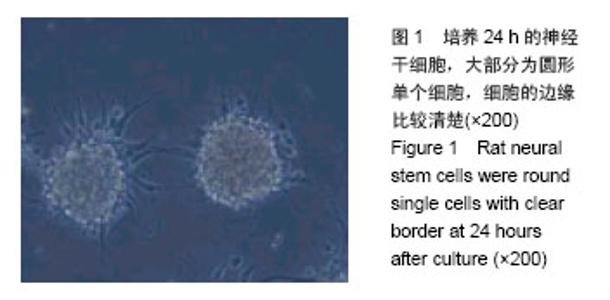
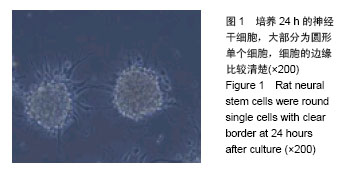
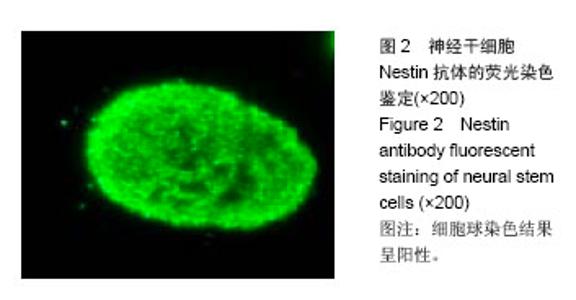
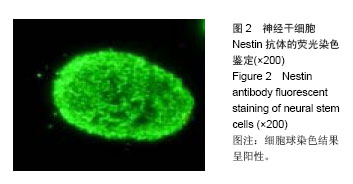
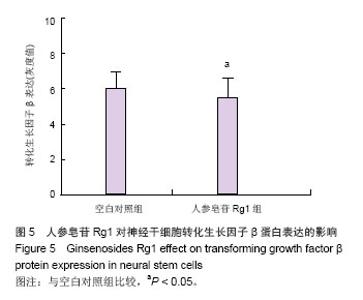
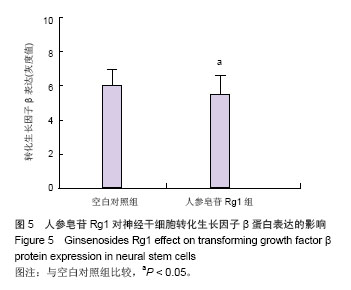
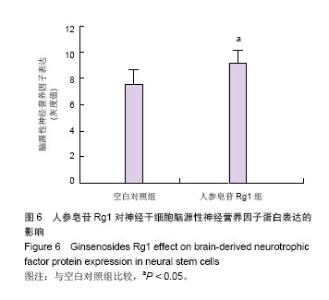
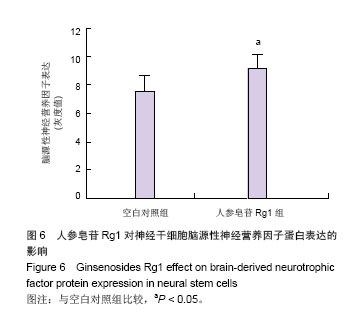
| [1]All AH, Gharibani P, Gupta S, et al. Early intervention for spinal cord injury with human induced pluripotent stem cells oligodendrocyte progenitors. PLoS One. 2015;10(1): e0116933.
[2]Wu GA, Bogie KM. Effects of conventional and alternating cushion weight-shifting in persons with spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2014;51(8):1265-1276.
[3]Long Y, Liang F, Gao C, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(11):4073-4081.
[4]Didangelos A, Iberl M, Vinsland E, et al. Regulation of IL-10 by chondroitinase ABC promotes a distinct immune response following spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2014;34(49):16424- 16432.
[5]Horie N, Hiu T, Nagata I. Stem cell transplantation enhances endogenous brain repair after experimental stroke. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015;55(2):107-112.
[6]Song L, Goldman E. Induced pluripotent stem cells are induced pluripotent stem cell-like cells. J Biomed Res. 2015; 29(1):1-2.
[7]Kong SY, Park MH, Lee M, et al. Kuwanon v inhibits proliferation, promotes cell survival and increases neurogenesis of neural stem cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0118188.
[8]张蕾,李晓莉.神经干细胞的分离培养和鉴定及体外长期培养[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2012,22(20):52-55.
[9]Gao J, Coggeshall RE, Tarasenko YI, et al. Human neural stem cell-derived cholinergic neurons innervate muscle in motoneuron deficient adult rats. Neuroscience. 2005;131(2): 257-262.
[10]Pluchino S, Cusimano M, Bacigaluppi M, et al. Remodelling the injured CNS through the establishment of atypical ectopic perivascular neural stem cell niches. Arch Ital Biol. 2010; 148(2):173-183.
[11]刘萍,涂彧. 表皮生长因子在新生大鼠神经干细胞培养中的作用[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2010,30(2):310-312.
[12]Kan EM, Ling EA, Lu J. Stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(36):4492-4510.
[13]Tarasenko YI, Gao J, Nie L, et al. Human fetal neural stem cells grafted into contusion-injured rat spinal cords improve behavior. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85(1):47-57.
[14]Du C, Yang D, Zhang P, et al. Single neural progenitor cells derived from EGFP expressing mice is useful after spinal cord injury in mice. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2007;35(4):405-414.
[15]Gao J, Coggeshall RE, Tarasenko YI, et al. Human neural stem cell-derived cholinergic neurons innervate muscle in motoneuron deficient adult rats. Neuroscience. 2005;131(2): 257-262.
[16]Vishwakarma SK, Bardia A, Tiwari SK, et al. Current concept in neural regeneration research: NSCs isolation, characterization and transplantation in various neurodegenerative diseases and stroke: A review. J Adv Res. 2014;5(3):277-294.
[17]Lee N, Park JW, Kim HJ, et al. Monitoring the differentiation and migration patterns of neural cells derived from human embryonic stem cells using a microfluidic culture system. Mol Cells. 2014;37(6):497-502.
[18]Walker TL, Kempermann G. One mouse, two cultures: isolation and culture of adult neural stem cells from the two neurogenic zones of individual mice. J Vis Exp. 2014;(84): e51225.
[19]Mengarelli I, Barberi T. Derivation of multiple cranial tissues and isolation of lens epithelium-like cells from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(2): 94-106.
[20]Pfaltzgraff ER, Mundell NA, Labosky PA. Isolation and culture of neural crest cells from embryonic murine neural tube. J Vis Exp. 2012;(64):e4134.
[21]Clarke L, Ballios BG, van der Kooy D. Generation and clonal isolation of retinal stem cells from human embryonic stem cells. Eur J Neurosci. 2012;36(1):1951-1959.
[22]Nefzger CM, Su CT, Fabb SA, et al. Lmx1a allows context-specific isolation of progenitors of GABAergic or dopaminergic neurons during neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30(7):1349-1361.
[23]Wang D, Liang J, Zhang J, et al. Mild hypothermia combined with a scaffold of NgR-silenced neural stem cells/Schwann cells to treat spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(24): 2189-2196.
[24]Mannoji C, Koda M, Kamiya K, et al. Transplantation of human bone marrow stromal cell-derived neuroregenrative cells promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury in mice. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2014;74(4):479-488.
[25]Wang D, Zhang J. Effects of hypothermia combined with neural stem cell transplantation on recovery of neurological function in rats with spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2015; 11(3):1759-1767.
[26]Dong Y, Yang L, Yang L, et al. Transplantation of neurotrophin-3-transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for the repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(16):1520-1524.
[27]Yuan N, Tian W, Sun L, et al. Neural stem cell transplantation in a double-layer collagen membrane with unequal pore sizes for spinal cord injury repair. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(10): 1014-1019.
[28]Najafzadeh N, Nobakht M, Pourheydar B, et al. Rat hair follicle stem cells differentiate and promote recovery following spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(36):3365-3372.
[29]Soejino A, Wihandani DM, Kuswardhani RA. Clinical applications of stem cell therapy for regenerating the heart. Acta Med Indones. 2010;42(4):243-257.
[30]Kelm JM, Breitbach M, Fischer G, et al. 3D microtissue formation of undifferentiated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells leads to elevated apoptosis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(7-8):692-702.
[31]Zhu H, Li F, Yu WJ, et al. Effect of hypoxia/reoxygenation on cell viability and expression and secretion of neurotrophic factors (NTFs) in primary cultured schwann cells. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010;293(5):865-870.
[32]Li C, Chen X, Qiao S, et al. Melatonin lowers edema after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(24):2205-2210.
[33]Lukovic D, Valdés-Sanchez L, Sanchez-Vera I, et al. Brief report: astrogliosis promotes functional recovery of completely transected spinal cord following transplantation of hESC-derived oligodendrocyte and motoneuron progenitors. Stem Cells. 2014;32(2):594-599. |