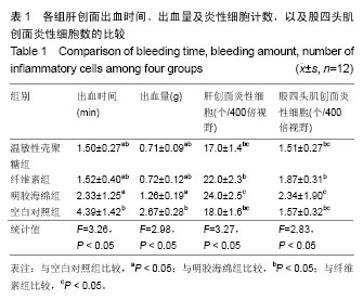
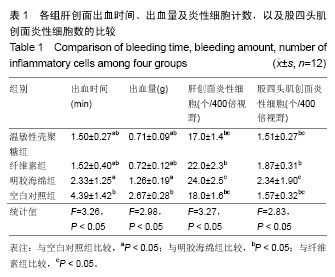
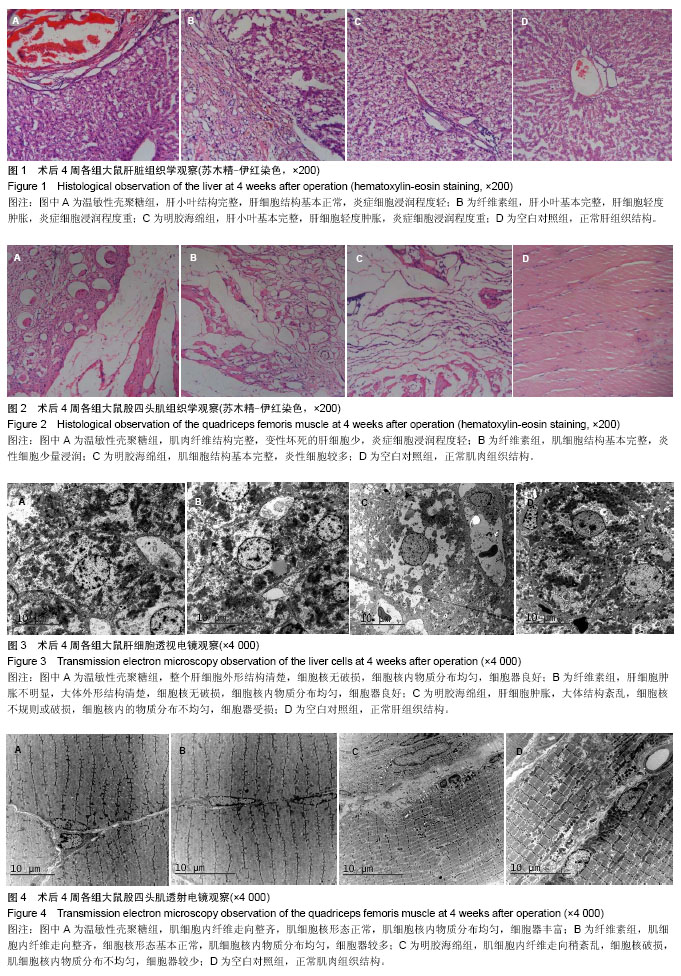
| [1] 侯春林,顾其胜.几丁质与医学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2001:65-69.
[2] Muzzarelli RAA,Muzzarelli C.Chitosan chemistry: relevance to the biomedical sciences.Adv Polym Sci.2005;186:151-209.
[3] Kumar MN,Muzzarelli RA,Muzzarelli C,et al.Chitosan chemistry and pharmaceutical perspectives.Chem Rev. 2004; 104(12):6017-6084.
[4] De Castro GP,Dowling MB,Kilbourne M,et al.Determination of efficacy of novel modified chitosan sponge dressing in a lethal arterial injury model in swine.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012; 72(4):889-907.
[5] 尹刚,魏长征,郭兴锋,等.温敏性壳聚糖止血膜止血作用的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(5):624-628.
[6] 井波,王志强.温敏性壳聚糖水凝胶研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2006,27(2):115-116.
[7] Lee JW,Jung MC,Park HD,et al.Synthesis and characterization of thermosensitive chitosan copolymer as a novel biomaterial.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2004;15(8):1067-1079.
[8] Wei CZ,Hou CL,Gu QS,et al.A thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogel barrier for post-operative adhesions’ prevention.Biomaterials.2009;30(29):5534-5540.
[9] Jackson MR,Taher MM,Burge R,et al.Hemostatic efficacy of a fibrin sealant dressing in an animal model of kidney injury.J Trauma.1998;45(4):662-665.
[10] 张少锋,洪加源.医用生物可吸收止血材料的研究现状与临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(21):3941-3944.
[11] Kent D,Wang G,Yu Z,et al.Strength enhancement of a biomedical titanium alloy through a modified accumulative roll bonding technique.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4(3): 405-416.
[12] Kanyanta V,Ivankovic A.Mechanical characterisation of polyurethane elastomer for biomedical applications.Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2010;3(1):51-62.
[13] 王春,谷天祥,喻磊,等.再生氧化纤维素在严重骨质疏松体外循环手术胸骨止血中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(25):4739-4742.
[14] Ereth MH,Schaff M,Ericson EF,et al.Comparative safetyand efficacy of topical hemostatic agents in a rat neurosurgical model.Neurosurgery.2008;63(4 suppl 2):369-372.
[15] Richmon JD,Tian Y,Husseman J,et al.Use of a sprayed fibrin hemostatic sealant after laser therapy for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia epistaxis. Am J Rhinol. 2007; 21(2):187-191.
[16] Xie H,Lucchesi L,Teach JS,et al.Long-term outcomes of a chitosan hemostatic dressing in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011.
[17] Ong SY,Wu J,Moochhala SM,et al.Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomaterials. 2008;29(32):4323-4332.
[18] Zhao A,Wang T,Yao M,et al.Effects of chitosan-TPP nanoparticles on hepatic tissue after severe bleeding.J Med Coll PLA.2011;26(5):187-191.
[19] Gustafson SB,Fulkerson P,Bildfell R, et al.Chitosan Dressing Provides Hemostasis in Swine Femoral Arterial Injury Model. Prehosp Emerg Care.2007;11(2):172-178.
[20] Hattori H,Amano Y,Nogami Y,et al.Hemostasis for Severe Hemorrhage with Photocrosslinkable Chitosan Hydrogel and Calcium Alginate.Ann Biomed Eng.2010;38(12):3724-3732.
[21] 张弩,吴宇.温敏性壳聚糖水凝胶复合细胞因子修复兔关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(34):6298-6302.
[22] Zhang W,Zhong D,Liu Q,et al.Effect of chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan on fibrinogen structure and blood coagulation. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 2013;24(13): 1549-1563. |