Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (17): 2703-2710.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3914
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular targets and mechanism of Bushen Huoxue Decoction in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head: an analysis based on network pharmacology and protein module
Liu Yuan1, Liu Jinbao1, 2, Xu Bo1, 2, Zhang Jingzhou1, Li Gang1, 2
- 1Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Microsurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-06Revised:2020-05-11Accepted:2020-05-28Online:2021-06-18Published:2021-01-08 -
Contact:Li Gang, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; Department of Microsurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Yuan, Master candidate, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Project), No. 81774333 (to LG); Shandong Provincial Key Research & Development Program, No. 2016GSF202022 (to LG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yuan, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Zhang Jingzhou, Li Gang. Molecular targets and mechanism of Bushen Huoxue Decoction in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head: an analysis based on network pharmacology and protein module[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2703-2710.
share this article

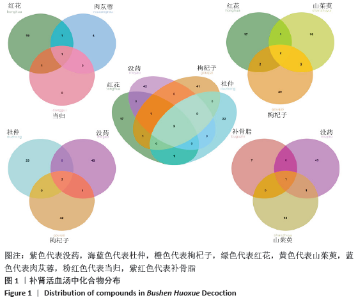
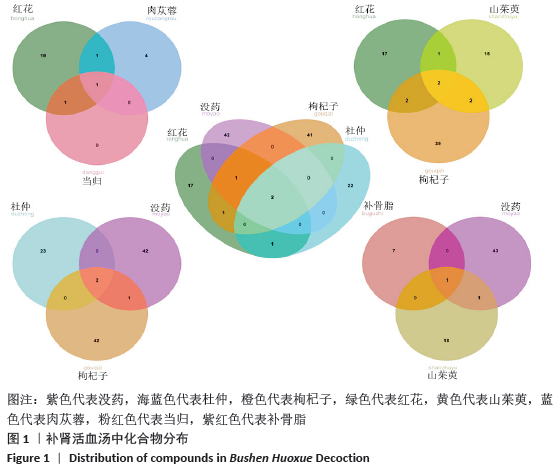
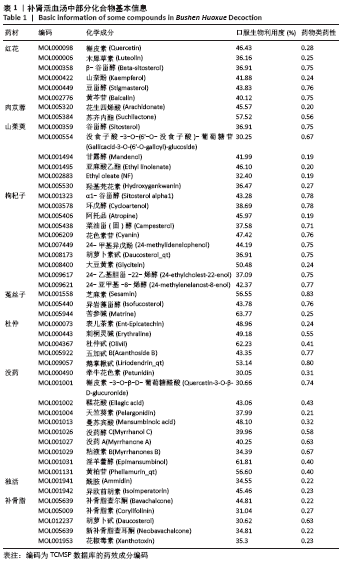
2.1 补肾活血汤中活性成分的筛选 通过TCMSP及TCMID检索到红花、当归、肉苁蓉、山茱萸、枸杞子、菟丝子、熟地黄、杜仲、没药、独活、补骨脂中化合物共1 427个,其中189个来自红花,125个来自当归,75个来自肉苁蓉,226个来自山茱萸,188个来自枸杞子,29个来自菟丝子,76个来自熟地黄,119个来自杜仲,276个来自没药,99个来自独活,25个来自补骨脂。以口服生物利用度≥30%且药物类药性≥0.18,筛选出活性化合物167个,其中22个来自红花,2个来自当归,6个来自肉苁蓉,20个来自山茱萸,45个来自枸杞子,11个来自菟丝子,2个来自熟地黄,25个来自杜仲,45个来自没药,9个来自独活,10个来自补骨脂。补肾活血汤中部分活性化合物基本信息见表1。 "
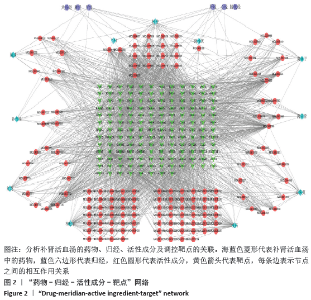
2.3 “药物-归经-活性成分-靶点”相互作用网络 根据《中华人民共和国药典》查询可知,红花归肝、心经;当归属心、肝、脾经;山茱萸归肝、肾经;枸杞子归肝、肾经;菟丝子肝、肾、脾经;熟地黄归心、肝、肾经;杜仲归肝、肾经;没药归心、肝经;独活归肾、膀胱经;补骨脂归脾、肾经;肉苁蓉归肾、大肠经。“药物-归经-活性成分-靶点”相互作用网络共包括311个节点(11个药物节点、6个归经节点、142个活性成分节点和151个靶点节点)和1 867条边,其中167个活性成分中有25个未参与网络构建,见图2。网络中的每条边代表药物所含有的活性成分以及活性成分与靶点基因之间的相互作用关系,每个节点的度值表示网络中与节点连接的路线数目。通过“Network analyze”功能对网络进行拓扑属性分析。筛选等级值(Degree)与中心度值(Betweenness Centrality,BC)较大的节点进行分析,这些节点在网络中起到了枢纽作用,可能是关键化合物或靶点。该网络中活性成分的平均度值为12.96,靶点平均度值为10.99。从活性成分方面分析,有37%的活性成分作用靶点≥12个,通过分析活性成分-靶点的中心度值和等级值等发现,其中槲皮素、淫羊藿醇、β-谷甾醇、山奈酚、木犀草素及补骨脂素分别能与20个以上的靶点蛋白发生作用。从靶点角度分析,共有39个靶点能与10个或10个以上的活性成分相互作用,排名前5位的是VEGFA,EGFR,DPP4,NOS2,PPARG,分别能与114,62,54,49,43个活性成分相互作用。 "
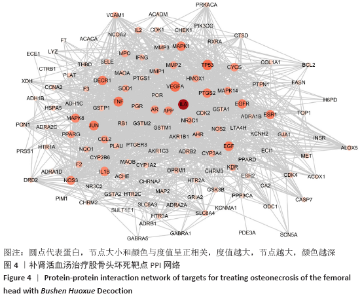
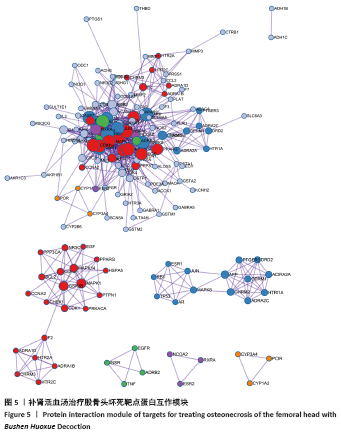
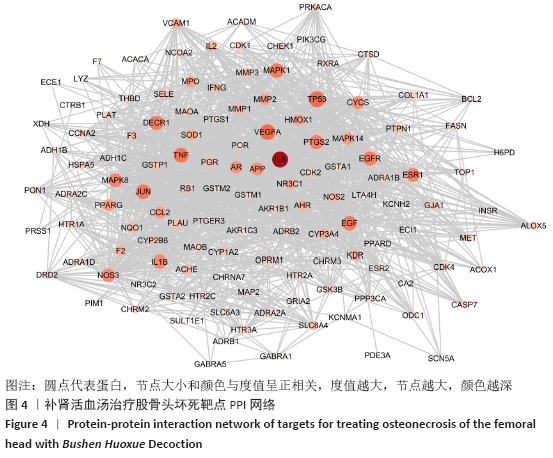
2.5 PPI网络分析结果 结果显示,除IGHG1蛋白与其他蛋白之间没有互作关系被排除,该网络包含128个节点及1 428条边,其中平均节点度值为22.31,见图4。以节点度值为评价参数,度值越大说明其在PPI网络中越重要,可能在发挥生物学功能中起着重要的作用。度值排名前10的靶点为白细胞介素6(IL-6)、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、表皮生长因子(EGF)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1(MAPK1)、表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、骨桥蛋白(OPN)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶8(MAPK8)、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体(PPARG)和叉头框转录因子2(Foxc2),这些靶点可能是补肾活血汤发挥治疗股骨头坏死功效的关键靶点。 "
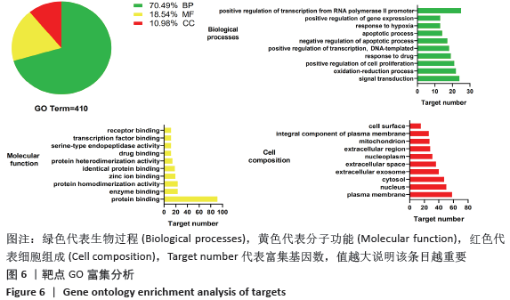
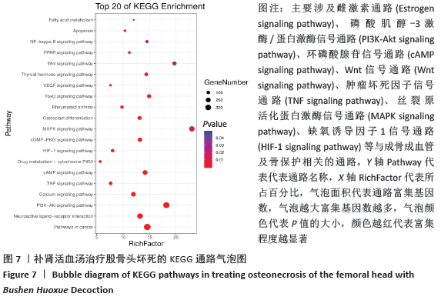
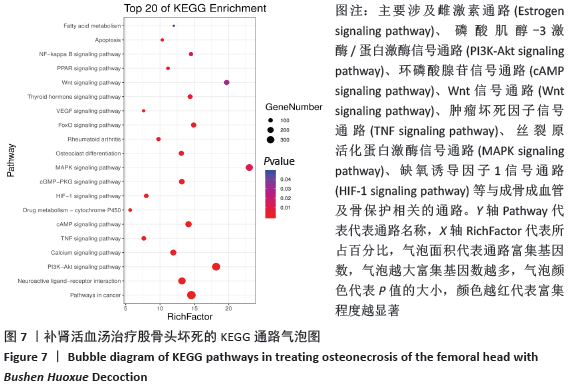
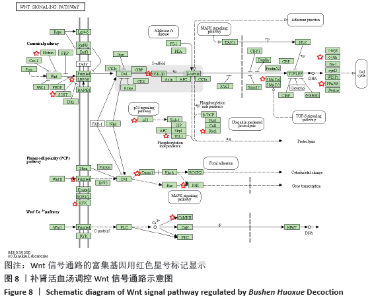
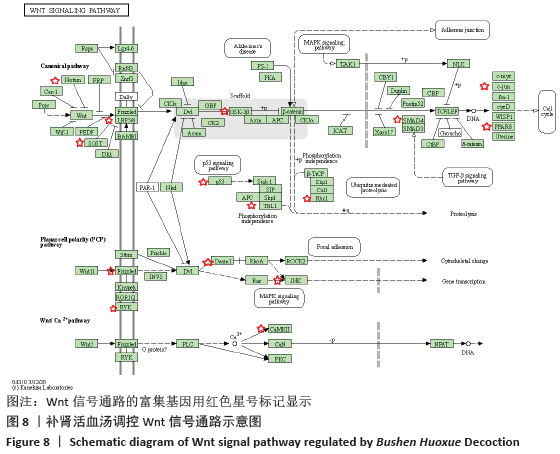
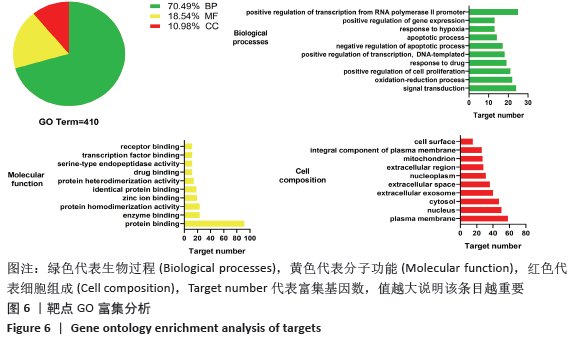
2.7 GO富集分析及KEGG通路分析结果 通过DAVID数据库共筛选得到 GO 条目410个(P < 0.05),其中生物过程(Biological processes,BP)条目289个,分子功能(Molecular function,MF)条目76个,细胞组成(Cell composition,CC)条目45个,分别占70%,19%,11%,其中BP主要涉及RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子转录的正调控、调控细胞增殖、对药物的反应、凋亡过程的负调控、G蛋白偶联受体信号通路和管生成等;分子功能主要涉及蛋白质结合、酶结合、蛋白质均二聚活性、蛋白质丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性和类固醇激素受体活性等方面;细胞组成方面主要涉及质膜、核、细胞外泌体、细胞外空间等方面。各类别前10的条目见图6。KEGG通路富集筛选得到110条信号通路(P < 0.05),其中排名前20的通路绘制气泡图,见图7。补肾活血汤调控Wnt信号通路图见图8。"
| [1] 虹霖,侯德才,魏波,等.基于筋骨并重理论中医内治法联合髓芯减压+人工骨植骨术治疗股骨头缺血性坏死[J].长春中医药大学学报,2020,36(2):402-405. [2] 李盛华,邓昶,周明旺,等.中医药防治股骨头坏死临床应用现状[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2018,25(6):137-140. [3] 曾宪峰,王进东,梁鼎天,等.补肾活血汤联合西医治疗早中期非创伤性股骨头缺血坏死(肾虚血瘀)随机平行对照研究[J].实用中医内科杂志,2019,33(5):38-41. [4] 滕加文.补肾活血汤治疗股骨头缺血性坏死45例[J].山东中医药大学学报,2011 ,35(1):36-37. [5] 张翔,吴泱,董晓俊,等.补肾活血方调控兔激素性股骨头坏死APN-AMPK信号通路的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2019,39(10):1234-1239. [6] LIU JF, HU AN, ZAN JF, et al. Network pharmacology deciphering mechanisms of volatiles of granule for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019: 7826769. [7] NIU B, ZHANG H, LI C, et al. Network pharmacology study on the active components of and the mechanism of their effect against cerebral ischemia. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:3009-3019. [8] 宗阳,丁美林,贾可可,等.基于网络药理学和分子对接法探寻达原饮治疗新型冠状病毒肺炎(COVID-19)活性化合物的研究[J].中草药,2020,51(4):836-844. [9] URSU O, RAYAN A, GOLDBLUM A, et al. Understanding drug-likeness. Wires Comput Mol Sci. 2011;1(5):760-781. [10] UNIPROT CONSORTIUM T. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(5):2699. [11] 《中华人民共和国药典》中药材名称与中药饮片名称对照表[J].西部中医药, 2017,30(03):21, 50. [12] STELZER G, ROSEN N, PLASCHKES I, et al. The Genecards suite: from gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016;54:1.30.1-1.30.33. [13] DAVIS AP, GRONDIN CJ, JOHNSON RJ, et al. The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: update 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D948-D954. [14] SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE AL, LYON D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D607-D613. [15] BADER GD. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003;4:2. [16] ZHOU Y, ZHOU B, PACHE L, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1523. [17] HUANG DA W, SHERMAN BT. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4:44-57. [18] 韦明照,李宏宇.股骨头缺血性坏死基因治疗的研究进展[J].中国临床新医学, 2020,13(3):305-309. [19] 卞伟,杨丽,孙宏,等.槲皮素对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和骨向分化的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2016,32(5):27-30. [20] 桂志鹏. 槲皮素对软骨细胞的生物学调控及其机理研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2018. [21] RAYALAM S, DELLA-FERA MA. Phytochemicals and regulation of the adipocyte life cycle. J Nutr Biochem. 2008; 19:717-726. [22] 孙卉,滕浩,杜密英,等.槲皮素降脂减肥机制研究进展[J].食品工业科技,2019, 40(16):349-353,362. [23] 周爱珍,王蕾,程斌.淫羊藿醇提工艺及醇提物对软骨细胞保护作用的研究[J].中国中药杂志,2020,45(5):1097-1104. [24] 瞿晶田,王家龙,柴士伟,等.补骨脂素和补骨脂酚舒张血管的作用机制研究[J].中国药房,2019,30(24):3364-3368. [25] 李洪波,魏云鹏,杨芳,等.补骨脂素对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].解剖科学进展,2020,26(1):18-21,26. [26] MA W, XIN K, CHEN K, et al. Relationship of common variants in VEGFA gene with osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a Han Chinese population based association study. Sci Rep. 2018;8:16221. [27] FANG B, WANG D, ZHENG J, et al. Involvement of tumor necrosis factor alpha in steroid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head: friend or foe? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:5. [28] BASAL O, ATAY T, CIRIS İM. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) promotes bone healing in surgically induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH). Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018;18:352-360. [29] WYLES CC, PARADISE CR, HOUDEK MT, et al. CORR® ORS richard a. brand award: disruption in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARG) increases osteonecrosis risk through genetic variance and pharmacologic modulation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477:1800-1812. [30] 温玉琴.研究揭示Wnt/β-连锁蛋白信号传导控制FOXC2表达的机制[J].广东药科大学学报,2018,34(5):553. [31] 史东梅,董明,陆颖,等.PI3K/Akt信号通路与骨破坏:问题与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(23):3716-3722. [32] WU F, JIAO J, LIU F, et al. Hypermethylation of Frizzled1 is associated with Wnt/β-catenin signaling inactivation in mesenchymal stem cells of patients with steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51:1-9. [33] 李莉莉,钟佩茹.非创伤性股骨头坏死发病相关因素及信号通路机制的研究进展[J].医学综述,2018,24(1):22-27. [34] HAN Y, SI M, ZHAO Y, et al. Progranulin protects against osteonecrosis of the femoral head by activating ERK1/2 pathway. Inflammation 2017;40:946-955. [35] 宋世雷,陈跃平,章晓云.PI3K/AKT信号通路调控股骨头坏死的相关机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(3):408-415. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||