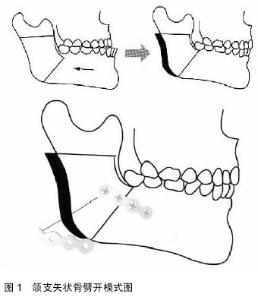
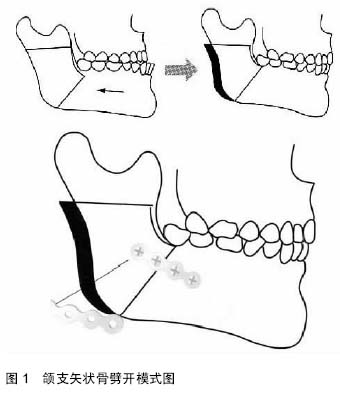
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (24): 3905-3909.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.24.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Morphologic characteristics of the mandibular ramus in patients with prognathism undergoing sagittal split ramus osteotomy
Ma Jia
- Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China
-
Online:2015-06-11Published:2015-06-11 -
About author:Ma Jia, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Plan of Shenyang City, No. F11-262-9-42; the Scientific Research Plan Project of Liaoning Province, No. 2013021005
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Jia. Morphologic characteristics of the mandibular ramus in patients with prognathism undergoing sagittal split ramus osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(24): 3905-3909.
share this article
| [1] Trauner R, Obwegeser H. The surgical correction of mandibular prognathism and retrognathia with consideration of genioplasty. I. Surgical procedures to correct mandibular prognathism and reshaping of the chin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1957;10(7):677-689; contd.
[2] Hunsuck EE. A modified intraoral sagittal splitting technic for correction of mandibular prognathism. J Oral Surg.1968; 26(4): 250-253.
[3] Epker BN. Modifications in the sagittal osteotomy of the mandible. J Oral Surg.1977;35(2):157-159.
[4] Loh FC. Technical modification of the sagittal split mandibular ramus osteotomy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1992; 74(6): 723-726.
[5] Fujimura K, Segami N, Kobayashi S. Anatomical study of the complications of intraoral vertico-sagittal ramus osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64(3):384-389.
[6] Acebal-Bianco F, Vuylsteke PL, Mommaerts MY, et al. Perioperative complications in corrective facial orthopedic surgery: a 5-year retrospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(7):754-760.
[7] Akal UK, Sayan NB, Aydo?an S, et al. Evaluation of the neurosensory deficiencies of oral and maxillofacial region following surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;29(5): 331-336.
[8] Kim HJ, Lee HY, Chung IH, et al. Mandibular anatomy related to sagittal split ramus osteotomy in Koreans. Yonsei Med J. 1997;38(1):19-25.
[9] Ribeiro DP, Gandelmann IH, Medeiros PJ. Comparison of mandibular rami width in patients with prognathism and retrognathia. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64(10):1506-1509.
[10] Muto T, Shigeo K, Yamamoto K, et al. Computed tomography morphology of the mandibular ramus in prognathism: effect on the medial osteotomy of the sagittal split ramus osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61(1):89-93.
[11] Smith BR, Rajchel JL, Waite DE, et al. Mandibular ramus anatomy as it relates to the medial osteotomy of the sagittal split ramus osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991;49(2): 112-116.
[12] Tsuji Y, Muto T, Kawakami J, et al. Computed tomographic analysis of the position and course of the mandibular canal: relevance to the sagittal split ramus osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;34(3):243-246.
[13] Yamamoto R, Nakamura A, Ohno K, et al. Relationship of the mandibular canal to the lateral cortex of the mandibular ramus as a factor in the development of neurosensory disturbance after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60(5):490-495.
[14] Al-Bishri A, Barghash Z, Rosenquist J, et al. Neurosensory disturbance after sagittal split and intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy: as reported in questionnaires and patients' records. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;34(3):247-251.
[15] Nesari S, Kahnberg KE, Rasmusson L. Neurosensory function of the inferior alveolar nerve after bilateral sagittal ramus osteotomy: a retrospective study of 68 patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;34(5):495-498.
[16] Rich J, Golden BA, Phillips C. Systematic review of preoperative mandibular canal position as it relates to postoperative neurosensory disturbance following the sagittal split ramus osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;43(9):1076-1081.
[17] Sekerci AE, Sahman H. Cone beam computed tomographic analyses of the position and course of the mandibular canal: relevance to the sagittal split ramus osteotomy. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:945671.
[18] Wittwer G, Adeyemo WL, Beinemann J, et al. Evaluation of risk of injury to the inferior alveolar nerve with classical sagittal split osteotomy technique and proposed alternative surgical techniques using computer-assisted surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41(1):79-86.
[19] Rich J, Golden BA, Phillips C. Systematic review of preoperative mandibular canal position as it relates to postoperative neurosensory disturbance following the sagittal split ramus osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;43(9):1076-1081.
[20] Tamás F. Position of the mandibular canal. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1987;16(1):65-69.
[21] Rajchel J, Ellis E 3rd, Fonseca RJ. The anatomical location of the mandibular canal: its relationship to the sagittal ramus osteotomy. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1986;1(1): 37-47.
[22] 华泽权,刘妍琼,宋九余,等.与下颌升支矢状劈开截骨相关的下颌管解剖研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志, 2003,17(5):444-445.
[23] Ylikontiola L, Moberg K, Huumonen S, et al. Comparison of three radiographic methods used to locate the mandibular canal in the buccolingual direction before bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93(6):736-742.
[24] 赵保东,李宁毅,周仰光,等.下颌骨的三维重建及实体解剖研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2002,20(1):21-23.
[25] Hara S, Mitsugi M, Kanno T, et al. Three-dimensional virtual operations can facilitate complicated surgical planning for the treatment of patients with jaw deformities associated with facial asymmetry: a case report. Int J Oral Sci. 2013;5(3):176-182.
[26] 华泽权,邹明宇,李树华.下颌升支截骨手术相关下颌管解剖标志的多层CT测量研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2006,22(1):3-4. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||