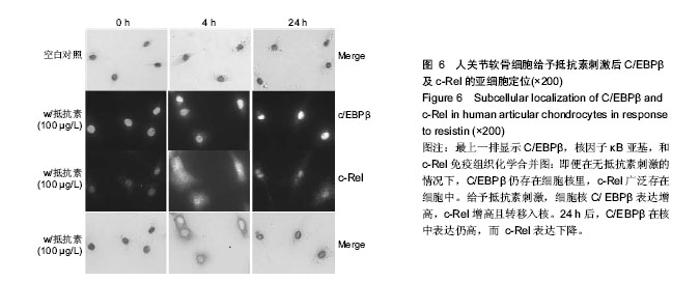
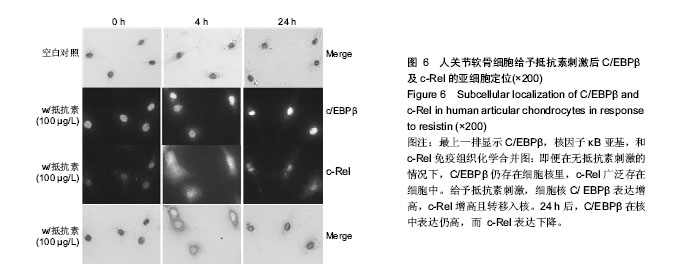
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (15): 2297-2304.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.15.001
Resisin stimulates the expression of CCL3 and CCL4 in chondrocytes
Zhang Zi-ji, Kang Yan, Yang Zi-bo, Hou Chang-he, Huang Guang-xin, Chen Wei-shen, Sheng Pu-yi, He Ai-shan, Fu Ming, Liao Wei-ming, Zhang Zhi-qi
- Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2015-03-17Online:2015-04-09Published:2015-04-09 -
Contact:Zhang Zhi-qi, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Zi-ji, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171709, 81301558, 81371941, 81201388; the National Research Foundation for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, No. 20130171120074; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. S2013040016269
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Zi-ji, Kang Yan, Yang Zi-bo, Hou Chang-he, Huang Guang-xin, Chen Wei-shen, Sheng Pu-yi, He Ai-shan, Fu Ming, Liao Wei-ming, Zhang Zhi-qi. Resisin stimulates the expression of CCL3 and CCL4 in chondrocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(15): 2297-2304.
share this article
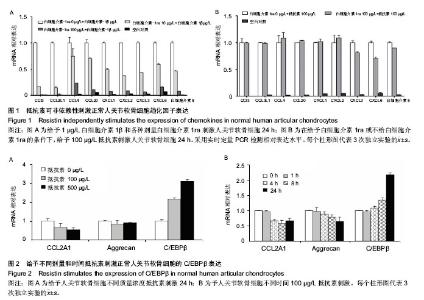
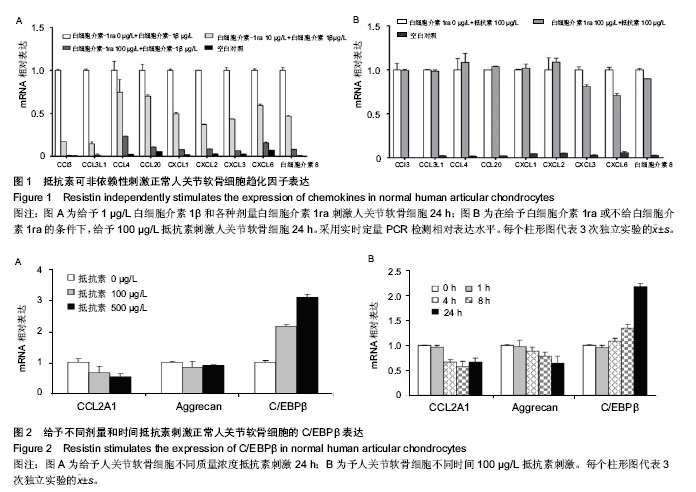
2.1 抵抗素可非依赖性刺激正常软骨细胞趋化因子基因表达 作者已经报道了正常成人和骨关节炎患者软骨组织受到抵抗素或白细胞介素1β刺激后产生大量趋化因子的表达上调,且抵抗素可刺激白细胞介素1β表达[8,13-14]。在本实验中,证明了即便给予有效白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂,重组人白细胞介素1ra(图1A),抵抗素刺激仍然可诱导人关节软骨细胞中细胞因子和趋化因子基因表达显著上调(图1B),进一步证实抵抗素发挥作用不依赖白细胞介素1刺激。2.2 抵抗素刺激软骨细胞 C/EBPβ表达 以往的计算分析和C/EBPβ共转染提示C/EBPβ参与抵抗素诱导的趋化因子基因表达上调[14]。COL2A1 基因下调及C/EBPβ上调显示剂量依赖性反应(图2A)。当给予细胞100 μg/L抵抗素刺激超过24 h,C/EBPβ mRNA表达水平逐渐增高达约3倍(图2B)。C/EBPβ在24 h内抑制人软骨细胞Ⅲ型胶原mRNA表达低至约60%,与预期相符(图2B),在大鼠软骨肉瘤细胞及人关节软骨细胞等以往研究也得到证实[8,13-14,29]。"
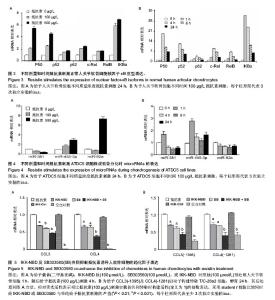
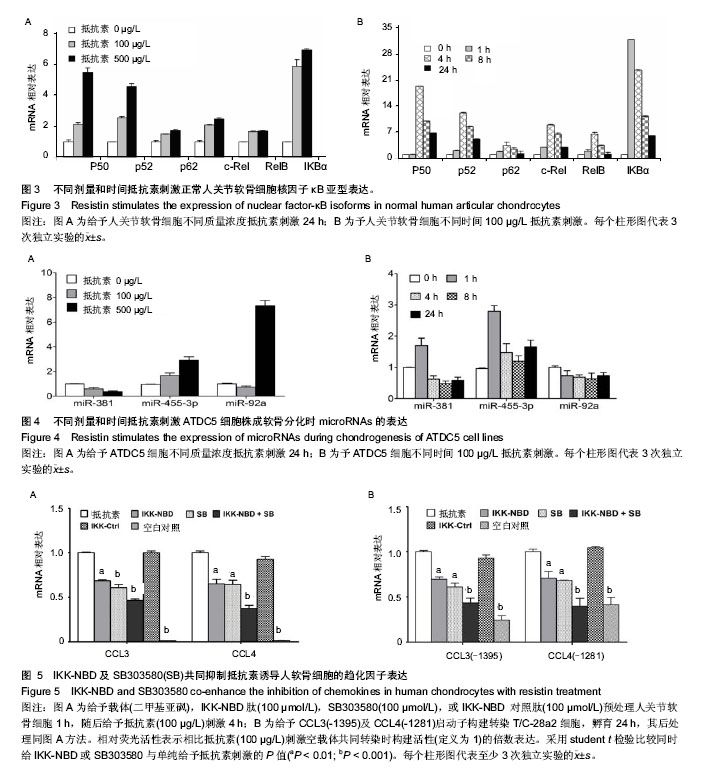
2.3 核因子κB参与调控抵抗素诱导的软骨细胞趋化因子基因表达上调结果 鉴于有研究表明核因子κB转录复合物通过核因子κB及C/EBPβ共同转染及抑制IKK-NBD来参与抵抗素诱导的多细胞因子和趋化因子基因表达上调,实验对C/EBPβ及核因子κB的相对作用进行探讨。对正常人关节软骨细胞中的核因子κB进行检测。给予不同剂量和时间抵抗素刺激软骨细胞,并且检测相应的核因子κB1(p50),核因子κB2(p52),RelA(p65),c-Rel,RelB,IκBα mRNAs水平。核因子κB亚型表达对抵抗素刺激存在剂量依赖性应答(图3A)。核因子κB亚型迅速增加,但在4 h后降低(图3B),其药动学与以往报道采用pNF-kappaB荧光素酶报告基因检测抵抗素刺激24 h对核因子κB作用的结果一致[8]。细胞中,与C/EBPβ浓度相比,核因子κB亚型浓度更低。在人骨细胞中,C/EBPβ的?C均值为1.73,相比核因子κB1低(5.33),而核因子κB2(5.46),RelA(18.23),c-Rel(6.89)及RelB(7.04)。然而,这些研究提示软骨细胞核因子κB亚基可能对抵抗素刺激产生应答。p50,p52及c-Rel的相对增高值最大。因此,上述结果提示核因子κB参与调节趋化因子表达,尤其在刺激4-8 h时。 2.4 抵抗素刺激软骨形成期ATDC5细胞miRNAs表达 ATDC5细胞为小鼠胚胎癌株,体外可成软骨分化,研究已经证实调控其成软骨分化的已知标记与在体相似[30]。给予不同剂量和时间的抵抗素刺激ATDC5细胞,探讨软骨形成和骨关节炎软骨组织中关键miRNAs(miR-455-3p,miR-92a及miR-381)水平,确定抵抗素诱导的转录后基因调节机制。所测miRNAs对抵抗素产生剂量依赖性应答(图4A)。miR-92a显示最高的相对增高值。miR-381及miR-455-3p在第1h迅速增高,但是4 h后下降(图4B),这与作者以往报道的核因子κB药动学一致[8]。这些研究提示miRNAs可能特异表达于抵抗素刺激ATDC5细胞软骨形成。因此,这些结果表明在给予抵抗素刺激,尤其是1-4 h时,miRNAs可能参与调控趋化因子表达。所以,这些miRNAs参与抵抗素诱导ATDC5细胞转录后调控机制。 2.5 C/EBPβ及核因子κB共同上调抵抗素诱导的人软骨细胞CCL3及CCL4 表达 以前结果显示C/EBPβ及核因子κB可导致CCL3及CCL4上调[14]。为进一步探讨C/EBPβ及核因子κB作用于CCL3及CCL4的具体机制,对转录因子C/EBPβ及核因子κB分别抑制和同时抑制后的效果进行检测。SB303580为抑制p38MAPK的C/EBPβ抑制剂[31-32], IKK-NBD为核因子κB特异性抑制剂,在同时给予两抑制剂时,给予抵抗素刺激,CCL3和CCL4表达降低,差异有显著性意义(图5A)。IKK-NBD及SB303580联合干预进一步降低CCL3及CCL4 mRNA表达,差异有显著性意义(图5A)。 根据计算数据评估显示CCL3(-1395)及CCL4(-1281)构建含很多可能C/EBPβ及核因子κB候选结合位点[14]。为证实两转录因子都起作用,在抑制转录因子后检测CCL3(-1395)及 CCL4(-1281)启动子活性。结果显示给予两转录因子抑制剂后CCL3及CCL4启动子活性显著下降,且IKK-NBD及SB303580联合促进CCL3及CCL4启动子活性下降,差异均有显著性意义(图5B)。"
| [1] Lee JH, Ort T, Ma K,et al.Resistin is elevated following traumatic joint injury and causes matrix degradation and release of inflammatory cytokines from articular cartilage in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2009; 17:613-620. [2] Schaffler A, Ehling A, Neumann E,et al. Adipocytokines in synovial fluid. JAMA. 2003; 290: 1709-1710. [3] Senolt L, Housa D, Vernerova Z,et al. Resistin in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue, synovial fluid and serum. Ann Rheum Dis.2007; 66: 458-463. [4] Presle N,Pottie P,Dumond H,et al.Differential distribution of adipokines between serum and synovial fluid in patients with osteoarthritis: contribution of joint tissues to their articular production. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2006; 14: 690-695. [5] Tilg H,Moschen AR.Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006; 6: 772-783. [6] Koerner A, Kratzsch J, Kiess W.Adipocytokines: leptin-the classical, resistin-the controversical, adiponectin-he promising, and more to come. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab.2005; 19: 525-546. [7] Bokarewa M, Nagaev I, Dahlberg L,et al. Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory properties. J Immunol. 2005; 174: 5789-5795. [8] Zhang Z,Xing X,Hensley G, et al. Resistin induces expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in human articular chondrocytes via transcription and messenger RNA stabilization. Arthritis Rheum.2010; 62: 1993-2003. [9] Imamura T,Imamura C,McAlinden A,et al.A novel tumor necrosis factor α-responsive CCA AT/enhancer binding protein site regulates expression of the cartilage-derived retinoic acid-sensitive protein gene in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58: 1366-1376. [10] Gerard C, Rollins BJ. Chemokines and disease. Nat Immunol. 2001; 2: 108-115. [11] Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol.2007; 213: 626-634. [12] Haringman JJ, Ludikhuize J, Tak PP. Chemokines in joint disease: the key to inflammation? Ann Rheum Dis.2004; 63: 1186-1194. [13] Sandell LJ, Xing X, Franz C, et al. Exuberant expression of chemokine genes by adult human articular chondrocytes in response to IL-1.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2008; 16:1560-1571. [14] Zhang Z, Bryan JL, DeLassus E, et al. CCAAT/ enhancer-binding protein β and NF-κB mediate high level expression of chemokine genes CCL3 and CCL4 by human chondrocytes in response to IL-1β. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285: 33092-33103. [15] Hao S, Baltimore D. The stability of mRNA influences the temporal order of the induction of genes encoding inflammatory molecules. Nat Immunol.2009; 10: 281-288. [16] Yan C, Wang Y, Shen XY,et al. MicroRNA regulation associated chondrogenesis of mouse MSCs grown on polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biomaterials.2011; 32: 6435-6444. [17] Suomi S, Taipaleenmaki H, Seppanen A, et al. MicroRNAs regulate osteogenesis and chondrogenesis of mouse bone marrow stromal cells. Gene Regul Syst Bio.2008; 2: 177-191. [18] Lin EA, Kong L, Bai XH,et al. miR-199a, a bone morphogenic protein 2-responsive MicroRNA, regulates chondrogenesis via direct targeting to Smad1. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284: 11326-11335. [19] Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 2009;136:642-655. [20] Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A,et al. Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell.2003;113:25-36. [21] Dostie J, Mourelatos Z, Yang M,et al. Numerous microRNPs in neuronal cells containing novel microRNAs. RNA.2003; 9: 180-186. [22] Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, et al. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 2004; 303: 83-86. [23] Kobayashi T, Lu J, Cobb BS, et al . Dicer-dependent pathways regulate chondrocyte prolif-eration and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 1949-1954. [24] Zhang Z, Kang Y, Zhang Z,et al. Expression of microRNAs during chondrogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2012;20:1638-1646. [25] Choi SJ, Oba T, Callander NS,et al. AML-1A and AML-1B regulation of MIP-1alpha expression in multiple myeloma. Blood 2003; 101: 3778-3783. [26] Tseng PC, Hsu HC, Janmanchi D,et al. Helioxanthin inhibits interleukin-1 beta-induced MIP-1 beta production by reduction of c-jun expression and binding of the c-jun/CREB1 complex to the AP-1/CRE site of the MIP-1 beta promoter in Huh7 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 2008; 76: 1121-1133. [27] Otero JE, Dai S, Alhawagri MA,et al. IKKbeta activation is sufficient for RANK-independent osteoclast differentiation and osteolysis. J Bone Miner Res 2010; 25:1282-1294. [28] He Y, Crouch E. Surfactant protein D gene regulation. Interactions among the conserved CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein elements. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 19530-19537. [29] Okazaki K, Yu H, Davies SR,et al. A promoter element of the CD-RAP gene is required for repression of gene expression in non-cartilage tissues in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Biochem.2006; 97:857-868. [30] Chen L, Fink T, Zhang XY,et al. Quantitative transcriptional profiling of ATDC5 mouse progenitor cells during chondrogenesis. Differentiation.2005;73: 350-363. [31] Venza I, Cucinotta M, Visalli M,et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces interleukin-8 (IL-8) gene expression in human conjunctiva through the recruitment of both RelA and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta to the IL-8 promoter. J Biol Chem.2009; 284: 4191-4199. [32] Basak C, Pathak SK, Bhattacharyya A, et al. NF-kappaB- and C/EBPbeta-driven interleukin-1beta gene expression and PAK1-mediated caspase-1 activation play essential roles in interleukin-1beta release from Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280: 4279-4288. [33] Hirata M, Kugimiya F, Fukai A,et al.C/EBPbeta Promotes transition from proliferation to hypertrophic differentiation of chondrocytes through transactivation of p57. PLoS One.2009; 4: e4543. [34] Esteves CL,Kelly V,Breton A,et al.Proinflammatory Cytokine Induction of 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 (11β-HSD1) in Human Adipocytes Is Mediated by MEK, C/EBPβ, and NF-κB/RelA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2014; 99: E160-168. [35] Rahman SM, Janssen RC, Choudhury M,et al. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ) expression regulates dietary-induced inflammation in macrophages and adipose tissue in mice. J Biol Chem.2012; 287: 34349-34360. [36] Fukui N, Ikeda Y,Ohnuki T,et al.Pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces bone morphogenetic protein-2 in chondrocytes via mRNA stabilization and transcriptional up-regulation.J Biol Chem.2006; 281: 27229-27241. [37] Tebo JM, Datta S, Kishore R,et al.Interleukin-1-mediated stabilization of mouse KC mRNA depends on sequences in both 5'- and 3'-untranslated regions. J Biol Chem.2000; 275: 12987-12993. [38] Swingler TE, Wheeler G, Carmont V,et al. The expression and function of microRNAs in chondrogenesis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum.2012; 64: 1909-1919. [39] Han J, Yang T, Gao J,et al . Speci fi c microRNA expression during chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Med.2010; 25: 377-384. [40] Yan C, Wang Y, Shen XY,et al. MicroRNA regulation associated chondrogenesis of mouse MSCs grown on polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biomaterials.2011; 32: 6435-6444. [41] Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R,et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007; 129: 1401-1414. [42] Hummel R, Wang T, Watson DI,et al. Chemotherapy-induced modification of microRNA expression in esophageal cancer. Oncol Rep.2011; 26: 1011-1017. [43] Moser JJ, Fritzler MJ. The microRNA and messengerRNA profile of the RNA-induced silencing complex in human primary astrocyte and astrocytoma cells. PLoS One. 2010; 5: e13445. [44] Ujifuku K, Mitsutake N, Takakura S,et al. miR-195, miR-455-3p and miR-10a(*) are implicated in acquired temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Lett.2010; 296: 241-248. |
| [1] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [2] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [3] | Tong Jie, Liao Ying, Chen Zhengyu, Sun Guanghua . Osteoarthritic chondrocyte autophagy and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3246-3251. |
| [4] | Wu Yukun, Han Jie, Wen Shuaibo. Mechanism of Runx2 gene in fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2274-2279. |
| [5] | Zhang Chuanhui, Li Jianjun, Yang Jun. Effects of dynamic pressure on the proliferation and mechanical properties of rabbit adipose mesenchymal stem cells transfected with insulin-like growth factor-1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1982-1987. |
| [6] | Huang Yongming, Huang Qiming, Liu Yanjie, Wang Jun, Cao Zhenwu, Tian Zhenjiang, Chen Bojian, Mai Xiujun, Feng Enhui. Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1016-1022. |
| [7] | Li Hui, Ma Yuhuan, Xu Limei, Wang Shengjie, Xu Yunteng, He Xiaojuan, Jia Liangliang, Zeng Jianwei, Wang Lili, Li Xihai, Ye Hongzhi. Duhuo Jisheng Decoction Disassembled Prescription inhibits chondrocyte inflammatory response throughbased on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5589-5594. |
| [8] | Lin Yicai, Wu Zhengyuan, Luo Yingli, Yao Jun. Effect of pterostilbene on oxidative stress induced apoptosis in chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5092-5096. |
| [9] | Wang Guoliang, Li Yanlin, Xiang Yaoyu, Jia Di, Li Canzhang, He Lu. MicroRNA expression profiles of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis induced by stromal cell derived factor 1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4948-4953. |
| [10] | Li Yuanqi, Lin Hai, Luo Hongrong, Zhang Xingdong. Relationship between mitochondrial autophagy and chondrogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4954-4960. |
| [11] | He Qiang, Qian Weiqing, Yao Nianwei, Zhou Mengling, Liu Yixin, Yin Hong. Protection of inflammatory osteoblasts in neonatal rats using catalpol from the root of Rehmannia glutinosa [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4626-4631. |
| [12] |
Li Jia, Wang Zhihui, Wu Di, Zhao Yang.
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in the treatment of orthopedic diseases: roles and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4068-4072. |
| [13] | Yang Fan, Liu Baoyi, Cao Meng, Zhu Xiaoshu, Zhang Yu, Qin Kairong, Zhao Dewei. Basic fibroblast growth factors protect chondrocytes by antagonizing extracellular inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3621-3626. |
| [14] | Ye Nan, Huang Jian, Wang Dan. Important roles of growth hormone-releasing peptide in bone growth and development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(20): 3226-3233. |
| [15] | Chen Hongyu, Han Hao, Chen Wei, Zhang Qiang . Effect of intermittent hydrostatic pressure on early cartilage differentiation of ATDC5 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2153-2157. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||