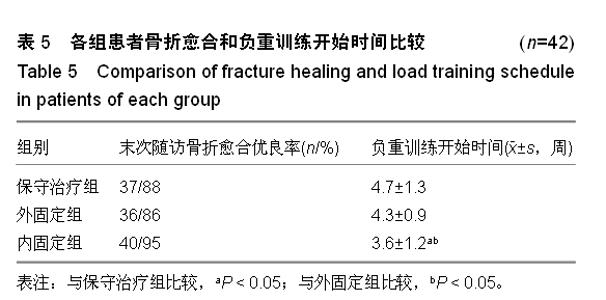
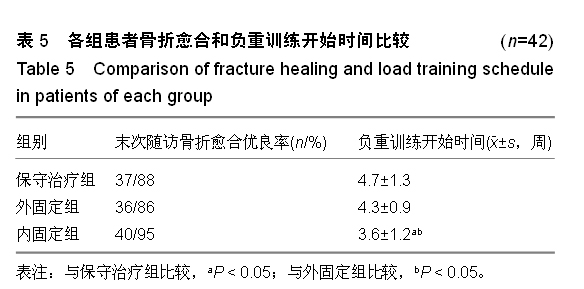
| [1] 王秋根,王谦.骨盆骨折损伤控制的回顾及展望[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2011,27(4):289-292.
[2] 岑怡彪,钟华,杨国俊,等.复杂不稳定型骨盆骨折手术治疗的临床分析[J].使用骨科杂志,2013,19(4):358-360.
[3] 田辉. 外固定支架联合手术治疗创伤性骨盆骨折患者42例[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,(10):138-140.
[4] 胡健,禹宝庆.骨盆骨折的手术入路及其选择[J].中华创伤杂志, 2014, 30(1):30-32.
[5] Lindahl J, Hirvensalo E, Bostman O, et al. Failure of reduction with an external fixator in the management of pelvic ring injuries. Long-term evaluation of 110 patients. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 1999;81(6):955-962.
[6] Majeed SA. Grading the outcome of pelvic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg(Br).1989;71(2):304-306.
[7] 杨俊骁,成亮,李康华.湖南省5市9家三级医院骨盆骨折流行病学调查[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2014,39(3):301-306.
[8] 董玉珍,宗海斌,赵红星,等. 不稳定骨盆骨折的手术治疗效果与影响因素分析[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(x2):367-369.
[9] 曲秀岭. 切开复位内固定治疗不稳定型骨盆骨折的临床分析[J]. 河北医药,2013,35(14):2155-2156.
[10] 谭春兴,林巧,谭丽萍,等. 损伤控制理论在骨盆骨折患者急诊护理中的应用[J].齐鲁护理杂志,2014,28(4):68-69.
[11] 吴肖红.骨盆骨折患者的围手术期护理[J].中医正骨,2013,25(6): 79-80.
[12] 尹安高.手术内固定治疗不稳定型骨盆骨折的疗效及预后[J].健康必读,2013,12(1):186-187.
[13] 孙跃力. 不稳定型骨盆骨折45例临床治疗[J].中国保健营养(下旬刊),2013,23(11):228-231.
[14] 冯雯,楚丽娟,代艳芳,等. 不稳定型骨盆骨折患者围手术期护理干预方法与效果观察[J].大家健康(下旬刊),2014,(8);473-475.
[15] 诸丽霞. 72例不稳定型骨盆骨折病人围手术期护理体会[J]. 中国卫生产业,2013,12(9):85-85.
[16] Zhu L, Wang L, Shen D, et al. Treatment of pelvic fractures through a less invasive ilioinguinal approach combined with a minimally invasive posterior approach. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:167.
[17] Wang T, Wang J, Li ZY, et al.[Surgical treatment of unstable pelvic fractures combined with acetabular fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(5):392-398.
[18] Wu T, Chen W, Zhang Q, et al. Therapeutic effects of minimally invasive adjustable and locking compression plate for unstablepelvic fractures via posterior approach. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):827-835.
[19] Li CL. Clinical comparative analysis on unstable pelvic fractures in the treatment with percutaneous sacroiliac screws and sacroiliac joint anterior plate fixation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(18):2704-2708.
[20] Mauffrey C, Cuellar DO 3rd, Pieracci F, et al. Strategies for the management of haemorrhage following pelvic fractures and associated trauma-induced coagulopathy. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(9):1143-1154.
[21] Ip KC, Lee KB. Standardised multidisciplinary protocol for haemodynamically unstable pelvic fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2014;22(2):177-180.
[22] Dong J, Hao W, Wang B, et al. Management and outcome of pelvic fractures in elderly patients: a retrospective study of 40 cases. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(15):2802-2807.
[23] Strobl FF, Haeussler SM, Paprottka PM, et al. Technical and clinical outcome of percutaneous CT fluoroscopy-guided screw placement in unstableinjuries of the posterior pelvic ring. Skeletal Radiol. 2014 Aug;43(8):1093-100.
[24] Scheyerer MJ, Zimmermann SM, Osterhoff G, et al. Anterior subcutaneous internal fixation for treatment of unstable pelvic fractures. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:133.
[25] Takeuchi N, Masumoto K, Nojiri J, et al. Open pelvic ring fracture and multiple fractures of the lower extremities: a case report. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi. 2014;105(1):22-27.
[26] Chen PH, Hsu WH, Li YY, et al. Outcome analysis of unstable posterior ring injury of the pelvis: comparison between percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation and conservative treatment. Biomed J. 2013;36(6):289-294.
[27] Moed BR, O'Boynick CP, Bledsoe JG. Locked versus standard unlocked plating of the symphysis pubis in a Type-C pelvic injury: a cadaver biomechanical study. Injury. 2014; 45(4):748-751.
[28] Queipo-de-Llano A, Perez-Blanca A, Ezquerro F, et al. Simultaneous anterior and posterior compression of the pelvic ring with external fixation using a pre-tensed curved bar: A biomechanical study. Injury. 2013;44(12):1787-1792.
[29] 朱智奇,侯明,谢小青,等.不稳定骨盆骨折手术治疗的预后影响因素研究[J].江西医药,2013,48(6):484-487. |