| [1] Tutuncu Z, Kavanaugh A. Rheumatic disease in the elderly: rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2007;33(1): 57-70.
[2] Goldring SR. Pathogenesis of bone and cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42 Suppl 2:ii11-16.
[3] Edwards JC, Wilkinson LS, Jones HM, et al. The formation of human synovial joint cavities: a possible role for hyaluronan and CD44 in altered interzone cohesion. J Anat. 1994;185 (Pt 2):355-367.
[4] Noss EH, Brenner MB. The role and therapeutic implications of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in inflammation and cartilage erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2008;223: 252-270.
[5] Kourilovitch M, Galarza-Maldonado C, Ortiz-Prado E. Diagnosis and classification of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:26-30.
[6] 中华医学会风湿病学分会.类风湿关节炎诊治指南(草案)[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2003,7(4):250-254.
[7] Neumann E, Lefèvre S, Zimmermann B, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis progression mediated by activated synovial fibroblasts. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16(10):458-468.
[8] Jakus Z, Simon E, Balázs B, et al. Genetic deficiency of Syk protects mice from autoantibody-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(7):1899-1910.
[9] van Oosterhout M, Bajema I, Levarht EW, et al. Differences in synovial tissue infiltrates between anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-positive rheumatoid arthritis and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-negative rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):53-60.
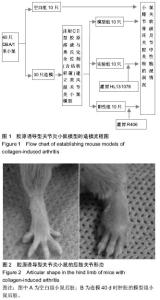
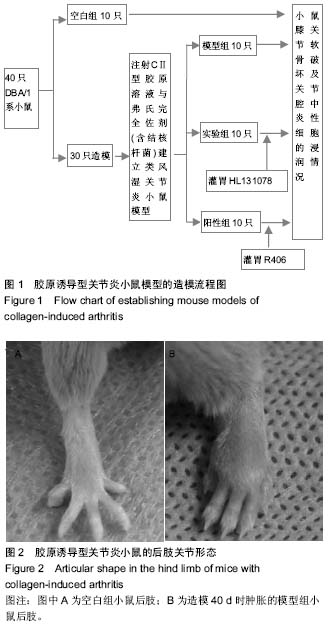
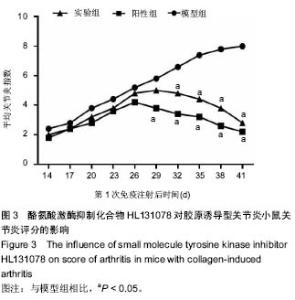
[10] 张玲玲,刘云洁,童彤,等. DBA/1小鼠胶原性关节炎模型建立方法及评价指标[J].中国药理学通报,2010,26(8):1108-1111.
[11] Pine PR, Chang B, Schoettler N, et al. Inflammation and bone erosion are suppressed in models of rheumatoid arthritis following treatment with a novel Syk inhibitor. Clin Immunol. 2007;124(3):244-257.
[12] Brand DD, Kang AH, Rosloniec EF. The mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis. Methods Mol Med. 2004;102: 295-312.
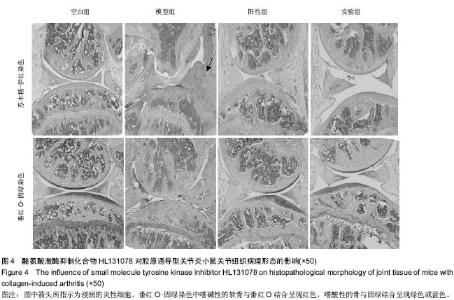
[13] 高改霞,卫小春,李凯,等.大鼠膝关节软骨不同染色方法的差异[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(24):4385-4389.
[14] Ulanova M, Duta F, Puttagunta L, et al. Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) as a novel target for allergic asthma and rhinitis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005;9(5):901-921.
[15] Lin S, Cicala C, Scharenberg AM, et al. The Fc(epsilon) RIbeta subunit functions as an amplifier of Fc(epsilon) RIgamma-mediated cell activation signals. Cell. 1996;85(7): 985-995.
[16] Fu C, Turck CW, Kurosaki T, et al. BLNK: a central linker protein in B cell activation. Immunity. 1998;9(1):93-103.
[17] Sedlik C, Orbach D, Veron P, et al. A critical role for Syk protein tyrosine kinase in Fc receptor-mediated antigen presentation and induction of dendritic cell maturation. J Immunol. 2003;170(2):846-852.
[18] Mócsai A, Humphrey MB, Van Ziffle JA, et al. The immunomodulatory adapter proteins DAP12 and Fc receptor gamma-chain (FcRgamma) regulate development of functional osteoclasts through the Syk tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(16):6158-6163.
[19] Xie DL, Hui F, Meyers R, et al. Cartilage chondrolysis by fibronectin fragments is associated with release of several proteinases: stromelysin plays a major role in chondrolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;311(2):205-212.
[20] Ozaki N, Suzuki S, Ishida M, et al. Syk-dependent signaling pathways in neutrophils and macrophages are indispensable in the pathogenesis of anti-collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Int Immunol. 2012;24(9):539-550. |