Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (51): 8353-8357.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.51.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
Tubulin and microtubule-associated substance in neurodegenerative diseases
Wang Peng1, 2, An Si-xun1, Wen Yu-xin1, Yu Shun2, He Xin1
- 1Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China; 2Laboratory of Neurobiology, Institute of Senile Diseases, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100053, China
-
Online:2014-12-10Published:2014-12-10 -
Contact:He Xin, Professor, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Wang Peng, Studying for doctorate, Lecturer, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China; Laboratory of Neurobiology, Institute of Senile Diseases, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100053, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Research Project of Jilin Provincial Education Bureau during the Twelfth Five-Year Period, No. [2012]137, [2012]392
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Peng, An Si-xun, Wen Yu-xin, Yu Shun, He Xin. Tubulin and microtubule-associated substance in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(51): 8353-8357.
share this article
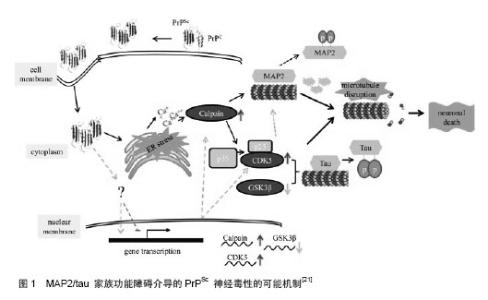
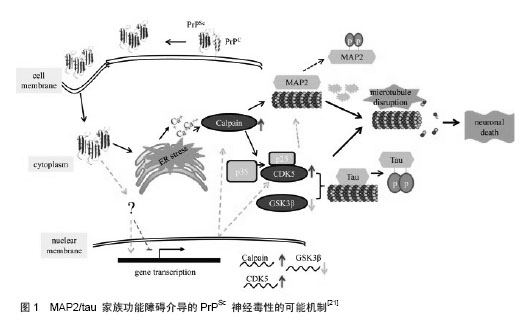
2.1 微管结构与功能 微管(microtubule)是中空管状结构,直径22-25 nm,在胞质中形成网络结构。微管广泛存在于各种细胞中,对细胞有明显的支持和定形作用,被认为是主要的“细胞骨骼”(cytoskeleton)。微管蛋白(tubulin)是微管的化学成分,相对分子质量11 000-12 000,20 ℃时其沉淀系数为4.8 S。每个微管蛋白分子解聚后可产生2个亚基,分别称α2微管蛋白和β2微管蛋白。两个亚基以化学键相连,形成双球菌样、长度为8 nm的微管蛋白。许多微管蛋白分子彼此首尾相接形成微管蛋白原丝,再由13条原丝环列组成圆筒状的微管。 微管具有支架作用,维持细胞正常形态。微管起细胞内物质运输的路轨作用,破坏微管会抑制细胞内的物质运输。在细胞分裂中期,微管蛋白可聚合形成纺锤体,在分裂细胞中牵引染色体到达分裂极。在神经细胞中,微管除具有在其他细胞中的一些功能外,还有一些特定功能。在神经细胞的轴突和树突中,微管束沿长轴排列,起支撑作用。在胚胎发育阶段微管帮助轴突生长,突入周围组织;在成熟的轴突中,微管是物质运输的路轨,参与神经递质的传递。微管的聚集和稳定性的增加是轴突成熟和维持形状所必须的,微管的暂时解聚可使轴突改变形状。定向的轴突延伸可能基于微管的稳定和聚集成束。在神经系统,微管系统的稳定性也是维持胞体和突起间营养转运的基础。 2.2 微管与神经退行性疾病相关蛋白 2.2.1 tau蛋白 tau蛋白是一种微管结合蛋白,属于微管相关蛋白(microtubule associated proteins, MAPs)家族,是其中含量最高的一种。tau蛋白作为一种与微管聚集和解聚共循环的蛋白而首次被发现[2],在成人脑中已发现6种蛋白异构体[3]。tau蛋白在中枢神经系统和外周神经系统中都很丰富,在大脑中,它们主要位于神经细胞中,而在阿尔茨海默病神经元纤维损伤时,则可出现在神经元、轴突和树突中,其作用是促进微管的形成以及提高微管的稳定性。大部分的研究表明tau蛋白可能没有严格的二级结构,分子的肽骨架处于随机弯曲状态。tau蛋白经过煮沸或溶于稀酸并不失去促进微管组装的功能[4]。tau蛋白异常聚积导致的轴突转运障碍不仅影响神经元的形态,而且影响其功能。Mandelkow研究小组[5]报道了有关tau蛋白过度表达导致神经细胞轴突转运障碍的直接证据,并提示这与微管蛋白的紊乱相关。 2.2.2 Synuclein 人突触核蛋白,是一个具有140个氨基酸的蛋白质,主要分布在脑组织。正常情况存在于突触前膜和核膜,并因此被命名。在人巨噬细胞的胞浆和胞核中经免疫染色发现也有分布。在亚细胞结构中主要存在于:肌浆网、胞浆、胞核、囊泡部分。在帕金森病中,是Lewy Body和Lewy neurite的主要成分。此外帕金森病和阿尔茨海默病病理中,在存活多巴胺能神经元的胞体和轴突中分布,尤以轴突中分布较胞体密集。目前研究认为,Syn参与细胞的信号转导,并对突触可塑性起到一定的作用,这些功能的阐述尚停留在假说中。 Alim等[6]利用特异吸附Syn的亲和层析柱,滤过人脑组织匀浆。经westernblot法和免疫共沉淀鉴定发现:在脑组织中微管蛋白和Syn在结构上存在着分子伴侣关系,并证实微管蛋白对Syn的纤维化聚合有启动和促进的作用,并且它们之间的相互作用不受tau蛋白的调节。Alim等[7]发现,Syn可以促进微管蛋白组聚合组装成微管。Jensen等[8]研究揭示Syn、tau蛋白和微管蛋白之间存在结合竞争关系,三者之间的结合强度关系为tubulin-Syn>tubulin-tau>Syn-tau。另据最新的研究[9],向原代培养的神经元培养基添加一定浓度的Syn,在神经元的生长初期,轴突的生长速度明显加快。可以推断,Syn可以促进生长初期原代培养神经元的轴突内微观的组装,这也为Syn促进微管蛋白的组装成微管提供了体内实验的证据。 2.3 与微管蛋白相关物质的一些研究 2.3.1 MPP+ (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium, MPP+),是由1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶(MPTP)在脑内转变而来。由于神经元错将MPP+当成是多巴胺,MPP+可由脑内的多巴胺能神经元选择性地吸收。在通过转运机制进入细胞后,它可以毁坏线粒体的能量转运体系,使ATP的合成受阻,导致dopamine神经元的供能障碍而死亡,并随之导致一系列的帕金森病症状。最新研究表明MPP+在体外,可以使纯化的微管蛋白在组装成的微管长度缩短,并使纯化的微管形成的中心体减少。进一步研究证实在微管合成中,MPP+特异性的针对微管合成的动力系统,致使其合成发生障碍。这一研究提示,正是由于MPP+的影响,使得微管合成中的动态稳定性发生变化,在帕金森病患者的多巴胺能神经元凋亡中起到重要作用[10]。 2.3.2 癌蛋白家族 Stathmin又名癌蛋白18,是一个磷酸化蛋白,对调节细胞增殖和分化的信号有协调和后延作用,在肿瘤细胞分裂时,可以稳定纺锤体,使染色体移动放缓甚至停滞,这一原理被应用于肿瘤药物的开发中。Clement等[11]发现一种结构与Stathmin相似的蛋白的N末端可以与微管蛋白结合,调节微管形成过程中的动力系统,促使微管蛋白形成异常的三聚体,阻碍微管的合成。这一功能短肽为Ⅰ19 L,NMR(Nuclear magnetic resonance)研究证明,形成发卡样结构与微管蛋白结合,磷酸化可以使其功能活性降低。 2.3.3 海洋天然产物 一些研究发现海洋中的化合物具有微管聚合的活性,并应用于抗肿瘤药物的开发。Eleutherobin和Sarcodictyins是从澳大利亚西海岸的软珊瑚Eleutherobia sp中分离得到促微管聚合的二萜苷类化合物[12]。Eleutherobin诱导微管蛋白的反应与紫杉醇驱动的反应相似[13],随MAPs、GTP 及反应温度的升高而加强,形成长而稳固无畸变的微管。Discodermolide,是Gunasekera等[14]从加勒比海海绵Discodermia dissolute中分离得到多羟基化合物。Ernst等研究发现该化合物具有极好的促微管聚合活性[15],在存在MAPs和0 ℃条件下,Discodermolide几乎可以使微管蛋白全部聚合;在不加入MAPs和GTP条件下,促微管组装作用更强;体外诱导微管蛋白聚合形成较短的聚合体,并且聚合物在0 ℃和高Ca2+条件下完全稳定。Laulimalide,是从海绵Cacospongia mycofijiensis, Fasciospongia rimosa 和Hyatella sp.中分离得到[16],该化合物具有促微管聚合活性。 2.4 微管蛋白和相关蛋白与神经退行性疾病 目前,神经退行性疾病作为一种常见病、多发病,成为当前研究热点。多个方向的研究在各自的领域在积极开展。围绕着微管相关物质,一些研究取得了不同程度的进展。其中以tau蛋白的研究最有代表性,至今已经阐明的相当一部分的阿尔茨海默病机制是从这一方向入手。 异常过度磷酸化的微管相关蛋白tau是神经原纤维缠结的主要成分。这些异常过度磷酸化的tau蛋白聚积在退变神经元的胞体并与阿尔茨海默病患者临床痴呆程度正相关[17],tau蛋白的病理改变出现在痴呆症状之前并独立于A异常[18],这些强烈提示tau蛋白过度磷酸化在促进神经细胞退行性变性中起重要作用。神经递质是在神经元的胞体产生,如多巴胺能神经元的囊泡运输等,都是依靠在轴浆中的微管系统来完成的。能够影响微管特性的物质,也就能够影响轴突中微管系统轴浆转运功能。过度磷酸化的tau蛋白不仅自身与微管蛋白的结合能力下降,而且这种异常的tau蛋白还与微管蛋白竞争性地结合正常的微管结合蛋白等,从而使微管解聚,微管系统的解聚影响了轴浆的运输,进而造成神经元的变性,最终引起痴呆的发生。在人野生型Syn和帕金森病的研究中,也可以发现,Syn与微管蛋白之间的共同作用关系,在其他方向的研究进展停滞的情况下,正在成为解开帕金森病病因的新的研究热点,进展快速并不断有新发现[14-16]。 在阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病等神经退行性疾病中,神经细胞的退行性变性可能是一种新的、神经元特有的细胞死亡形式[19],即神经退行性变性死亡。过度表达全长tau蛋白的小脑颗粒细胞甚至可对抗凋亡[20]。这种细胞慢性死亡可能与细胞凋亡一样,也是在一系列分子的有序调控下进行的。 微管系统的紊乱并导致胞内物质运输失调,可能是在细胞接受不良刺激后不同时段使神经细胞逃逸凋亡和进入退行性变性机制的重要环节。当细胞受到不良刺激时,发生微管相关物质的不良代谢,导致微管系统产生结构的紊乱和功能的障碍,胞内物质异常堆积,并通过一系列目前尚待阐明的调控机制使细胞逃逸凋亡,从而进入退行性变性(图1)[21-25];如果及时清除不良刺激,细胞可以恢复正常生存和代谢。 根据最新研究,作者认为当处于细胞环境中的微管受到某种直接的诱因发生紊乱时,也会影响和微管存在密切关系的物质,导致其发生转运失调堆积等代谢紊乱,并引起胞内一系列代谢失常,最终也会导致退行性病变的发生。发生这种慢性退行性变性的细胞尚保存部分细胞功能,因而不能充分调动具分化潜能的神经祖细胞或其他补救机制发挥代偿作用。可见,这种退行性变性对细胞的损害可能比凋亡的后果更严重,呈弥散性病变。因此探讨这一过程的调节机制和关键性调节分子,设法在阻止细胞凋亡的同时,遏制微管和微管相关代谢物质的代谢紊乱,对预防和延缓神经细胞的退行性变性具有重要意义。 "
| [1]Diaz-Corrales FJ, Asanuma M, Miyazaki I,et al. Rotenone induces aggregation of gamma-tubulin protein and subsequent disorganization of the centrosome: relevance to formation of inclusion bodies and neurodegeneration. Neuroscience. 2005;133(1):117-135. [2]Weingarten MD, Lockwood AH, Hwo SY,et al. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1975;72:1858-1862. [3]Geodert M,Jakes R.Expression of esparate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J.1990;9: 4225-4230. [4]Fellous A, Francon J, Lennon AM, et al. Microtubule assembly in vitro. J. Biochem.1997;78:167-174. [5]Mandelkow EM, Stamer K, Vogel R, et al. Clogging of axons by tau, inhibition of axonal traffic and starvation of synapses. Neurobiol Aging.2003;24(8):1079-1085. [6]Alim MA, Hossain MS, Arima K, et al. Tubulin seeds synuclein fibril formation.J Biol Chem. 2002;277(3):2112-2117. [7]Alim MA, Ma QL, Takeda K, et al.Demonstration of a role for synuclein as a functional microtubule-associated protein. J Alzheimers Dis. 2004;6(4):435-442. [8]Jensen PH, Hager H, Nielsen MS,et al.synuclein binds to tau and stimulates the protein kinase A-catalyzed tau phosphorylation of serine residues 262 and 356, J Biol Chem. 1999;(274):25481-25489. [9]Guangwei L, Wang P, Xin L, et al. Alpha-synuclein promotes early neurite outgrowth in cultured primary neurons. Neural Transm.2013;120(9):1331-1343. [10]Cappelletti G, Surrey T, Maci R. The parkinsonism producing neurotoxin MPP+ affects microtubule dynamics by acting as a destabilising factor. FEBS Lett. 2005; 579(21): 4781-4786. [11]Clement MJ, Jourdain I, Lachkar S, et al, N-Terminal Stathmin-like Peptides Bind Tubulin and Impede Microtubule Assembly.Biochemistry.2005; 44(44):14616-14625. [12]Hamel E, Sackett DL, Vourloumis D, et al. The coral-derived natural products eleutherobin and sarcodictyins A and B: effects on the assembly of purified tubulin with and without microtubule-associated proteins and binding at the polymer taxoid site. Bio-chemistry.1999;38(17): 5490. [13]Plosker GL, Hurst M. Paclitaxel: a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in non2small cell lung cancer. Pharmacoeconomics. 2001;19(11):1111. [14]Gunasekera SP, Gunasekera M, Longley RE, et al. Dicodermolide: a new bioactive polydroxylated lactone from the marine sponge, Discodermia dissolute. J Org Chem. 1991;56 (3):1346. [15]Gunasekera SP,Longley RE,Isbrucker RA.Semisynthetic analogues of the microtubule2stabilizing agent discodermolide: preparation and biological activity. J Nat Prod.2002;65 (12):1830. [16]Pryor DE, O’ Brate A, Bilcer G, et al.The microtubule stabilizing agent laulimalide does not bind in the taxoid site , kills cells resistant to paclitaxel and epothilones , and may not require its epoxide moiety for activity. Biochemistry.2002;41(29): 9109. [17]Iqbal K, Alonso Adel C, El-Akkad E,et al. Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration: therapeutic targets and high-throughput assays. J Mol Neurosci. 2003; 20(3):425-429. [18]Delacourte A, Sergeant N, Champain D, et al. Nonoverlapping but synergetic tau and APP pathologies in sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology.2002;59(3):398-407. [19]王建枝,刘世杰.神经退行性疾病神经细胞死亡机理[J].国外医学:分子生物学分册, 2003, 25(1):41-44. [20]Amadoro G, Serafino AL, Barbato C, et al. Role of N-terminal tau domain integrity on the survival of cerebellar granule neurons. Cell Death Differ.2004; 11(2):217-230. [21]Zhang J, Dong XP. Dysfunction of microtubule-associated proteins of MAP2/tau family in Prion disease.Prion. 2012;6(4): 334-338. [22]Wolfe MS.Tau mutations in neurodegenerative diseases.J Biol Chem.2009;284(10):6021-6025. [23]Souter S, Lee G.Tubulin-independent tau in Alzheimer's disease and cancer: implications for disease pathogenesis and treatment.Curr Alzheimer Res.2010;7(8):697-707. [24]Baird FJ, Bennett CL.Microtubule defects & Neurodegeneration.J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2013;4:203. [25]Yu D, LaPointe NE, Guzman E,et al.Tau proteins harboring neurodegeneration-linked mutations impair kinesin translocation in vitro.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;39(2):301-314. [26]Brunden KR, Yao Y, Potuzak JS,et al.The characterization of microtubule-stabilizing drugs as possible therapeutic agents for Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies.Pharmacol Res. 2011;63(4):341-351. |
| [1] | Zhang Lin1, Liu Jinjie1, Zhao Yan2, Liu Yi1, Lin Jianwen1. N-butylphthalide affects cognitive function of APP/PS1 transgenic mice (Alzheimer’s disease model) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Gao Hua1, 2, Li Yanxia1, Wang Dan1, Yang Xinling1 . Protective effects and the mechanism of lipoic acid on cell model of Parkinson’s disease induced by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 447-452. |
| [3] | Chen Li, Hu Lan, Peng Yanan, Yang Liu, Shen Hui, Wang Tan, Zhao Zhenqiang. Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into dopaminergic neurons: security risk for heterogeneity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 118-124. |
| [4] | Gao Ming-long, Shi Shao-xia, Zhang Kun, Zhang Ying-dong, Li Na, Yu Ming, Wang Yong-liang. Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-modified human amniotic membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on learning and memory abilities of Alzheimer's disease rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1419-1424. |
| [5] | He Jia, Yan Bo, Song Xiao-zheng, Wu Xue-ying. Effects of placental mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on behaviors and neurotransmitters in Alzheimer disease rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4650-4656. |
| [6] | Zhang Lin1, Yang Jing2, Liu Zan-hua1 . STEP61 negatively regulates amyloid beta-mediated ERK signaling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease cell model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4507-4512. |
| [7] | Han Xue-jie1, 2, Halleda•Balikarthan2, Gao Hua3, Yang Xin-ling2. Baicalin increases connexin 43 expression in striatal astrocytes of rats with Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(16): 2542-2548. |
| [8] | Shi Cheng-kui, Chen Zhi-qiang. Effect of microglia on iron metabolism in midbrain dopaminergic neurons and the underlying mechanism: study protocol for an in vitro cellular experiment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(8): 1262-1267. |
| [9] |
Su Feng, Yun Peng, Liu Xue, Shen Xin, Li Cheng-long, Li Rong-ye.
Novel bio-mimetic receptors for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(34): 5552-5557.
|
| [10] | Zhou Jing, Bao Li-wen, Liang Jing. Behavior improvement and inflammatory regulation in Parkinson’s disease rats after neural stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(33): 5299-5304. |
| [11] | Peng Ya-nan, Hu Lan, Wang Tan, Li Ke, Yang Liu, Chen Li, Chen Xiao-wu, Chen Zhi-bin,Zhao Zhen-qiang. Functional differentiation of dopaminergic neurons derived from human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(33): 5360-5368. |
| [12] | Zhu Shi-qi, Li Feng. Research advances in induced pluripotent stem cells in Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(21): 3426-3431. |
| [13] | Zhou Jun, Zhou De-sheng . Different doses of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve learning and memory ability of dementia rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(50): 7524-7529. |
| [14] | Wang Gai-feng. Effects of Bushen Yizhi Decoction on Alzheimer’s disease model rats induced by D-galactose combined with amyloid-beta 25-35 and the underlying mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7307-7313. |
| [15] | Wu Ya-dan, Liang Pei-ri, Long Deng-yi, Gao Bing-miao. Effects of Ginkgo biloba Pingchan Recipe on loss and apoptosis of dopamine neurons in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7327-7333. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||