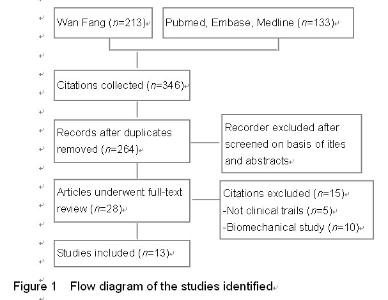
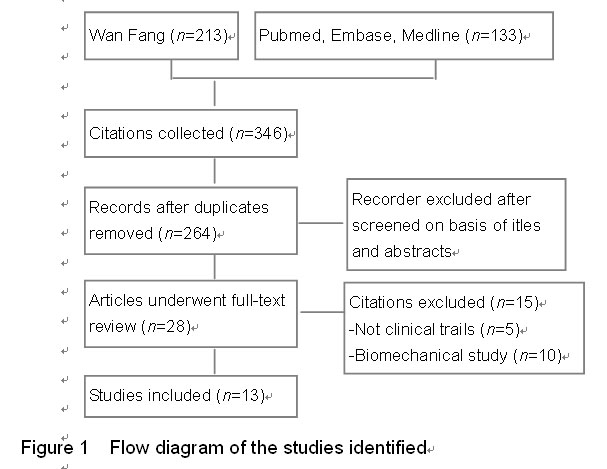
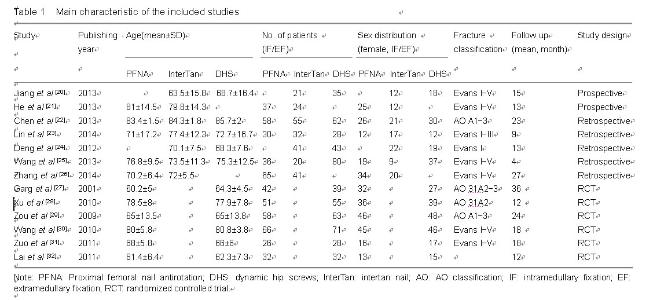
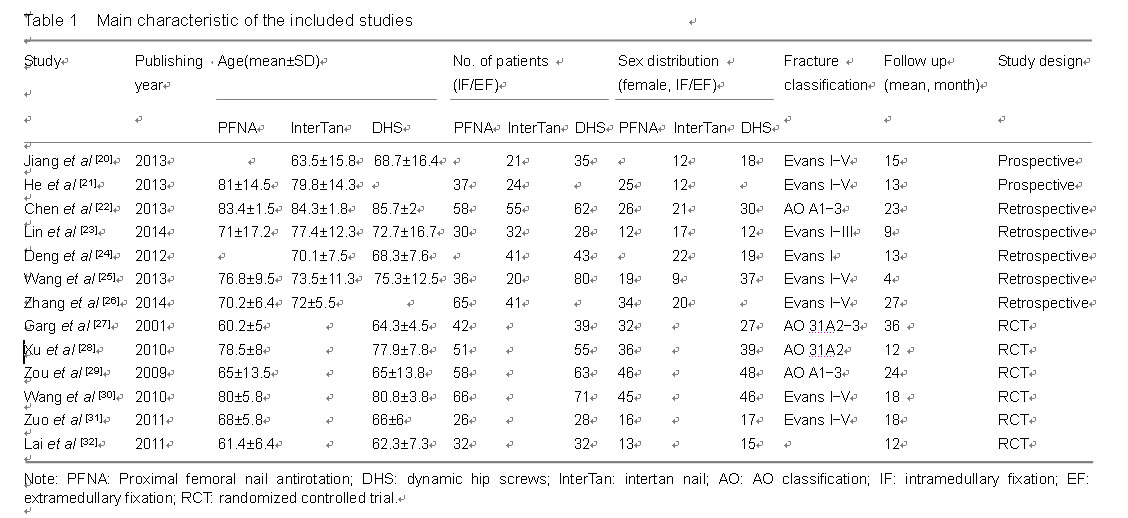
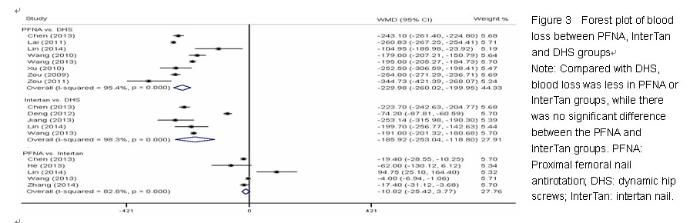
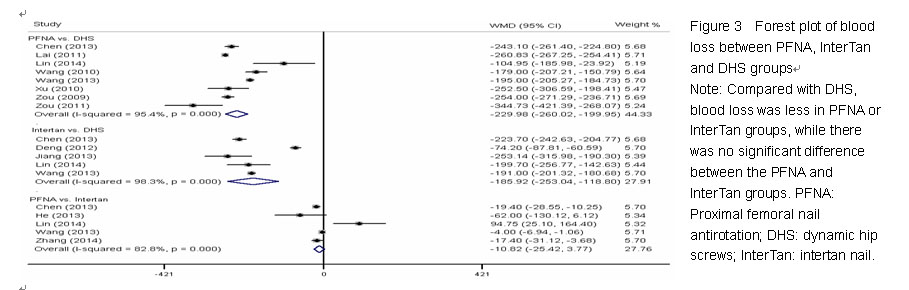
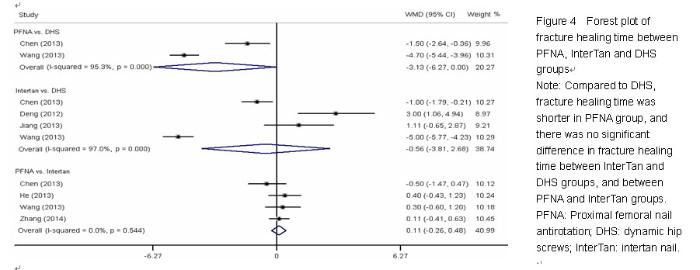
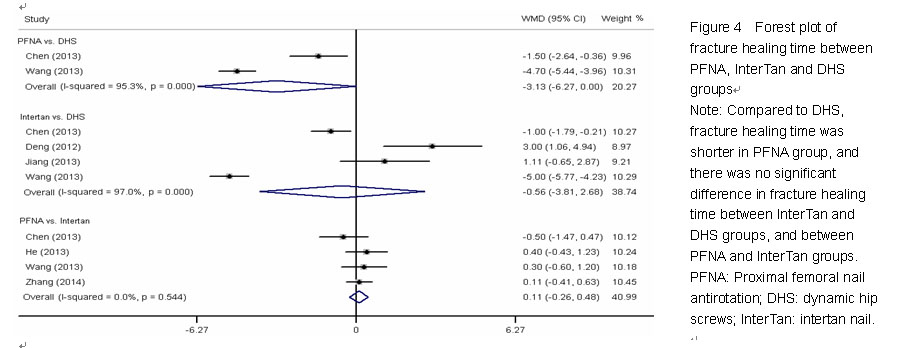
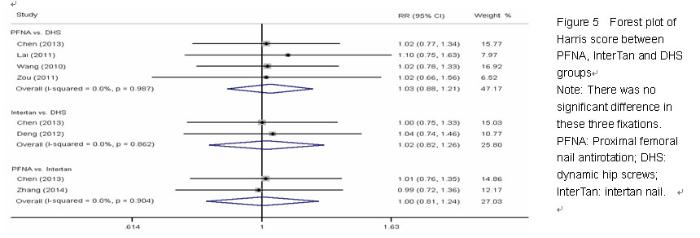
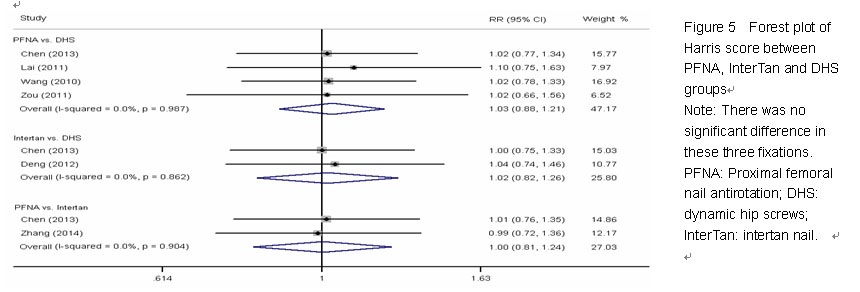
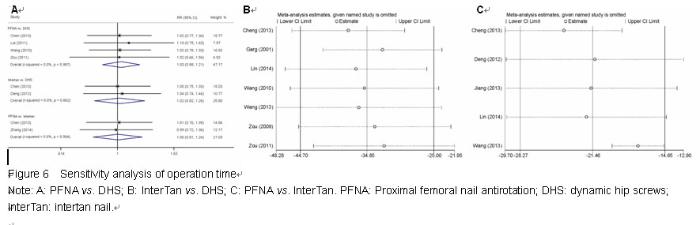
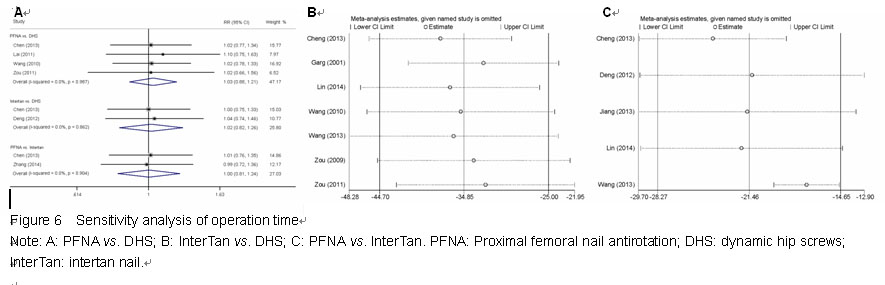
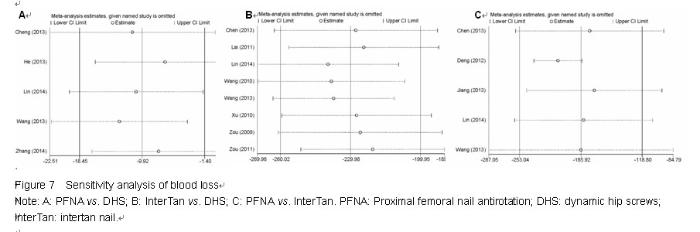
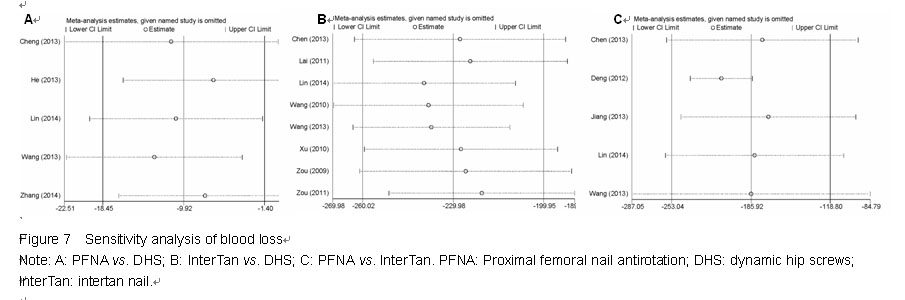
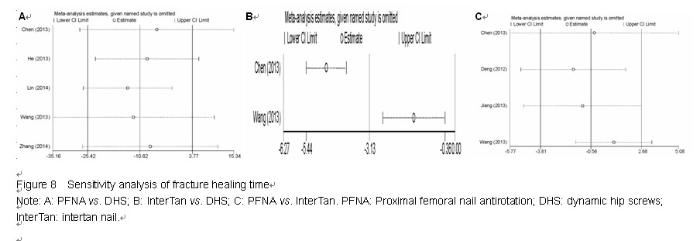
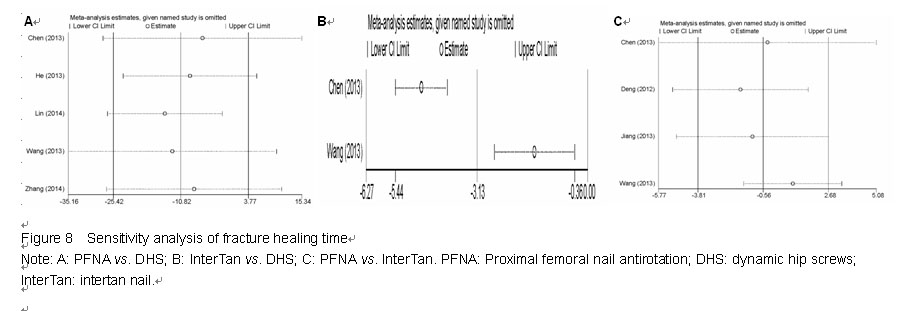
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (22): 3543-3549.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.22.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dynamic hip screw, proximal femoral nail antirotation and InterTan nail for intertrochanteric fractures
Shao Jin, Yang Tie-yi, Wang Zhi, Zhang Yan, Liu Shu-yi
- Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200135, China
-
Received:2015-05-08Online:2015-05-28Published:2015-05-28 -
Contact:Yang Tie-yi, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200135, China -
About author:Shao Jin, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200135, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81201367; the Key Discipline Construction Project of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai, No. PWZx2014-09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shao Jin, Yang Tie-yi, Wang Zhi, Zhang Yan, Liu Shu-yi. Dynamic hip screw, proximal femoral nail antirotation and InterTan nail for intertrochanteric fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(22): 3543-3549.
share this article
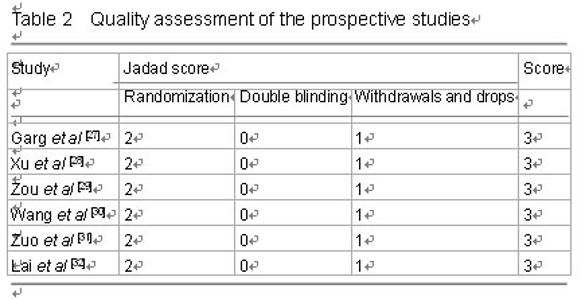
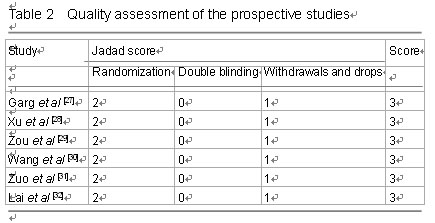
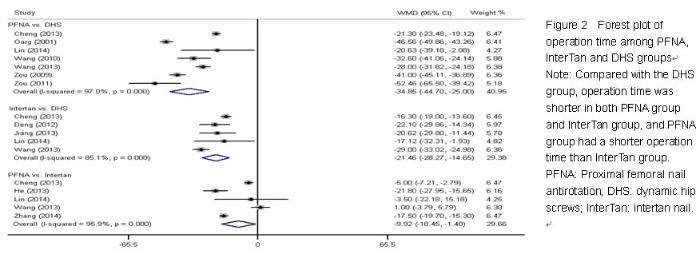
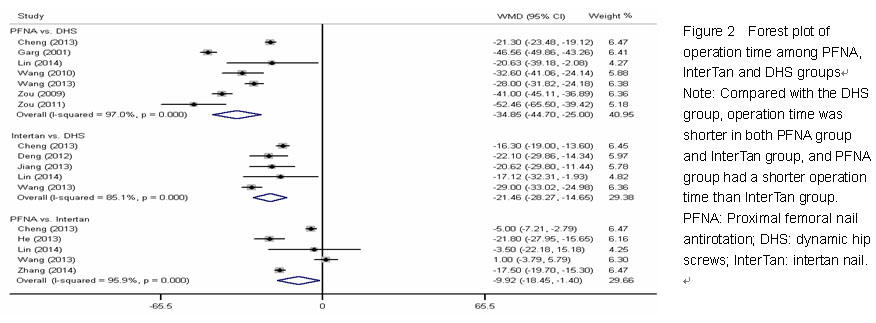
| [1] Butler M, Forte ML, Joglekar SB, et al. Evidence summary: systematic review of surgical treatments for geriatric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(12):1104-1115. [2] Swart E, Makhni EC, Macaulay W, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of fixation options for intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(19):1612-1620. [3] Haidukewych GJ. Intertrochanteric fractures: ten tips to improve results. Instr Course Lect. 2010;59:503-509. [4] Zhang K, Zhang S, Yang J, et al. Proximal femoral nail vs. dynamic hip screw in treatment of intertrochanteric fractures: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20:1628-1633. [5] Albareda J, Laderiga A, Palanca D, et al. Complications and technical problems with the gamma nail. Int Orthop. 1996; 20(1):47-50. [6] Miedel R, Ponzer S, Törnkvist H, et al. The standard Gamma nail or the Medoff sliding plate for unstable trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures. A randomised, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(1):68-75. [7] Windolf J, Hollander DA, Hakimi M, et al. Pitfalls and complications in the use of the proximal femoral nail. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2005;390(1):59-65. [8] Chen Y, Liu S, Lin P, et al. Comparative biomechanical study of reversed less invasive stabilization system and proximal femoral nail antirotation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(23):4124-4129. [9] Li J, Cheng L, Jing J. The Asia proximal femoral nail antirotation versus the standard proximal femoral antirotation nail for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly Chinese patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(2):143-146. [10] Huang Y, Zhang C, Luo Y. A comparative biomechanical study of proximal femoral nail (InterTAN) and proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures. Int Orthop. 2013; 37(12):2465-2473. [11] Rupprecht M, Grossterlinden L, Ruecker AH, et al. A comparative biomechanical analysis of fixation devices for unstable femoral neck fractures: the Intertan versus cannulated screws or a dynamic hip screw. J Trauma. 2011;71(3):625-634. [12] Wang Q, Yang X, He HZ, et al. Comparative study of InterTAN and Dynamic Hip Screw in treatment of femoral intertrochanteric injury and wound. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(12):5578-5582. [13] Utrilla AL, Reig JS, Muñoz FM, et al. Trochanteric gamma nail and compression hip screw for trochanteric fractures: a randomized, prospective, comparative study in 210 elderly patients with a new design of the gamma nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(4):229-233. [14] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12. [15] Zeng L, Liang X, Liu Q, et al. The Predictive Value of Circulating Tumor Cells in Ovarian Cancer: A Meta Analysis. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015. in press. [16] Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005;5:13. [17] Shao Y, Geng Y, Gu W, et al. Prognostic significance of microRNA-375 downregulation in solid tumors: a meta-analysis. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:626185. [18] Tobias A. Assessing the Influence of a Single Study in the Meta-Analysis Estimate. Stata Tech Bul. 1999;8:15-17. [19] van Enst WA, Ochodo E, Scholten RJ, et al. Investigation of publication bias in meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy: a meta-epidemiological study. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:70. [20] Jiang ZH, Li NJ, Zhu QJ, et al. Comparison of InterTAN and dynamic hip screw in treatment of femoral intertrochanteric fractures. Zhongguo Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi. 2013; 36(5):4-7. [21] He JP, Zhang SM, Qiao L, et al. Comparative study of the selection of intramedullary fixation in the treatment of femoral intertrochanteric fractures in senile osteoporotic patients. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2013;19(3): 268-270. [22] Chen H, Yin YS, Chen Y, et al. Comparison of Intertan, PFNA and Dynamic Hip Screw in Treatment of Femorai Intertrochanteric Fractures. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan. 2013; 1(35):405-406. [23] Lin YJ, Li J, Lin YS, et al. Comparison of the curative effect on treatment of intertrochanteric fractures with InterTAN、PFNA and DHS. Jinan Daxue Xuebao: Ziran Kexue yu Yixue Ban. 2014;35(3):294-298. [24] Deng JF, Zhou S, Niu HQ. Type of intertrochanteric fracture and choice of internal fixation screw. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(48):8976-8982. [25] Wang YG, Chen M, Hu JK, et al. Comparison of three fixations for treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures in the elderly. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(8):651-655. [26] Zhang XD, Liu YW, Jia YD, et al. Comparison of Three Fixation for Treatment of Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures. Shiyong Guke Zazhi. 2014;20(4):350-354. [27] Garg B, Marimuthu K, Kumar V, et al. Outcome of short proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw for fixation of unstable trochanteric fractures. A randomised prospective comparative trial. Hip Int. 2011;21(5):531-536. [28] Xu YZ, Geng DC, Mao HQ, et al. A comparison of the proximal femoral nail antirotation device and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fracture. J Int Med Res. 2010;38(4):1266-1275. [29] Zou J, Xu Y, Yang H. A comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw devices in trochanteric fractures. J Int Med Res. 2009;37(4):1057-1064. [30] Wang XB, Xu YZ, Geng DC, et al. Comparison of the rapeutic effect of Pfna with Dhs for intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. Suzhou Daxue Xuebao: Yixue Ban. 2010;30(3):639-641. [31] Zuo WS, Dai ZT, Tian JW. Comparison of therapeutic effect of PFNA with DHS in intertrochanteric fractures. Zhongguo Xiandai Yixue Zazhi. 2011;21(4):475-478. [32] Lai XL, Li F, Liu DX, et al. Comparison of the rapeutic effect of Pfna with Dhs for intertrochanteric fractures. Zhongguo Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi. 2011;34(26):70-72. [33] Simmonds MC, Higgins JP, Stewart LA, et al. Meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomized trials: a review of methods used in practice. Clin Trials. 2005;2(3):209-217. 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
|
| [1] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [2] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [5] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [6] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [7] | Cheng Shigao, , Wang Wanchun, Jiang Dong, Li Tengfei, Li Xun, Ren Lian. Comparison of the standard and long-stem bone cement prosthesis replacement in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 362-367. |
| [8] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [9] | Xiang Feifan, Ye Junwu, Zhang Xihai, Ge Jianhua, Tang Lian, Yang Yunkang. Comparison of three different internal fixation methods in treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 403-408. |
| [10] | Fan Yinuo, Guan Zhiying, Li Weifeng, Chen Lixin, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Research status and development trend of bibliometrics and visualization analysis in the assessment of femoroacetabular impingement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 414-419. |
| [11] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| [12] | Wang Yan, Dong Benchao, Wang Ying, Sun Lei, Lu Bin, Bai Haohao, Tian Aixian, Ma Jianxiong, Ma Xinlong. Animal models of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: modeling methods and characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 292-297. |
| [13] | Li Haifeng, Liu Yu, Yin Qudong, Sun Zhenzhong, Rui Yongjun, Gu Sanjun. Risk of complications of early postoperative weight-bearing after internal fixation of intracapsular femoral neck fractures: 2-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2875-2880. |
| [14] | Yang Kun, Fei Chen, Wang Pengfei, Zhang Binfei, Yang Na, Tian Ding, Zhuang Yan, Zhang Kun . Meta-analysis of the efficacy of robot-assisted and traditional manual implantation of cannulated screws in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2938-2944. |
| [15] | Liu Yuan, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Zhang Jingzhou, Li Gang. Molecular targets and mechanism of Bushen Huoxue Decoction in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head: an analysis based on network pharmacology and protein module [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2703-2710. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||