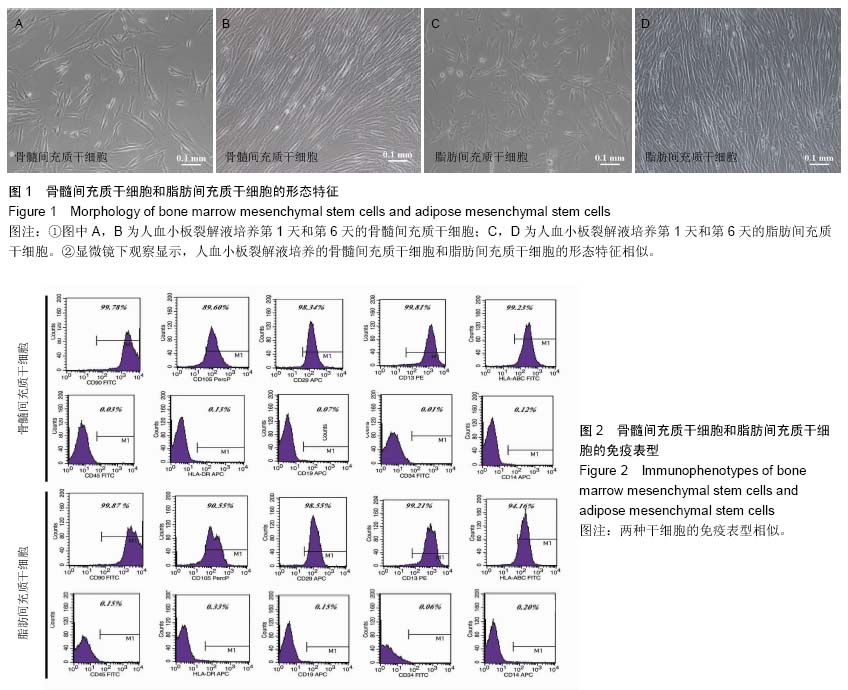
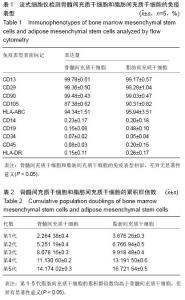
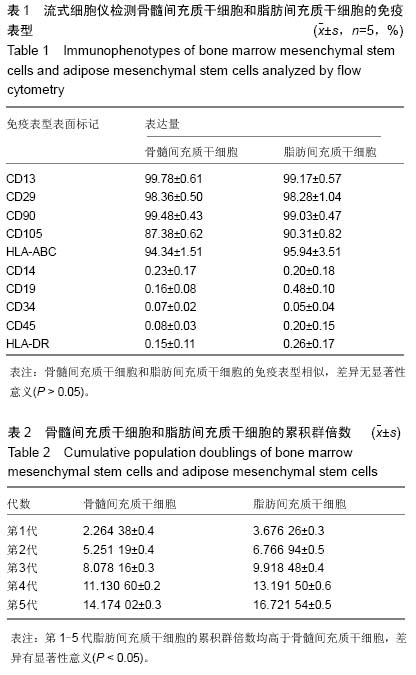
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (23): 3723-3728.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.23.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of platelet lysate on the biological characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells
Wu Di1, Wu Xiao-yun2, Wu Yan1
- 1Department of Histology and Embryology, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China;
2Beijing Jingmeng Stem Cell High-Tech Co., Ltd., Beijing 100085, China
-
Online:2015-06-04Published:2015-06-04 -
Contact:Wu Yan, M.D., Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Histology and Embryology, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wu Di, Physician, Department of Histology and Embryology, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Stem Cell Application Technology Innovation Team Foundation of Department of Technology of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. KJT0020947
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Di, Wu Xiao-yun, Wu Yan. Effect of platelet lysate on the biological characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(23): 3723-3728.
share this article
| [1] Hoogduijn MJ, Dor FJ. Mesenchymal stem cells: are we ready for clinical application in transplantation and tissue regeneration. Front Immunol. 2013;4:144. [2] Hua J, Gong J, Meng H, et al. Comparison of different methods for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord matrix: proliferation and multilineage differentiation as compared to mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood and bone marrow. Cell Biol Int. 2014; 38(2):198-210. [3] Mazhari R, Hare JM. Mechanisms of action of mesenchymal stem cells in cardiac repair: potential influences on the cardiac stem cell niche. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007;4 Suppl 1:S21-26. [4] Wang TH, Lee YS, Hwang SM. Transcriptome analysis of common gene expression in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from four different origins. Methods Mol Biol. 2011; 698:405-417. [5] Hsiao ST, Asgari A, Lokmic Z, et al. Comparative analysis of paracrine factor expression in human adult mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose, and dermal tissue. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(12):2189-2203. [6] Jin HJ, Bae YK, Kim M, et al. Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood as sources of cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(9):17986-18001. [7] Aldahmash A, Zaher W, Al-Nbaheen M, et al. Human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells: basic biology and current clinical use for tissue regeneration. Ann Saudi Med. 2012;32(1): 68-77. [8] van der Valk J, Brunner D, De Smet K, et al. Optimization of chemically defined cell culture media--replacing fetal bovine serum in mammalian in vitro methods. Toxicol In Vitro. 2010; 24(4):1053-1063. [9] Hemeda H, Giebel B, Wagner W. Evaluation of human platelet lysate versus fetal bovine serum for culture of mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(2): 170-180. [10] Gottipamula S, Sharma A, Krishnamurthy S, et al. Human platelet lysate is an alternative to fetal bovine serum for large-scale expansion of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2012;34(7):1367-1374. [11] Fekete N, Gadelorge M, Fürst D, et al. Platelet lysate from whole blood-derived pooled platelet concentrates and apheresis-derived platelet concentrates for the isolation and expansion of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells: production process, content and identification of active components. Cytotherapy. 2012;14(5):540-554. [12] Jonsdottir-Buch SM, Lieder R, Sigurjonsson OE. Platelet lysates produced from expired platelet concentrates support growth and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e68984. [13] Santo VE, Duarte AR, Popa EG, et al. Enhancement of osteogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells by the controlled release of platelet lysates from hybrid scaffolds produced by supercritical fluid foaming. J Control Release. 2012;162(1):19-27. [14] Jose S, Hughbanks ML, Binder BY, et al. Enhanced trophic factor secretion by mesenchymal stem/stromal cells with Glycine-Histidine-Lysine (GHK)-modified alginate hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):1955-1964. [15] Bieback K, Hecker A, Kocaömer A, et al. Human alternatives to fetal bovine serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2009;27(9):2331-2341. [16] De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A, et al. Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(3):101-109. [17] Parker A, Shang H, Khurgel M, et al. Low serum and serum-free culture of multipotential human adipose stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2007;9(7):637-646. [18] Shanskii YD, Sergeeva NS, Sviridova IK, et al. Human platelet lysate as a promising growth-stimulating additive for culturing of stem cells and other cell types. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2013;156(1):146-151. [19] Shih DT, Burnouf T. Preparation, quality criteria, and properties of human blood platelet lysate supplements for ex vivo stem cell expansion. N Biotechnol. 2015;32(1):199-211. [20] Russell KA, Koch TG. Equine platelet lysate as an alternative to fetal bovine serum in equine mesenchymal stromal cell culture - too much of a good thing. Equine Vet J. 2015 Mar 16. [Epub ahead of print] [21] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [22] Mead B, Berry M, Logan A, et al. Stem cell treatment of degenerative eye disease. Stem Cell Res. 2015;14(3): 243-257. [23] Kfoury Y, Scadden DT. Mesenchymal cell contributions to the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(3):239-253. [24] Frausin S, Viventi S, Verga Falzacappa L, et al. Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stromal cells: Biological properties, induction of neuronal phenotype and current applications in neurodegeneration research.Acta Histochem. 2015 Mar 3. [Epub ahead of print] [25] Mahmood Z, Muhammad K, Schmalzing M, et al. CD27-IgD- memory B cells are modulated by in vivo interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) blockade in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):61. [26] Henry CJ, Sedjo RL, Rozhok A, et al. Lack of significant association between serum inflammatory cytokine profiles and the presence of colorectal adenoma. BMC Cancer. 2015; 15:123.
|
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||