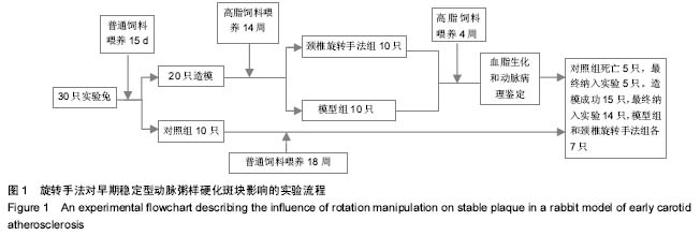
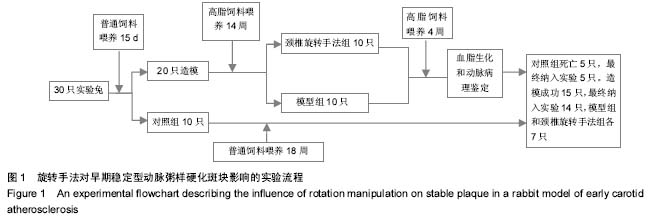
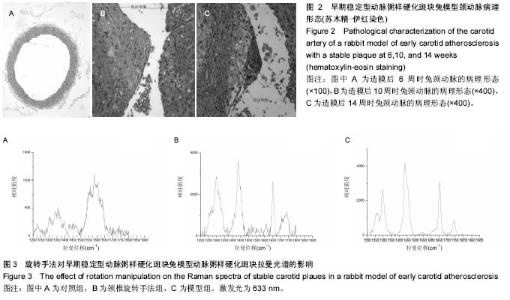
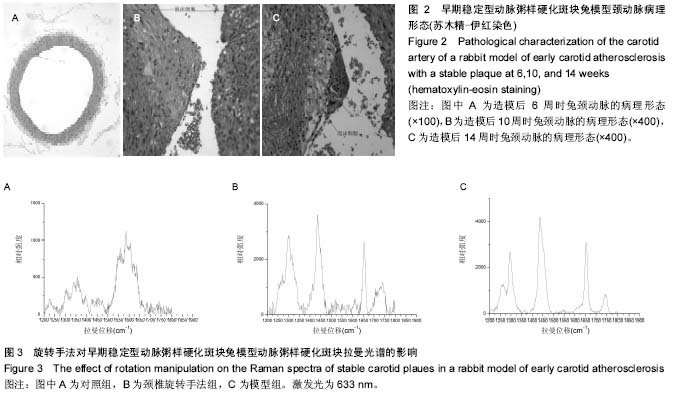
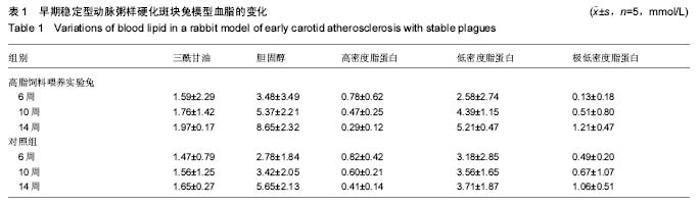
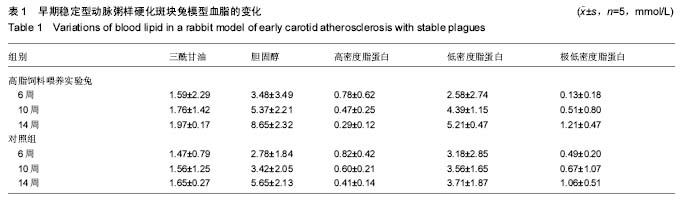
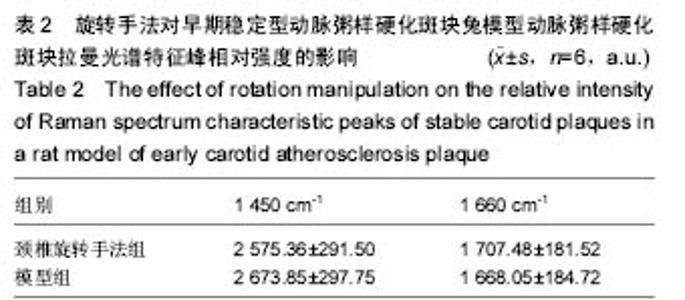
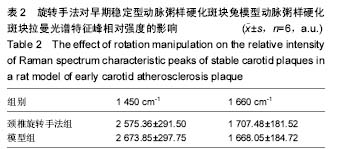
| [1] |
Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao.
Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317.
|
| [2] |
Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu.
Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin.
Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339.
|
| [4] |
Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun.
Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392.
|
| [5] |
Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi.
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397.
|
| [6] |
Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng.
Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Wei, Hu Jiang, Tang Liuyi, Wan Lun, Yu Yang, Lin Shu, Tang Zhi, Wang Fei.
Advantages of robot assisted percutaneous biopsy in the diagnosis of spinal lesions
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 844-848.
|
| [8] |
He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian.
Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889.
|
| [9] |
Xie Zhifeng, Liu Qing, Liu Bing, Zhang Tao, Li Kun, Zhang Chunqiu, Sun Yanfang.
Biomechanical characteristics of the lumbar disc after fatigue injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 339-343.
|
| [10] |
Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Zhu Zhenqi, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya.
Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of sciatic scoliosis caused by lumbar disc herniation: a 2-year follow-up of coronal and sagittal balance
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 409-413.
|
| [11] |
Yu Langbo, Qing Mingsong, Zhao Chuntao, Peng Jiachen.
Hot issues in clinical application of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in orthopedics
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 449-455.
|
| [12] |
Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji.
Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809.
|
| [13] |
Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin.
Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825.
|
| [14] |
Wang Ziao, Song Wenhui, Liu Changwen .
Short-segment fixation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: method modification and strategies to reduce failure
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3902-3907.
|
| [15] |
Lin Dongxin, Huang Xuecheng, Qin Qingguang, Yang Yang, Deng Yuping, Tan Jinchuan, Wang Mian, Su Weiwei, Huang Tao, Huang Wenhua.
Comparison of motion range of cervical spine after two cervical manipulations based on motion capture technique
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3281-3285.
|