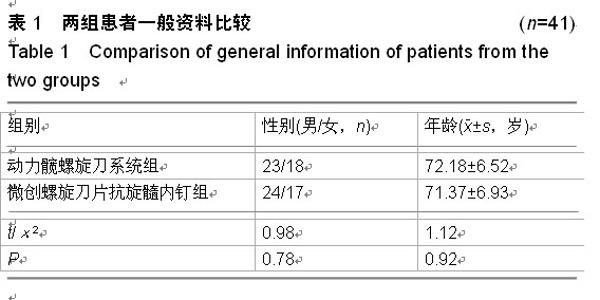
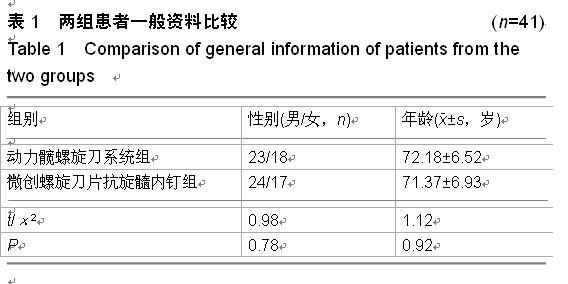
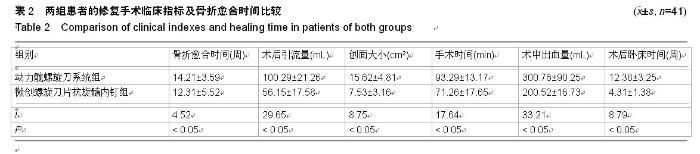
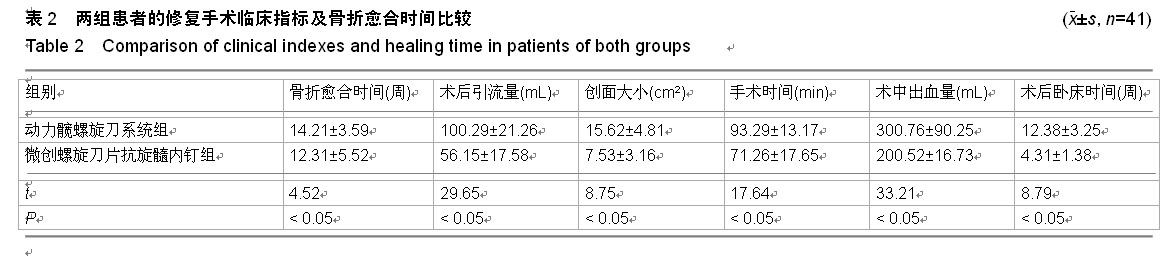
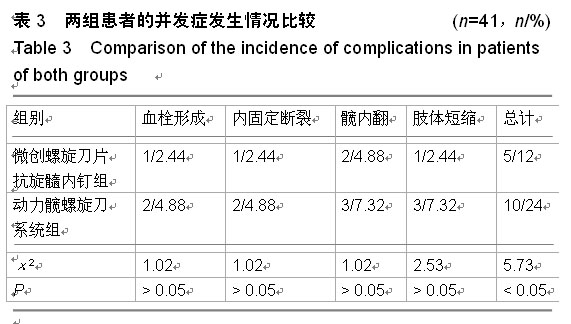
| [1] 王世强,韩晓松,徐林,等.人工双动股骨头置换高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折40例回顾分析[J].重庆医学,2014,45(24):3230-3231, 3232.
[2] 李江伟,宁旭,叶川,等.手术治疗高龄不稳定型转子间骨折患者102例回顾分析[J].重庆医学,2014,43(24):3243-3245.
[3] 陈宝,陈国俊,龚遂良,等.降钙素在老年不稳定型股骨转子间骨折应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(1):24-28.
[4] 杨建伟,唐坚,孙月华,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉和 Gamma 钉治疗老年不稳定型股骨转子间骨折疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志, 2014,26(5):566-568,571.
[5] 王培波,万兆玉,张若申,等.骨水泥型加长柄人工股骨头置换治疗合并股骨颈骨折畸形愈合的高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2014,14(20):3739-3741.
[6] 辛锋,朱国兴,顾羊林,等.动力髋螺钉与防旋阻挡钉联合修复不稳定型股骨转子间骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(48): 7786-7791.
[7] 秦伟光,李忠华,张秀华,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与解剖型锁定钢板治疗老年不稳定型股骨转子间骨折疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,28(3):324-326,329.
[8] 郑晓青,郑秋坚,昌耘冰,等.抗旋型股骨近端髓内钉在不稳定型股骨转子间骨折治疗中的应用[J].广东医学,2012,33(23): 3583- 3585.
[9] 韦树杰,覃立耿,黎勤鸿,等.骨水泥型加长柄人工双极人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折33例[J].广西医科大学学报,2014,31(4):655-656.
[10] 杨朝君,孙智文,张爱民,等.骨水泥型加长柄关节置换治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2014, 9(3):57-60.
[11] 汤发强,胡世平,吴宏,等.高龄骨质疏松患者股骨转子间骨折的微创治疗[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,32(24):6963-6965.
[12] 张麒云,吕南千,费青,等.经皮微创动力髋螺钉治疗股骨转子间骨折术后并发髋部巨大血肿1例[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 19(z1): 28-29.
[13] 高冲,徐静,宫福良,等.InterTAN治疗老年股骨转子间骨折疗效的影响因素分析[J].实用医学杂志,2014,11(22):3638-3640.
[14] 魏巍,刘军,霍维玲,等.几种内固定方法治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,25(21):6213-6214.
[15] 沈宏江,郭亮.股骨近端髓内钉与动力髋螺钉内固定修复老年股骨转子间骨折:12个月随访并发症发生率比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(44):7146-7150.
[16] 周修五,李雪飞,王铁军,等.InterTan和DHS治疗老年股骨转子间骨折围术期失血量的比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,27(24): 7101-7102.
[17] 郎涛.动力髋螺钉与股骨微创内固定手术器械钢板倒置治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的效果比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,21(6): 1580-1581.
[18] 王蒙,周雪峰,白克文,等.损害控制技术在高龄股骨转子间骨折治疗中的应用[J].中华创伤杂志,2014,30(12):1196-1200.
[19] 徐厚高.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与动力髋螺钉修复老年股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(35):5611-5615.
[20] 文浩,段戡,袁长深,等.股骨近端锁定钢板与动力髋螺钉修复股骨转子间骨折的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,41(35): 5715-5722.
[21] 贾鹏,赵栋,王志强,等.InterTan系统治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的疗效和安全性[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(12):2911-2913.
[22] 唐晓明,朱国太,孙海浪,等.DHS内固定治疗老年不稳定性股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].山东医药,2013,53(25):77-79.
[23] 刘宾,张亮,杨亚林,等.高龄股骨转子间骨折围手术期不同抗凝药物疗效分析[J].天津医药,2013,26(8):824-825.
[24] 曹燕明,雷昱,唐程,等.研制治疗股骨转子间骨折的具有可扩张翼型拉力螺钉的动力髋螺钉[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(12): 1950-1952.
[25] 郭晓亮,卫小春,王小虎,等.股骨转子间骨折髓内固定物治疗的优劣评说[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,12(26):4904-4911.
[26] 陈鹏,朱国兴,杨玉生,等.动力髋螺钉钢板辅以阻挡钉治疗股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,29(4):338-340.
[27] 张飞,陈伟,张晓琳,等.成人股骨转子间骨折的临床特点及其变化:单中心3201例分析[J].中华外科杂志,2014,52(9):697-701.
[28] 姚绍平,孙先润,李维朝,等.不稳定型股骨转子间骨折人工股骨头置换和股骨近端髓内钉内固定疗效分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2015, 22(2):131-134.
[29] 苏厂尧,谢文伟,姚汉刚,等.人工关节置换术与动力髋钢板治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折110例[J].实用医学杂志,2012, 28(14):2407-2409.
[30] 甄平,李旭升,周胜虎,等.股骨生物柄假体人工关节置换术治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(2): 173-175.
[31] 汪秀平.解剖钢板与DHS治疗老年不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的对比分析[J].海南医学,2013,24(16):2433-2435.
[32] 陈述祥,刘彦,陈丽君,等.老年股骨转子间骨折不同治疗方法的评价[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2014,17(2):177-181.
[33] 张晓岗,阿斯哈尔江•买买提依明,曹力,等.非骨水泥型人工关节置换治疗老年不稳定股骨转子间骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2012, 32(7):631-636.
[34] 李伟,石艳丽,许艳华,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年不稳定型股骨转子间骨折[J].中国伤残医学,2014,43(24):57-57,58.
[35] 王强,董利军,汪正宇,等.股骨近端髓内钉 InterTAN 和股骨近端抗旋髓内钉治疗不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的临床回顾研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2015,15(1):67-71.
[36] 叶少腾,陈凯宁,蓝创新,等.半髋置换在高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折治疗中的价值[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2013,12(8): 574-576.
[37] 林杨景,李杰,林炎水,等.InterTAN、PFNA和DHS治疗股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2014, 27(3):294-298.
[38] 鲁大路,吕先俊,李斌,等.联合加压交锁髓内钉修复股骨转子间骨折的临床应用和设计优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,17(31): 4957-4961.
[39] 方超,谢加兵,徐祝军,等.亚洲型防旋股骨近端髓内钉微创修复股骨转子间骨折:可为高龄患者首选[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 24(22):3469-3474.
[40] 黄海晶,辛景义,马宝通,等.Gamma3型髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折手术并发症的原因分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(7): 736-742. |