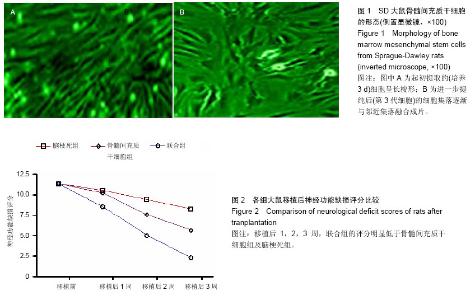
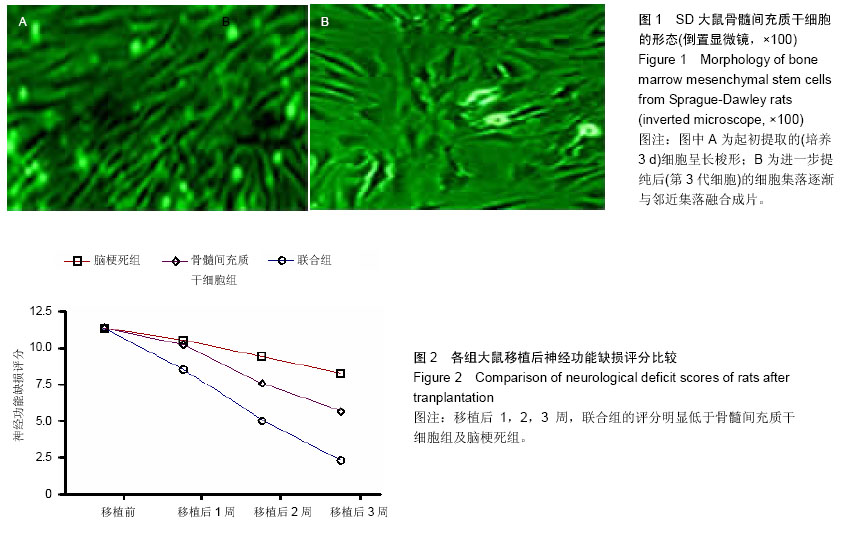
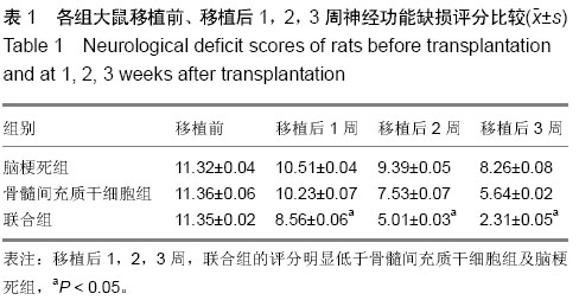
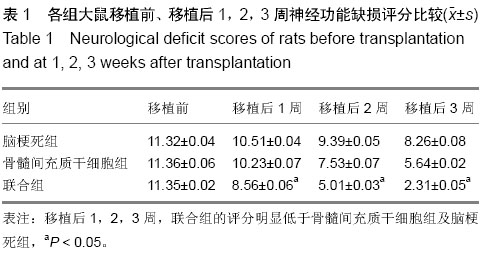
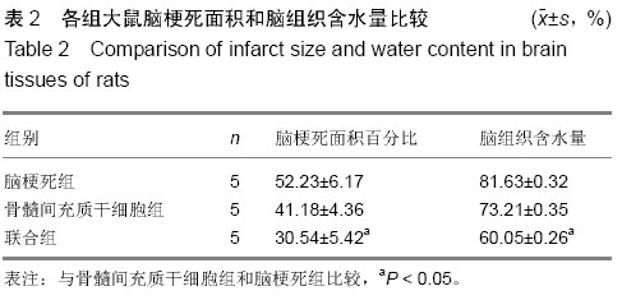
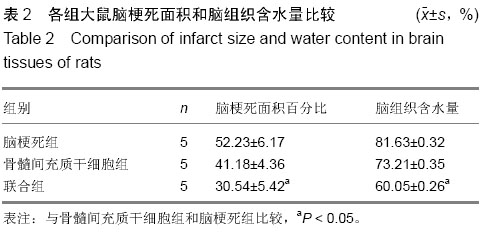
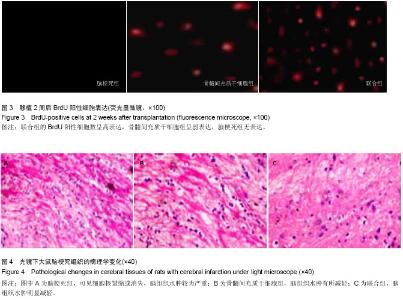
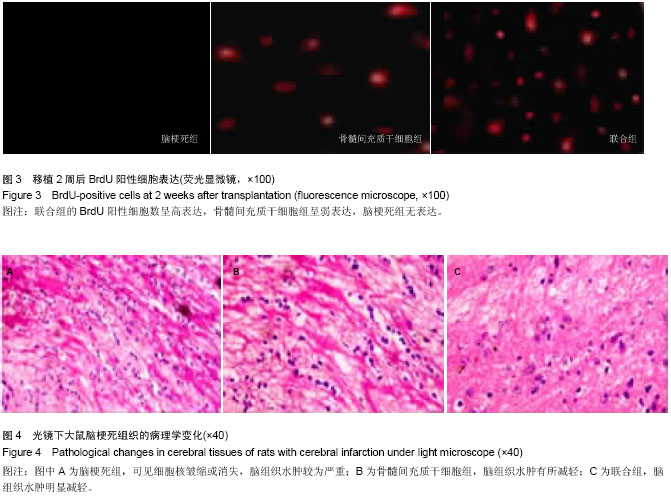
| [1] Ben Azouna N, Jenhani F, Regaya Z, et al. Phenotypical and functional characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow: comparison of culture using different media supplemented with human platelet lysate or fetal bovine serum. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(1):6.
[2] 张维颉,顾润国.大鼠骨髓基质干细胞分离、纯化与诱导分化的研究进展[J].医学综述,2012,18(22):3743-3746.
[3] Knoop K, Schwenk N, Dolp P, et al. Stromal targeting of sodium iodide symporter using mesenchymal stem cells allows enhanced imaging and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Gene Ther. 2013;24(3):306-316.
[4] Heo JS, Choi SM, Kim HO, et al. Neural transdifferentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on hydrophobic polymer-modified surface and therapeutic effects in an animal model of ischemic stroke. Neuroscience. 2013;238:305-318.
[5] Yu YL, Chou RH, Shyu WC, et al. Smurf2-mediated degradation of EZH2 enhances neuron differentiation and improves functional recovery after ischaemic stroke. MBO Mol Med. 2013;5(4):531-547.
[6] 张骏,于娜,吴岳洲,等.灯盏花素治疗急性脑梗死近期疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2001,10(4):295-296.
[7] Komatsu K, Honmou O, Suzuki J, et al. Therapeutic time window of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2010;1334:84-92.
[8] 姜秀娥.灯盏花素的药理作用研究进展[J].医学理论与实践, 2009, 22(8):915-917.
[9] Zheng W, Honmou O, Miyata K, et al. Therapeutic benefits of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2010;1310:8-16.
[10] Akiyama K, You YO, Yamaza T, et al. Characterization of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells in suspension. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(5):40.
[11] 王鲁民,吴群玫,尹作民,等.BDNF修饰神经干细胞移植对脑缺血损伤的影响[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2005,20(4):298-300.
[12] 张鹏,周国庆,孙晶晶,等.丹红注射液联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑梗死[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23): 4286-4291.
[13] Guo JW, Chen C, Huang Y, et al. Combinatorial effects of naomai yihao capsules and vascular endothelial growth factor gene-transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on angiogenesis in cerebral ischemic tissues in rats. J Tradit Chin Med. 2012;32(1):87-92.
[14] Pineda JR, Daynac M, Chicheportiche A, et al. Vascular-derived TGF-β increases in the stem cell niche and perturbs neurogenesis during aging and following irradiation in the adult mouse brain. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(4):548-562.
[15] Kawabori M, Kuroda S, Ito M, et al. Timing and cell dose determine therapeutic effects of bone marrow stromal cell transplantation in rat model of cerebral infarct. Neuropathology. 2013;33(2):140-148.
[16] Young W, Rappaport ZH, Chalif DJ, et al. Regional brain sodium, potassium, and water changes in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model of ischemia. Stroke. 1987; 18(4):751-759.
[17] Yoo SW, Kim SS, Lee SY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote proliferation of endogenous neural stem cells and survival of newborn cells in a rat stroke model. Exp Mol Med. 2008;40(4):387-397.
[18] 周国庆,金怡,张鹏,等.沉默RhoA基因对骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗脑梗死大鼠的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(45):8416-8420.
[19] Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, et al. IFATS collection: in vivo therapeutic potential of human adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells after transplantation into mice with liver injury. Stem Cells. 2008;26(10):2705-2712.
[20] Qin W,Yang L,Guo HM,et al.Pro-urokinase promotes angiogenesis but does not reduce neuronal apoptosis in infarcted cerebral tissue. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(5): 502-503.
[21] Wakabayashi K, Nagai A, Sheikh AM,et al. Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells promotes functional improvement and increased expression of neurotrophic factors in a rat focal cerebral ischemia model. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(5):1017-1025.
[22] 蔡磊,李雅娜,刘桂香,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死的研究进展[J].滨州医学院学报,2009,32(1):52-54.
[23] Wang Y, Deng Y, Zhou GQ. SDF-1alpha/CXCR4-mediated migration of systemically transplanted bone marrow stromal cells towards ischemic brain lesion in a rat model. Brain Res. 2008;1195:104-112.
[24] Hou HL,Zhang GJ,Wang HY,et al.High matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression induces angiogenesis and basement membrane degradation in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats after cerebral infarction. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(11): 1154-1162.
[25] Zhu W, Fan Y, Hao Q, et al. Postischemic IGF-1 gene transfer promotes neurovascular regeneration after experimental stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 200929(9):1528-1537.
[26] 李军,杜金荣,戴艳萍.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑梗死的研究[J].黑龙江医学,2011,35(9):663-664.
[27] Kawabori M, Kuroda S, Ito M, et al. Timing and cell dose determine therapeutic effects of bone marrow stromal cell transplantation in rat model of cerebral infarct. Neuropathology. 2013;33(2):140-148.
[28] Liu Z, Li Y, Zhang ZG, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells enhance inter- and intracortical axonal connections after ischemic stroke in adult rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30(7):1288-1295.
[29] Zuo XL, Wu P, Ji AM. ylon filament coated with paraffin for intraluminal permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. eurosci Lett. 2012;519(1):42-46.
[30] Solaroglu I, Cahill J, Tsubokawa T, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor protects the brain against experimental stroke via inhibition of apoptosis and inflammation. Neurol Res. 2009;31(2):167-172.
[31] 杨晓文. 灯盏细辛注射液治疗急性脑梗塞52例[J].内蒙古中医药,2007,26(2):16.
[32] Loseva EV, Podgorny? OV, Poltavtseva RA, et al. Effects of human cultural neuronal and mesenchymal stem cells on the rat learning and brain state after acute hypoxia. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2011;97(2):155-168.
[33] 吕曙华,解军波,吕归宝.灯盏细辛的研究进展[J].天津药学,2003, 15(2):46-48.
[34] 史小琴,陈玉敏,王宇,等.灯盏花素的研究进展[J].河北职工医学院学报,2008,25(4):80-81.
[35] Zhang XH,Chen JJ.The mechanism of astragaloside IV promoting sciatic nerve regeneration.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(24): 2256-2265.
[36] Charbord P, Livne E, Gross G, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: a systematic reappraisal via the genostem experience. tem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1):32-42.
[37] 张洪连,吴晓牧.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死及存在问题[J].中华脑血管病杂志:电子版,2010,4(4):300-307.
[38] 田甜,车念聪,龙建飞,等. 大脑中动脉栓塞大鼠缺血半暗区神经可塑性蛋白及神经因子的表达[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2015,41(1):15-19,25.
[39] 黄蕊,艾长顺. 神经系统特异性生长相关蛋白43的研究进展[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2015,10(1):55-58.
[40] 吴丹红,周红,孙姬,等. 马来酸桂哌齐特对大脑中动脉缺血再灌注小鼠的脑保护作用及神经生长相关蛋白43早期表达的影响[J].临床内科杂志,2014,31(12):849-852.
[41] 王莉,夏韵. 复方蒲黄颗粒对脑缺血再灌注大鼠GAP-43表达的影响及动态变化规律[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2013,37(1):5-8. |