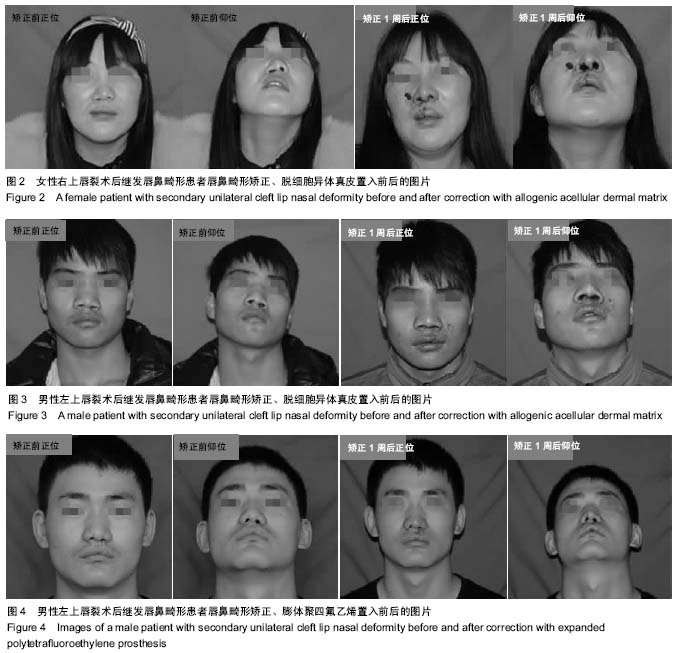
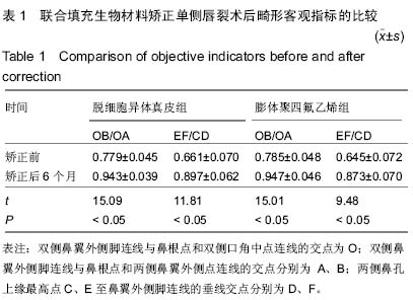
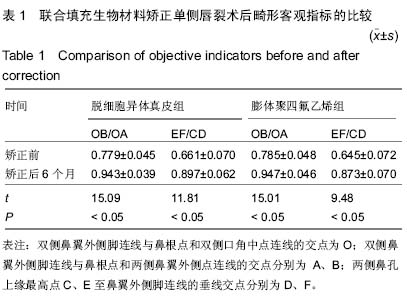
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (21): 3434-3439.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.21.029
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comprehensive procedures with biomaterial filling for secondary unilateral cleft lip nasal deformity
Wan Cheng, Wang Xi-mei, Guo Li-li, Dong Hai-jiang, Li Xiang
- Department of Plastic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Online:2015-05-21Published:2015-05-21 -
Contact:Wang Xi-mei, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Master and Doctoral supervisor, Department of Plastic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wan Cheng, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Plastic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wan Cheng, Wang Xi-mei, Guo Li-li, Dong Hai-jiang, Li Xiang . Comprehensive procedures with biomaterial filling for secondary unilateral cleft lip nasal deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(21): 3434-3439.
share this article
| [1] 王炜.整形外科学[M].杭州:浙江科学技术出版社,1999:644-697. [2] Kalaskar R,Kalaskar A,Naqvi FS,et al. Prevalence and evaluation of environmental risk factors associated with cleft lip and palate in a central Indian population.Pediatr Dent.2013; 35(3):279-283.
[3] Fisher DM,Lo LJ,Chen YR,et al.Three-dimensional computed tomographic analysis of the primary nasal deformity in 3-month—old infants with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate.Plast Reconstr Surg.1999;103(7):1826-1834.
[4] 朱光辉,庞晓刚.单侧唇裂鼻畸形矫正的临床进展[J].中国美容医学,2013,22(15):1651-1653.
[5] 付茂东,刁成山,李成华,等.单侧唇裂继发鼻畸形整复的临床研究[J].中国美容医学,2014,23(17):1438-1440.
[6] Fisher MD,Fisher DM,Marcus JR.Correction of the Cleft Nasal Deformity. Clin Plast Surg.2014;41(2):283-299.
[7] 潘葵,陈兵.利用鼻底双旋转皮瓣修复单侧唇裂继发鼻底畸形[J].中国美容医学,2012, 21(6):915-916.
[8] Byrd HS, El-Musa KA, Yazdani A.Definitive repair of the unilateral cleft lip nasal deformity.Plast Reconstr Surg.2007; 120(5):1348-1356.
[9] 施泽宏,李平松,周羽.鼻侧Medpor假体置入矫正单侧唇裂术后患侧上颌骨发育不足[J].中国美容医学,2011,20(12):1884-1886.
[10] Lee HY,Yang HJ, Rhie JW,et al. Adipose Tissue Regeneration In Vivo Using Micronized Acellular Allogenic Dermis as an Injectable Scaffold.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38(5): 1001-1010.
[11] 罗志军,黎洪棉,王和庚,等.脱细胞异体真皮基质与人脂肪干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(25):4616-4621.
[12] 杨建民,王配合,李建全,等.脱细胞异体真皮和自体刃厚皮复合移植在功能部位深度烧伤中的应用[J].解放军医药杂志,2014, 26(5):45-47,50.
[13] 张琼阁,王喜梅,郭丽丽,等.硅胶假体及脱细胞真皮辅助女性Poland综合征患者的乳房再造[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(21):3425-3430.
[14] 徐祥,吕大伦.脱细胞真皮基质临床研究及应用进展[J].临床医学工程,2014,21(3):396-398.
[15] 殷艳丽,王倩婷,赵蕾.脱细胞真皮基质用于牙周病学领域研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014,7(7):434-439.
[16] 王健诚,王炜,张科,等邹世镇.脱细胞异体真皮基质填塞修复高位肛瘘[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(34):5497-5502.
[17] 邹永红,高山,田方兴,等.自体耳软骨联合膨体聚四氟乙烯矫正短鼻畸形[J].中国美容医学,2013,22(24):2345-2347.
[18] 付德林,薛轶群,李丹阳. EPTFE隆鼻与耳软骨移植做支架纠正鼻背低平伴鼻头肥大低垂[J]. 中国美容医学,2012,21(7): 1143-1145.
[19] Carter PR,LeBlanc KA,Hausmann MG,et al.Does expanded polytetrafluoroethylene mesh really shrink after laparoscopic ventral hernia repair?Hernia.2012;16(3):321-325.
[20] 缪冬华.四种隆鼻材料在临床应用中的生物学性能比较[J].中国医疗美容,2014,5(1):42-45.
[21] 李俊,杨涛,周蓓,等.膨体聚四氟乙烯与固体硅胶隆鼻术后肿胀的临床分析比较[J].中国美容医学,2014,23(10):801-804.
[22] 王涛. 单侧完全性唇裂同期鼻整形联合鼻撑矫形效果的评价研究[D].第四军医大学,2012.
[23] 张力平,孙家和,管宇,等.改良Bardach法矫治单侧唇裂术后鼻畸形远期效果分析[J].中华医学美容杂志,1999,1(5):7-9.
[24] 杨小平.唇裂术后继发畸形的分类及治疗原则[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2013,7(4):261-264.
[25] 史劲松,陈伟.不同手术方法修复单侧完全性唇裂的临床分析[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2013,23(3):209-211.
[26] Rossell-Perry P,Romero-Narvaez C.Evaluation of the use of auricular composite graft for secondary unilateral cleft lip nasal alar deformity repair.Plast Surg Int. 2014;2014:270285.
[27] 肖文芝,刘华,陈涌,等.单侧唇裂继发鼻畸形的临床整复[J].中国美容医学, 2014,23(3):183-186.
[28] 谢娟,赵宇,曹东升.软骨重建在单侧唇裂术后鼻畸形修复中的应用[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2014,10(3):161-163.
[29] 仝润泽,吕启凤,厉建华,等. e-PTFE在唇裂术后继发鼻畸形修复中的拓展应用[J].中国美容医学,2014,22(2):93-96.
[30] Narasimhan S, Aslam S, Lin PH,et al.Bacterial translocation across ePTFE vascular graft surfaces.J Infect. 2010;60(6): 486-490.
[31] Cohen M, Morris DE, White AD, et al.Functional and aesthetic correction of secondary unilateral cleft lip nasal deformities. Indian J Plast Surg.2009;42 Suppl:S91-S101. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||