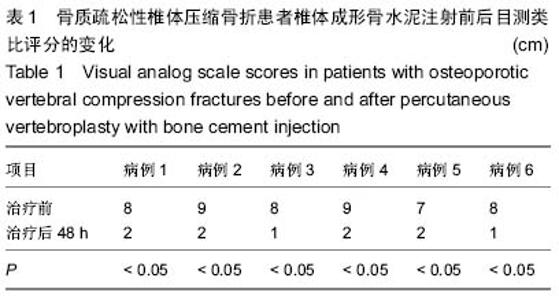
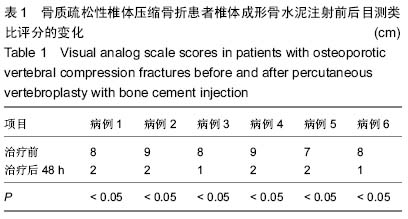
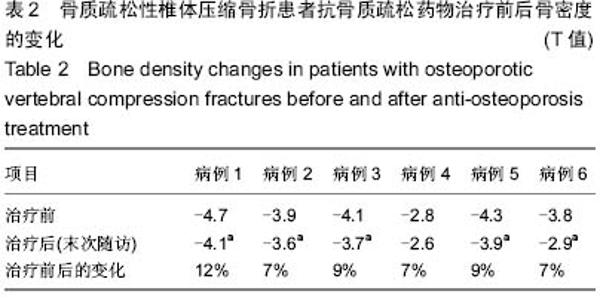
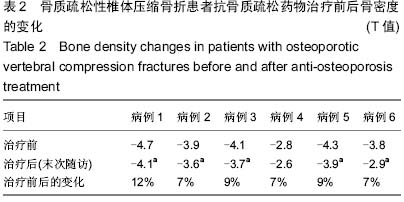
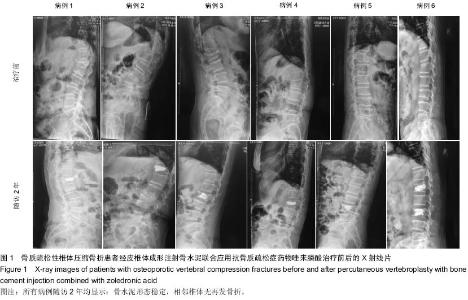
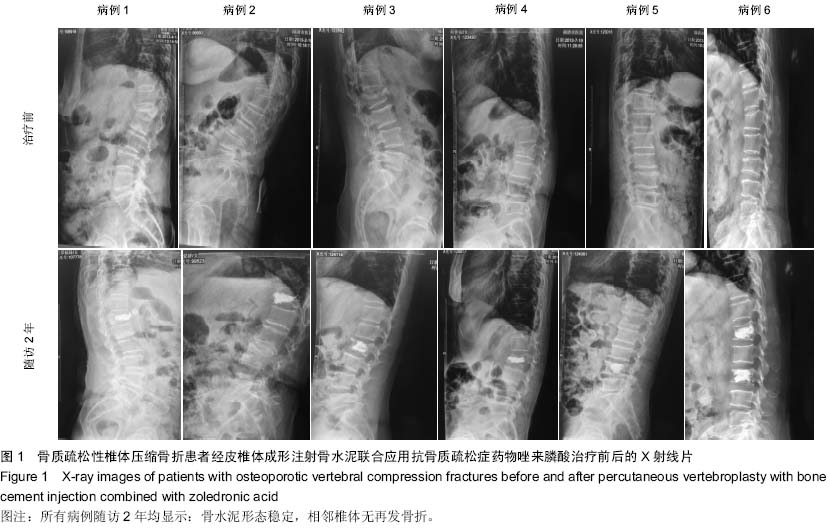
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (25): 3937-3941.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.25.001
Bone cement combined with zoledronic acid to repair osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Xue Feng, Ye Yu-song
- Sixth Ward, Department of General Surgery, Fuqing Municipal Hospital, Fuqing 350300, Fujian Province, China
-
Online:2015-06-18Published:2015-06-18 -
About author:Xue Feng, Associate chief physician, Sixth Ward, Department of General Surgery, Fuqing Municipal Hospital, Fuqing 350300, Fujian Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xue Feng, Ye Yu-song. Bone cement combined with zoledronic acid to repair osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(25): 3937-3941.
share this article
| [1] 徐苓.骨质疏松症[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2011:279.
[2] 中华医学会骨科学分会.骨质疏松骨折诊疗指南[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2009,8(5):287-291.
[3] 李安杰.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形治疗骨质疏松压缩性骨质的临床研究[J].医药前沿,2014,4(31):124-125.
[4] 朱洲,王生介,厉晓龙,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形与保守治疗胸腰椎体新鲜骨质疏松性压缩骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(39):6271-6275.
[5] 胡成栋,刘曦,周玉军,等.椎体成形治疗中聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(21):3823-3830.
[6] 周英杰,赵刚,李森,等.经皮聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形结合手法牵引复位治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(21):3823-3827.
[7] Lin PP,Kang HG,Kim YI,et al.Minimally invasive surgery for femoral neck fractures using bone cement infusible hollow-perforated screw in high-risk patients with advanced cancer.Surg Oncol.2015. pii: S0960-7404(15)00042-0. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2015.05.003.[Epub ahead of print]
[8] Chen J, Yu J, He Q, et al.A novel injectable porous surface modified bioactive bone cement for vertebroplasty: an in vivo biomechanical and osteogenic study in a rabbit osteoporosis model.J Transl Res.2015;7(3):548-257.
[9] Ghonim MR,Shabana YK,Ashraf B,et al.Anatomical reposition of incus after transmastoid facial nerve decompression using bone cement: preliminary results in 17 patients.Clin Otolaryngol.2015. doi: 10.1111/coa.12467.[Epub ahead of print]
[10] Matos AC,Marques CF,Pinto RV,et al.Novel doped calcium phosphate-PMMA bone cement composites as levofloxacin delivery systems.Int J Pharm.2015;490(1-2):200-208.
[11] Colón-Emeric C,Nordsletten L,Olson S,et al.Association between timing of zoledronic acid infusion and hip fracture healing.Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(8):2329-2336.
[12] 秦德安,宋洁富,魏杰,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折椎体成形术后继发骨折原因分析[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(9):730-733.
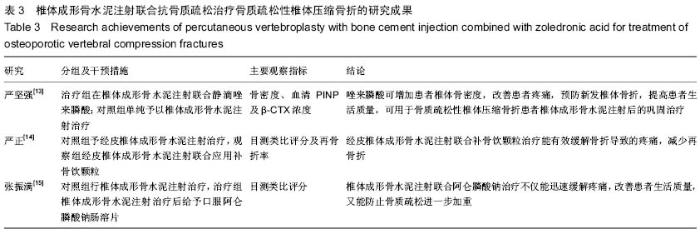
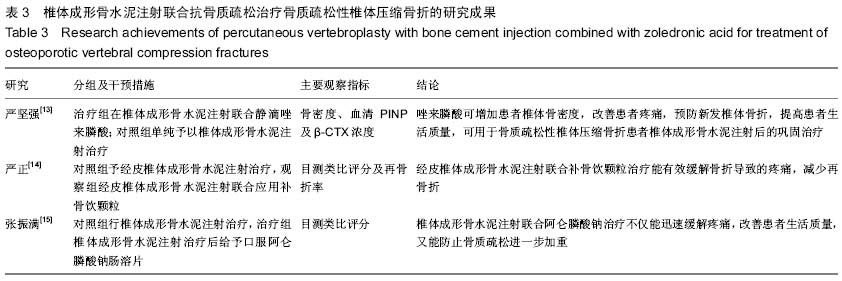
[13] 严坚强,孙奎,梁必如,等.唑来膦酸在骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术后的临床应用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(12): 1428-1431.
[14] 严正,李献城,赖斌,等.经皮椎成形术联合补骨饮颗粒治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床研究[J].中国初级卫生保健,2015, 29(3):89-90.
[15] 张振满,冯和林.椎体成形术联合阿仑膦酸钠治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床观察[J].中国临床医生,2014,43(7): 65-66.
[16] Nas OF,Inecikli MF,Kacar E,et al.Effectiveness of percutaneous vertebroplasty in cases of vertebral metastases.Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015. pii: S2211-5684(15)00191-6. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2015.05.001. [Epub ahead of print]
[17] Wang S,Shi G,Meng X.Clinical curative effect of Percutaneous vertebroplasty combined with (125)I-seed implantation in treating spinal metastatic tumor.J Pharm Sci. 2015;28(3 Suppl):1039-1042.
[18] Guo Z,Yang J,Zheng Y,et al.Thoracolumbar fascia injury associated with residual back pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a compelling study.Osteoporos Int. 2015 Jun 6. [Epub ahead of print] No abstract available.
[19] Li HD,Xu CJ,Wang H,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for single osteoporotic vertebral body compression fracture: Results of unilateral 3-D percutaneous puncture technique. Indian J Orthop.2015;49(2):245-250.
[20] Ke ZY,Wang Y,Zhong YL,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty combined with percutaneous pediculoplasty for lytic vertebral body and pedicle lesions of metastatic tumors.Pain Physician. 2015;18(3):E347-353.
[21] Wang H,Sribastav SS,Ye F,et al.Comparison of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Single Level Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Meta-analysis of the Literature.Pain Physician. 2015;18(3): 209-222.
[22] Macías-Hernández SI,Chávez-Arias DD,Miranda-Duarte A,et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Versus Conservative Treatment and Rehabilitation in Women with Vertebral Fractures due to Osteoporosis: A Prospective Comparative Study.Rev Invest Clin. 2015;67(2):98-103.
[23] Wang C,Zhao F.Type-B Leaks in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty should be defined as Leaks through Basivertebral Foramen and Related Posterior Wall Defect instead of merely through Basivertebral Vein.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2015.[Epub ahead of print] No abstract available.
[24] Gu YT,Zhu DH,Liu HF,et al.Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty for preventing secondary fracture after vertebroplasty.J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10(1):31.
[25] Sun HL,Li CD,Zhu JL,et al.Clinical research of percutaneous vertebroplasty or percutaneous kyphoplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures induced by glucocorticosteroid.Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015;47(2): 242-247.
[26] Zhao DH,Chen K,Zhu J,et al.Postoperative Functional Evaluation of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Compared With Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Vertebral Compression Fractures.Am J Ther.2015.[Epub ahead of print]
[27] Sun H,Yang Z,Xu Y,et al.Safety of percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of metastatic spinal tumors in patients with posterior wall defects.Eur Spine J.2015. [Epub ahead of print]
[28] Falco MD,Masala S,Stefanini M,et al.Patient skin dose measurements using a cable free system MOSFETs based in fluoroscopically guided percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous disc decompression, radiofrequency medial branch neurolysis, and endovascular critical limb ischemia.J Appl Clin Med Phys.2015;16(1):5020.
[29] 田云虎,刘亚,管春和.椎体成形术的临床应用[J].实用骨科杂志, 2013, 9(2):109-111.
[30] Gehlbach SH, Bigelow C, Heimisdottir M, et al.Recognition of vertebral fracture in a clinical setting.Osteoporos Int.2000; 11(7): 577-582. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||