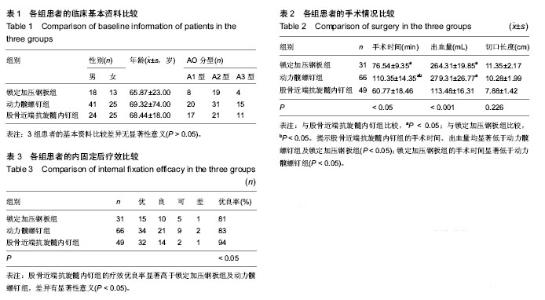
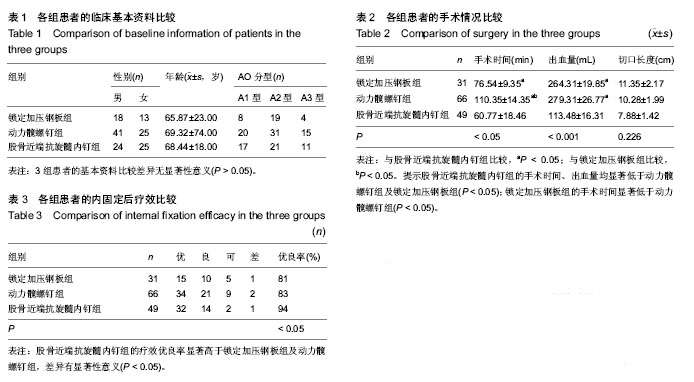
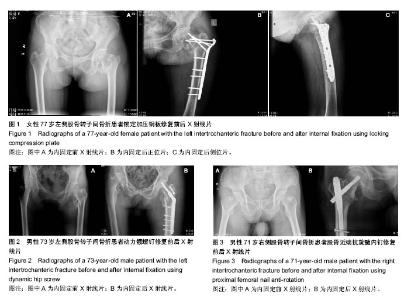
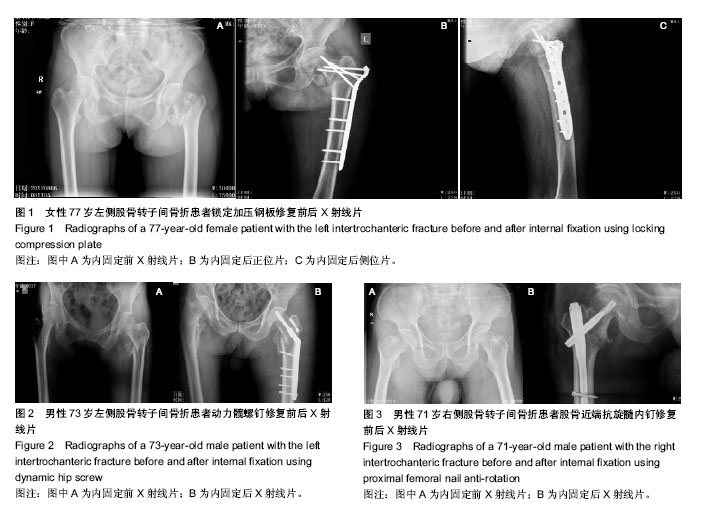
| [1] 宁兆刚, 于建华, 张铁良. DHS治疗老年股骨转子间骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2006,21(3):225-226.
[2] 王鹏建, 李海峰, 阮狄克, 等.股骨粗隆间骨折内固定术后并发症原因分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2010,25(1):27-29.
[3] Mullerler ME, Nazarian S. The comprehensive classification of fractures of the long bones. Newyork :Springer-Verlag, 1990:118.
[4] 朱江涛, 卫小春.股骨粗隆间骨折分型[J].实用骨科杂志, 2007, 13(7):410-413.
[5] Haidukewych GJ, Israel TA. Reverse obliquity fractures ofthe intertrochanteric region of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A(5):643-650.
[6] Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures:Treatment by mold arthroplasty.An end-result studyusing a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755.
[7] Evans EM. Trochantericfractures:Areviewof 110 cases treated byhail-platefixation. J BonejointSurg (Br). 1951;33(2): 192-194.
[8] Li YJ, Li ZB, Yu WH, et al. Case-control study on dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation for the treatment of unstableintertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013; 26(12):977-980.
[9] 王申宇, 徐南伟, 黄勇, 等.防旋型股骨近端髓内钉与动力髋螺钉治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].实用临床医药杂志, 2014, 18(16):67-69.
[10] 陈源. DHS、PFNA、锁定加压钢板治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2012,22(25):2272-2273.
[11] 施慧鹏.复杂不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折多种固定方式的生物力学研究[D].苏州大学,2013.
[12] Kyle RF, Wright TM, Burstein AH. Biomechanical analysis of the sliding characteristics of compression hip screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62:1308-1314.
[13] Cill JB,Jensen L,Chin PC, et al. Intenrochanteric hipfracturestreated withthe trochanteric fixation nail and sliding hip screw. J surg Orthop Adv. 2007;16(2):62-66.
[14] 周业松, 张道前, 邵卫东, 等.动力髋螺钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折失败原因分析及对策[J].中国全科医学, 2013,13(8):2738-2740.
[15] 罗永忠, 李佩佳, 赵汉平, 等.人工关节置换治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2005,13(20):1542-1544.
[16] Yuan X, Yao Q, Ni J, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation versus dynamic hip screw for intertrochanteric fracture in elders: A meta-analysis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014; 94(11):836-839.
[17] Wang YG, Chen M, Hu JK, et al. Comparison of three fixations for treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures in the elderly. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(8):651-655.
[18] Zhang PX, Xue F, An S, et al. Clinical analysis of obvious and hidden blood loss in inter-trochanter fracture patients treated with proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and dynamic hip screw. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012;44(6):891-894.
[19] Huang CG, Ye JJ. Comparison of three methods for the treatment of aged femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(7):549-553.
[20] 侯国进, 周方, 张志山, 等.不同内固定方式治疗老年股骨粗隆问骨折围手术期的失血特点分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(5):738-741.
[21] Zeng C, Wang YR, Wei J, et al. Treatment of trochanteric fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation or dynamic hip screw systems: A meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 2012;40(3): 839-851. |