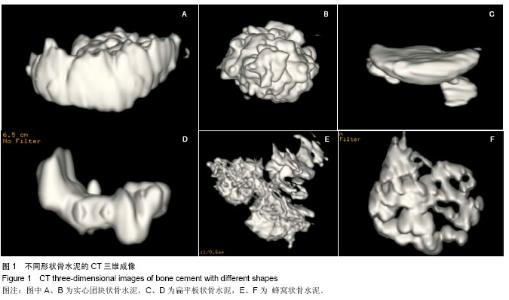
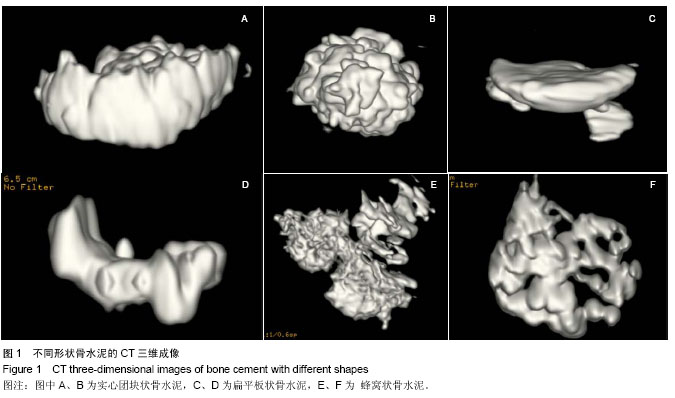
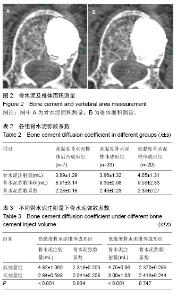
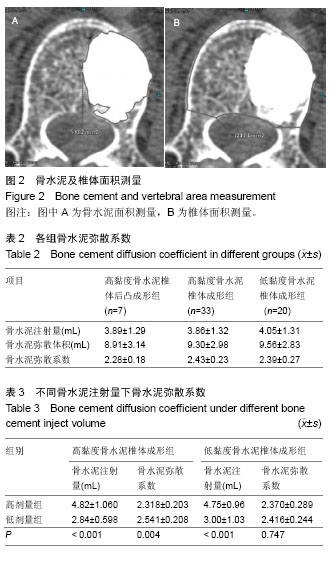
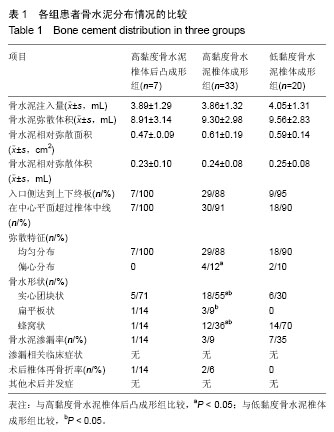
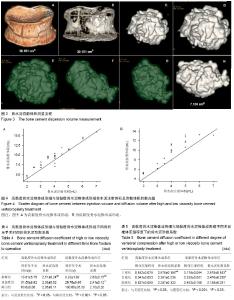
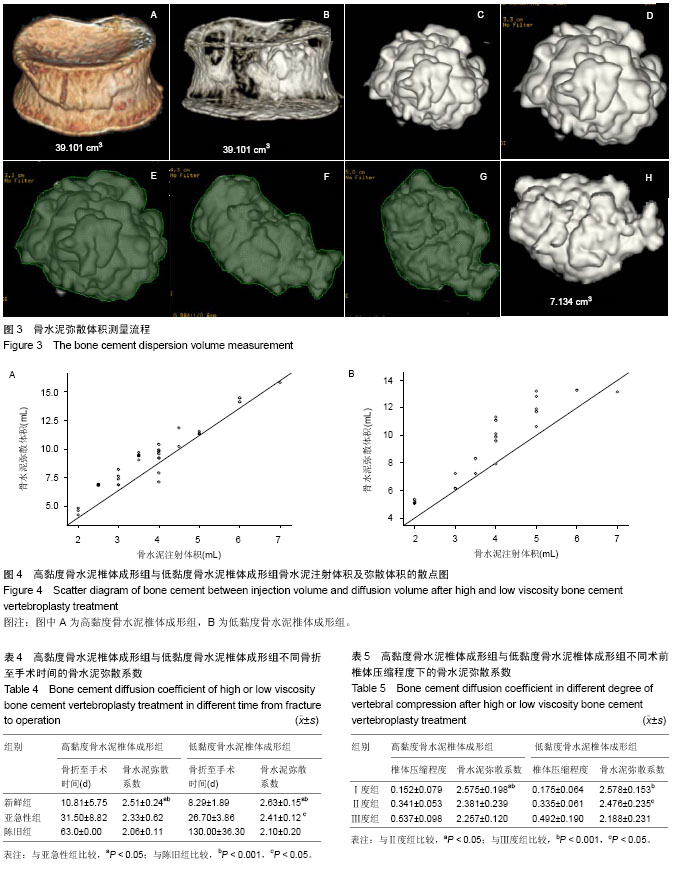
| [1] Galibert P,Deramond H,Rosat P,et al.Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty.Neurochirurgie. 1987;33(2):166-168.
[2] 余卫.脊柱骨折影像诊断(骨质疏松椎体骨折的评估及鉴别)[C].中华医学会第七次全国骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病学术会议论文汇编,2013.
[3] 张亮,高梁斌,李健,等.椎体成形术中椎体骨密度对骨水泥弥散体积的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(11):915-918.
[4] 赵永生.老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折的微创治疗对策[D].山东大学,2013.
[5] 王尔天,易伟宏,黄曹,等.PVP与PKP治疗骨质疏松性压缩骨折时骨水泥填充效果及弥散方式的比较研究[J].中国伤残医学, 2010, 18(5):2-4.
[6] 郑召民,李佛宝.经皮椎体成型术和经皮椎体后凸成形术-问题与对策[J].中华医学杂志,2006,86(27):1878-1880.
[7] Jin YJ,Yoon SH,Park KW,et al. The volumetric analysis of cement in vertebroplasty:relationship with clinical outcome and complications.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(12): 761-772.
[8] 王岩,毛克亚,刘保卫,等.椎体强化在骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中的应用[J].中国骨科,2005,25(4):18-20.
[9] 李春海,刘尚礼,叶伟,等.高黏度骨水泥在经皮椎体成形术中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(4):259-262.
[10] Anselmetti GC,Zoarski G,Manca A,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty and bone cement leakage: clinical experience with a new high-viscosity bone cement and delivery system for vertebral augmentation in Benign and Malignant compression fractures. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008;31(5):937-947.
[11] 蔺福辉,易小波,任志宏,等. 高粘度骨水泥在椎体成形术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(1):66-67.
[12] Georgy BA.Clinical experience with high-viscosity cements for percutaneous vertebral body augmentation: occurrence, degree, and location of cement leakage compared with kyphoplasty. AJNR.2010;31(3):504-508.
[13] 包拥政.高粘度骨水泥椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的近期疗效观察[D].汕头大学,2011. |