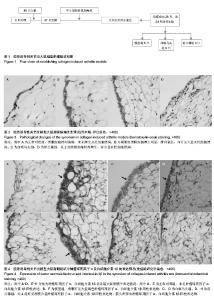
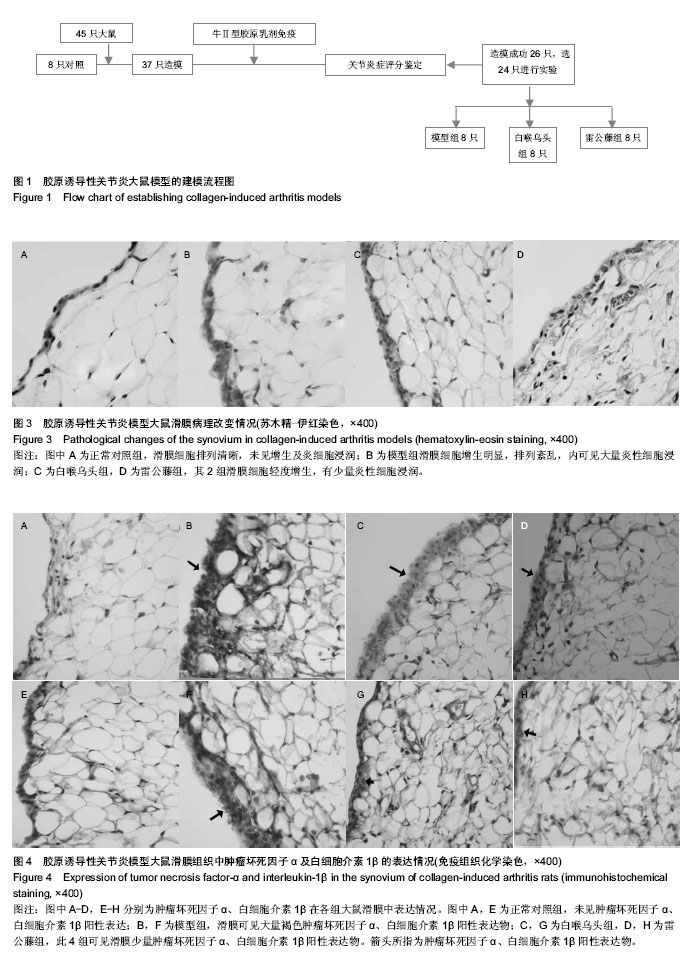
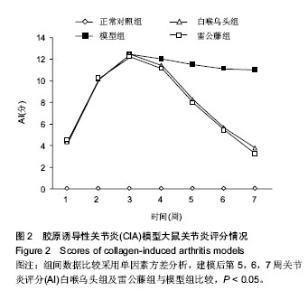
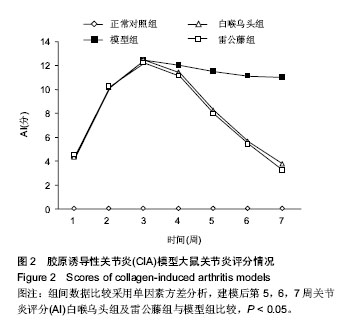
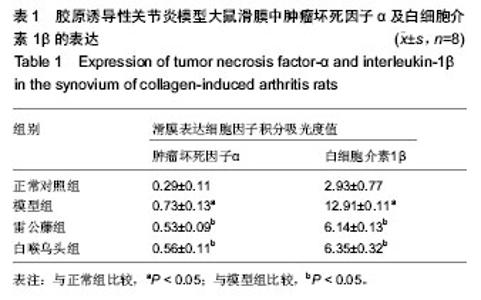
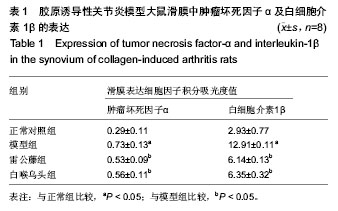
| [1] Kourilovitch M, Galarza-Maldonado C, Ortiz-Prado E3. Diagnosis and classification of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:26-30.
[2] ScottDL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1094-1108.
[3] 叶伟胜,张铁良.类风湿关节炎流行病学进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2009,3(3):144-147.
[4] endas-Baum R, Wallenstein GV, Koncz T, et al. Evaluating the efficacy of sequential biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor-αinhibitors. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(1):25-28.
[5] Schleinitz N, Vély F, Harlé JR, et al. Natural killer cells in human autoimmune diseases. Immunology. 2010;131(4):451-458.
[6] Ohta S, Harigai M, Tanaka M, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) converting enzyme contributes to production of TNF-alpha in synovial tissues from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(8):1756-1763
[7] Abramson SB, Amin A. Blocking the effects of IL-1 in rheumatoid arthritis protects bone and cartilage. Rheumatology. 2002;41(9):972-980.
[8] Zwerina J, Redlich K, Schett G, et al. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: targeting cytokines. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1051:716-729.
[9] Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, et al. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;117(2):244-279.
[10] Le Loët X, Nordstrëm D, Rodriguez M. Effect of anakinra on functional status in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant therapy with traditional disease modifying antirheumatic drugs: evidence from the omega trial. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(8):1538-1544.
[11] Voulgari, Paraskevi V, Drosos, et al. Adalimumab in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Opin Biol Ther. 2014; 14(4):549-561.
[12] Goldblatt F, Isenberg DA. New therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;140(2):195-204.
[13] 吴沅皞,刘维.中成药治疗类风湿关节炎的实验研究近况[J].中华中医药杂志,2010,25(11):1846-1849.
[14] 徐新,巴哈尔古丽•黄尔汗.哈萨克药志(第一卷)[M].北京:民族出版社,2009.
[15] Han W, Xiong Y, Li Y, et al. Anti-arthritic effects of clematichinenoside (AR-6) on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and TNF-α associated with collagen-induced arthritis. Pharm Biol. 2013;51(1):13-22.
[16] Cuzzocrea S, McDonald MC, Mota-Filipe H. Beneficial effects of tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, in a rodent model of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheuma. 2000;43(2):320-328.
[17] 刘悦,蔡冬梅,哈木拉提,等.哈药白喉乌头对小鼠的急性毒性实验研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2011,(7):694-696.
[18] 应晓君,冯君.甲氨蝶呤对CIA大鼠滑膜IL-1β、IL-8、VEGF表达的影响[J].哈尔滨医药,2013,(3):170-172.
[19] 周强,吕厚山,栗占国.胶原诱导的关节炎动物模型研究现状及进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2003,7(4):227-231.
[20] 吾买尔夏提,魏岩.新疆药用乌头的民族植物学[J].中国野生植物资源杂志,2004,(4):29-30.
[21] Lv QW, Zhang FC. Comparison of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F with methotrexate in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis (TRIFRA): a randomised, controlled clinical trial. 2014. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204807.
[22] 薛蕾,闫德友.雷公藤化学成分、生物活性及其资源利用概述[J].青海农林科技,2013,(4):24-28.
[23] 赵翡翠;雷蕊;聂继红.分光光度法测定新疆不同产地白喉乌头不同部位总生物碱的含量[J].中药材,2013,(9):1406-1408.
[24] Chen BJ. Triptolide, a novel immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory agent purified from a Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001;42(3): 253-265.
[25] 谢希,陈进伟,彭佑铭.抗肿瘤坏死因子α治疗类风湿关节炎致感染风险的Meta分析[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2013,(7): 722-736.
[26] 黄蓓,汪庆童,刘亢亢,等.类风湿关节炎发生发展中TNF-α信号通路与CD4+T细胞的关系[J].中国药理学通报,2013,(7): 900-903.
[27] Dinarello CA. The IL-1 family and inflammatory diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002;20(27):1-13.
[28] Fox SW, Fuller K, Chambers TJ. Activation of osteoclasts by interleukin-1: divergent responsiveness in osteoclasts formed in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2000;184(3):334-340.
[29] Kobayashi M, Squires GR, Mousa A, et al. Role of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in matrix degradation of human osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2005;52(1):128-135.
[30] Coxon A, Bolon B, Estrada J, et al. Inhibition of interleukin-1 but not tumor necrosis factor suppresses neovascularization in rat models of corneal angiogenesis and adjuvant arthritis. Arthritis Rheuma. 2002;46(10):2604-2612.
[31] 王志中,王勇,方勇飞,等.血小板、与活动期类风湿关节炎的相关性研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(5):469-472 |