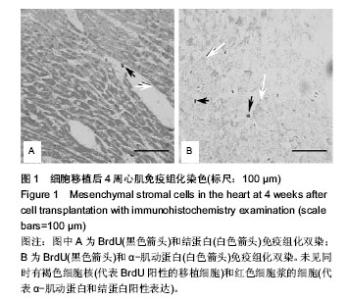
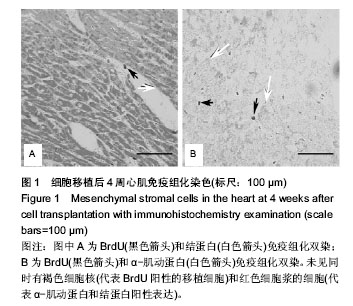
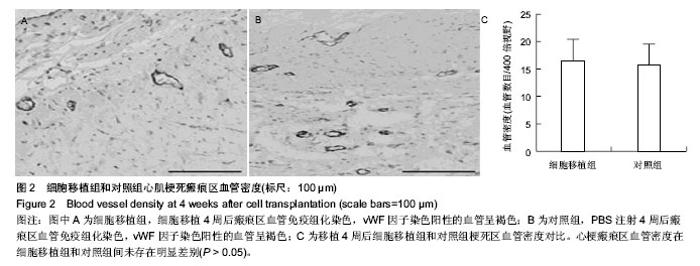
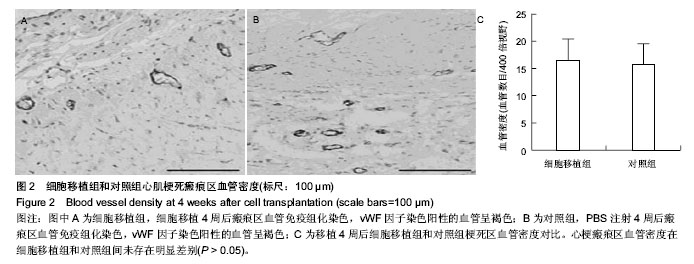
| [1]Fatkhudinov T, Bolshakova G, Arutyunyan I, et al. Bone marrow-derived multipotent stromal cells promote myocardial fibrosis and reverse remodeling of the left ventricle. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:746873.
[2]Hare JM, Traverse JH, Henry TD, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study of intravenous adult human mesenchymal stem cells (prochymal) after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(24):2277-2286.
[3]Nagaya N, Fujii T, Iwase T, et al. Intravenous administration of mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in rats with acute myocardial infarction through angiogenesis and myogenesis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;287(6):H2670-2676.
[4]Al Kindi A, Ge Y, Shum-Tim D, et al. Cellular cardiomyoplasty: routes of cell delivery and retention. Front Biosci. 2008;13:2421-2434.
[5]Mazo M, Gavira JJ, Abizanda G, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells exerts a greater long-term effect than bone marrow mononuclear cells in a chronic myocardial infarction model in rat. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(3):313-328.
[6]Williams AR, Hatzistergos KE, Addicott B, et al. Enhanced effect of combining human cardiac stem cells and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to reduce infarct size and to restore cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2013;127(2):213-223.
[7]Amado LC, Saliaris AP, Schuleri KH, et al. Cardiac repair with intramyocardial injection of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(32):11474-11479.
[8]Tse HF, Kwong YL, Chan JK, et al. Angiogenesis in ischaemic myocardium by intramyocardial autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell implantation. Lancet. 2003;361(9351): 47-49.
[9]Wang W, Jiang Q, Zhang H, et al. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells is safe for the lung in a chronic myocardial infarction model. Regen Med. 2011;6(2):179-190.
[10]Hendrikx M, Hensen K, Clijsters C, et al. Recovery of regional but not global contractile function by the direct intramyocardial autologous bone marrow transplantation: results from a randomized controlled clinical trial. Circulation. 2006;114 (1 Suppl):I101-107.
[11]Hou M, Yang KM, Zhang H, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow improves damaged heart function in rats. Int J Cardiol. 2007;115(2): 220-228.
[12]Dai W, Hale SL, Martin BJ, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in postinfarcted rat myocardium: short- and long-term effects. Circulation. 2005;112(2): 214-223.
[13]Dimmeler S, Burchfield J, Zeiher AM. Cell-based therapy of myocardial infarction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008; 28(2):208-216.
[14]Sherman W, Martens TP, Viles-Gonzalez JF, et al. Catheter-based delivery of cells to the heart. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2006;3 Suppl 1:S57-64.
[15]Tsubokawa T, Yagi K, Nakanishi C, et al. Impact of anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with transient overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 on myocardial ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;298(5):H1320-329.
[16]Zeng B, Lin G, Ren X, et al. Over-expression of HO-1 on mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis and improves myocardial function in infarcted myocardium. J Biomed Sci. 2010;17:80.
[17]Mathieu E, Lamirault G, Toquet C, et al. Intramyocardial delivery of mesenchymal stem cell-seeded hydrogel preserves cardiac function and attenuates ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2012; 7(12):e51991.
[18]Harting MT, Jimenez F, Xue H, et al. Intravenous mesenchymal stem cell therapy for traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2009;110(6):1189-1197.
[19]Okita K, Ichisaka T, Yamanaka S. Generation of germline- competent induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2007; 448(7151):313-317.
[20]Bearzi C, Gargioli C, Baci D, et al. PlGF-MMP9-engineered iPS cells supported on a PEG-fibrinogen hydrogel scaffold possess an enhanced capacity to repair damaged myocardium. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e105
[21]Lalit PA, Hei DJ, Raval AN, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells for post-myocardial infarction repair: remarkable opportunities and challenges. Circ Res. 2014;114(8): 1328-1345. |