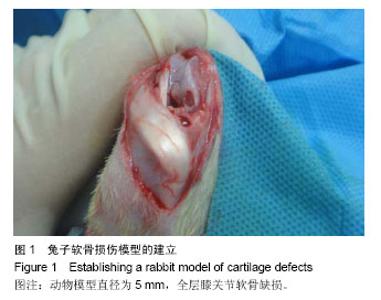
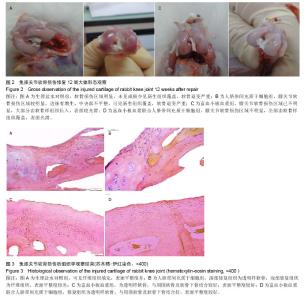
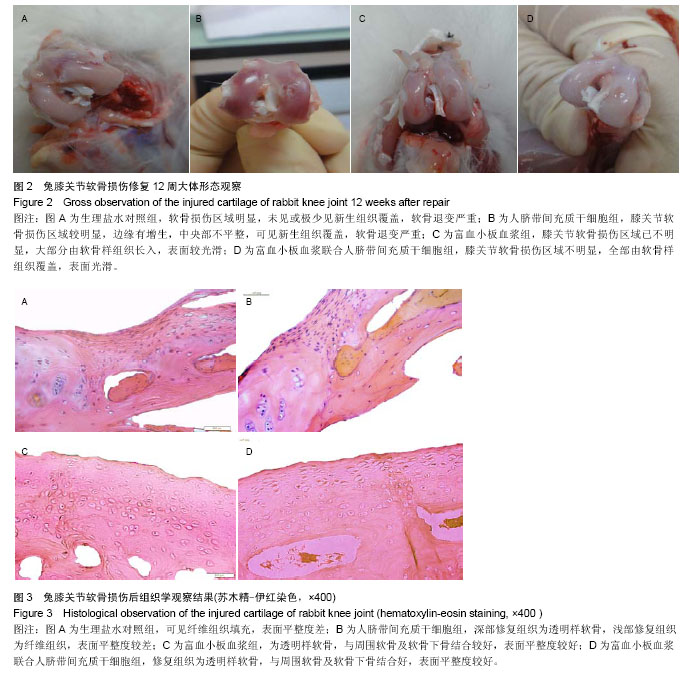
| [1] 周斌,廖琦.富血小板血浆促进骨修复的机制及应用.中国组织工程研究[J].2012,16(33):6228-6232.
[2] 杜刚,李林,张波,等.富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞对兔股骨头坏死的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(16): 205- 208.
[3] Chen L, Dong SW, Liu JP,et al. Synergy of Tendon Stem Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Tendon Healing. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(6):991-997
[4] Sanchez M, Anitua E, Orive G,et al. Platelet-rich therapies in the treatment of orthopaedic sport injuries. Sports Med.2009; 39(5):345-354.
[5] Hall MP, Band PA, Meislin RJ,et al. Plateletrich plasma: current concepts and application in sports medicine. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2009;17(10):602-608.
[6] Mifuneyz Y, Matsumotoyz T, Takayamayz K,et al .The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the regenerative therapy of muscle derived stem cells for articular cartilage repair.Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2012:1-11.
[7] 李明,张长青.富血小板血浆临床应用及其生物材料性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(8):1445-1448.
[8] Drengk A,Zapf A,Sturmer EK,et al.Influence of platelet-rich plasma on chondrogenic differentiation and proliferation of chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs.2009;189(5):317-326.
[9] 刘晓芳,王韫芳,李亚里,等.干细胞治疗糖尿病的研究现状及展望[J].中国科学:生命科学,2013,43(4):291-297.
[10] 陈国昌,王熙然.干细胞移植治疗糖尿病的国内外研究趋势分析.中国组织工程研究[J].2012,16(36):6834-6840.
[11] 曲志国,野向阳,林辉,等.人脐带间充质干细胞诱导成骨及治疗骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(45): 8503- 8507.
[12] Weibrich G,Hansen T,Kleis W,et al.Effect of platelet concentration in plate-rich plasma on peri-implant bone regeneration.Bone.2004;34:665-671.
[13] Petrungaro PS. ComPend Contin Educ Dent.2001; 22(9): 729-732.
[14] Sun Y, Feng Y, Zhang CQ, et al.The regenerative effect of Platelet-rich Plasma on healing in large osteochondral defects.International OrthoPaedics (SICOT).2010; 34: 589–597.
[15] Dominici M,Le Blanc K,Mueller I,et al.Minimal criteria for defining multiPotent mesenchymal stromal cells.The International Society for Cellular TheraPy Position statement. CytotheraPy.2006,8(4):315-317.
[16] Weiss ML,Medicetty S,Bledsoe AR,et al. Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells:Preliminary characterization and effect of transPlantation in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Stem Cell.2006;24(3):781-792.
[17] 陈其春.磁共振T2 maPPing成像评估膝关节软骨的损伤与修复[D].南京:南京医科大学.南京医科大学第一临床学院.2012.
[18] Mitchell KE, Weiss ML, Mitchell BM, et al.Matrix cells from Whartons jelly form neurons and glia. Stem Cells.2003; 21(1): 50-60.
[19] 黄鹏,马廉.人脐带间充质干细胞的应用研究现状[J].中国输血杂志.2009,22,(3):169-172.
[20] 柳菁,许超,宇丽,等.两种培养体系条件下人脐带间充质干细胞向软骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(41):7625- 7630.
[21] Xie X, Zhang C, Tuan RS.Biology of platelet-rich plasma and its clinical application in cartilage repair.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):204.
[22] Abrams GD, Frank RM, Fortier LA,et al.Platelet-rich plasma for articular cartilage repair.Sports Med Arthrosc. 2013;21(4): 213-219.
[23] Betsch M, Schneppendahl J, Thuns S, et al.Bone marrow aspiration concentrate and platelet rich plasma for osteochondral repair in a porcine osteochondral defect model. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e71602.
[24] Lee JC, Min HJ, Park HJ,et al.Synovial membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells supported by platelet-rich plasma can repair osteochondral defects in a rabbit model. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(6):1034-1046.
[25] Smyth NA, Murawski CD, Fortier LA,et al.Platelet-rich plasma in the pathologic processes of cartilage: review of basic science evidence.Arthroscopy.2013;29(8):1399-1409.
[26] Mifune Y, Matsumoto T, Takayama K, et al.The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the regenerative therapy of muscle derived stem cells for articular cartilage repair.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):175-185.
[27] Hildner F, Albrecht C, Gabriel C,et al.State of the art and future perspectives of articular cartilage regeneration: a focus on adipose-derived stem cells and platelet-derived products.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(4):e36-51.
[28] Ye FG, Li HY,Qiao GX,et al. Platelet-rich plasma gel in combination with Schwann cells for repair of sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res.2012;7(29): 2286-2292. |