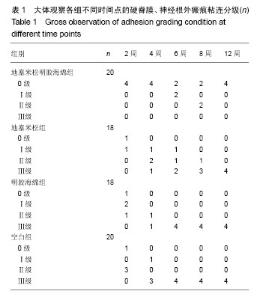
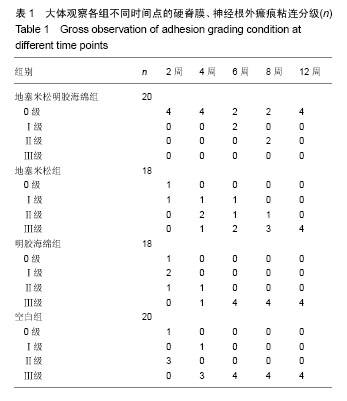
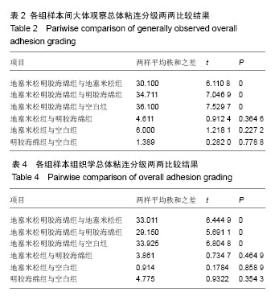
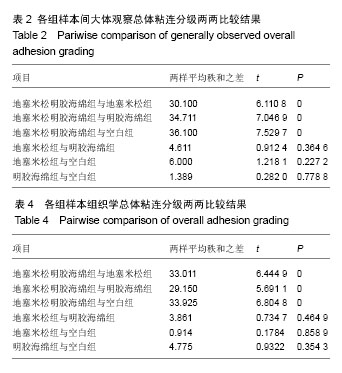
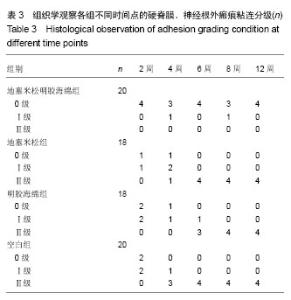
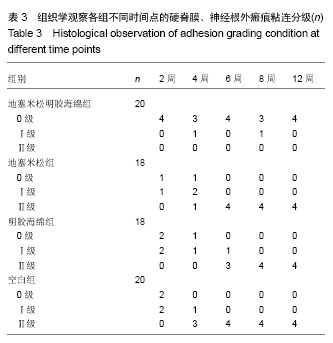
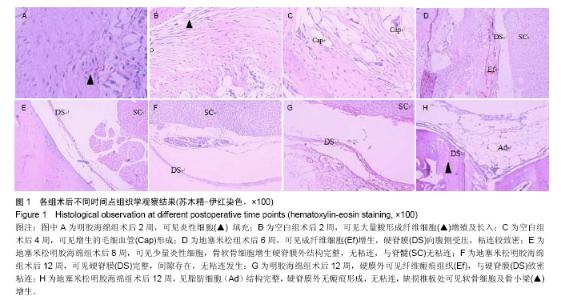
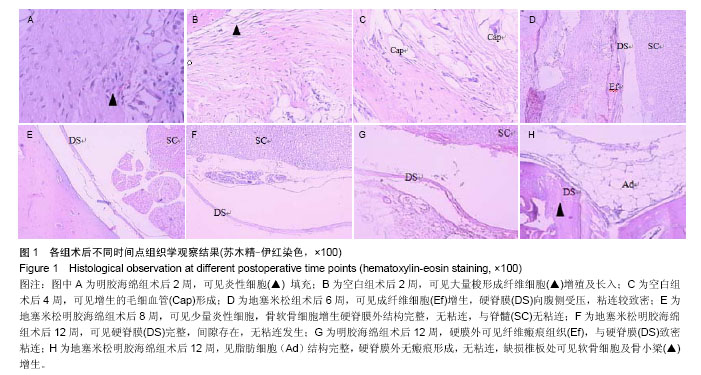
| [1] Hu RW,Jaglal S,Axcell T,et al.A population-based study of reoperations after back surgery.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1997; 22(19):2265-2271.
[2] Mimatsu K. New laminoplasty after thoracic and lumbar laminectomy. J Spinal Disord. 1997;10(1):20-26.
[3] Morimoto T,Okuno S,Nakase H,et al.Cervical myelopathy due to dynamic compression by the laminectomy membrane: dynamic MR imaging study.J Spinal Disord. 1999;12(2):172-173.
[4] Alkalay RN,Kim DH,Urry DW,et al.Prevention of postlaminectomy epidural fibrosis using bioelastic materials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003;28:1659-1665.
[5] 秦国斌.局部筋膜翻转预防椎板切除术后椎管粘连的研究报告[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2000,11(11):1098-1101.
[6] 尹海磊,邹云雯,褚言琛,等.角蛋白人工腱膜预防全椎板切除术后硬脊膜黏连[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,18(4):287-289.
[7] 张宇,周初松,蒋刚彪,等.壳聚糖/聚乙二醇琥珀酸酯/丝裂霉素C释药系统预防椎板切除术后硬脊膜外瘢痕粘连实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(10):1222-1226.
[8] 何幕舜,曾月东,曲志强.自体真皮移植预防硬膜外纤维化及粘连的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(8):765-770.
[9] 成亮,王东来,邹天明,等.自体脂肪颗粒与尿激酶联合应用预防硬膜外粘连[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(2):294-297.
[10] 杨冬松,张绍昆,闫明,等.可降解医用膜预防硬膜外粘连的研究概况[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(42): 7907-7910.
[11] 方怀玺,张明.预防腰椎术后硬脊膜外粘连的临床研究[J].医药前沿, 2013,3(4):96-97.
[12] 张文作,罗小珍.地塞米松明胶海绵预防腰椎管狭窄症减压术后硬脊膜外瘢痕粘连的研究[J].微创医学,2013,8(4):425-426.
[13] 陈东,张文作.双侧开窗减压加地塞米松明胶海绵治疗腰椎管狭窄症的疗效观察[J].医学信息,2014,28(11):411.
[14] Rydell NW,Balazs EA.Effects of ostearhritics on granulation tissue for mation. Clin Orthop.1971;11(3):139-142.
[15] Nussbaum CE,McDonald JV,Baggs RB.Use of vicry1 (polyglacting910) mesh to limit epidural scar formation after laminectomy.Neurosurgery.1990;26:649.
[16] 孙康,姜长明.不同材料预防椎板切除后硬膜粘连的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,1996, 34(6):339-343.
[17] Songer MN,Ghosh I,Spencer DL.Effects of sodium hyaluronate on peridural fibrosis after laminectomy and discectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1990;15:550-554.
[18] Choi HJ,Kim KB,Kwon YM.Effect of amniotic membrane to reduce postlaminectomy epidural adhesion on a rat model.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2011;49(6):323-328.
[19] Ulrich MM,Verkerk M,Reijnen L,et al.Expression profile of proteins involved in scar formation in the healing process of full thickness excisional wounds in the porcine model.Wound Repair Regen.2007;15(4):482-490.
[20] Nartan PK,Van Dellen JR,Bhoola KD.A clinical pathological stidy of Collagen Sponge as a dural graft in neurosurgery.J neurosurg.1995;82(3):406.
[21] 宫良泰,许复郁,戴国锋,等.明胶海绵对硬脊膜作用的实验研究[J].山东医科大学学报, 2001,39(4):373-374.
[22] 万小明.丹参预防硬膜外粘连的组织学和超微结构研究[J].江西医学院学报,2004,11(4):120-123.
[23] 张仲文,肖光,朱东,等.硬膜外瘢痕粘连与脊髓中P物质C-FOS的表达[J].中国现代医学杂志,2001,11(2):6-7.
[24] 杨茂伟.塞来昔布预防椎板切除术后硬脊膜外粘连的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2003,13(16):12-14. |