Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (38): 6194-6199.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.38.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osteoporotic chronic pain: how to understand and prevent it?
Wei Xin-wei1, Chen Zhi-xin2
- 1The First Clinical Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2First Department of Orthopedics, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2014-08-19Online:2014-09-10Published:2014-09-10 -
Contact:Chen Zhi-xin, M. D., Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, First Department of Orthopedics, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Wei Xin-wei, Studying for master’s degree, the First Clinical Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Xin-wei1, Chen Zhi-xin2. Osteoporotic chronic pain: how to understand and prevent it?[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(38): 6194-6199.
share this article
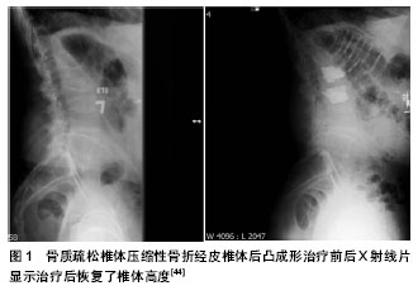
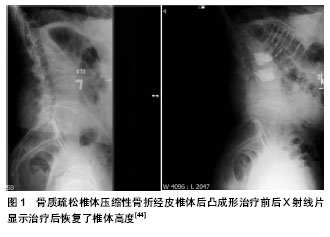
2.1 骨质疏松性慢性疼痛的特点 骨质疏松症是以骨量减少、骨组织显微结构退化(松质骨骨小梁变细、断裂、数量减少;皮质骨多孔、变薄)为特征,以致骨的脆性增高及骨折危险性增加的一种全身性骨病[3]。骨质疏松症临床表现主要有疼痛、身高缩短、驼背,骨折以及呼吸系统障碍。其中,骨质疏松性疼痛是其最常见,最主要的临床症状,约占临床症状的58%,其中腰背痛占70%-80%,多为钝痛,无固定压痛点,并向脊柱两侧扩散;年龄越大发病率越高,女性症状重于男性,女性停经后重于停经前,久坐、久站疼痛加重,平卧时疼痛有所缓解,深夜及清晨醒来时身体肌肉僵硬,骨骼疼痛感加剧,而白天则常常缓解;若用力咳嗽、大便时,疼痛加剧。 据有关资料统计,骨质疏松患者中67%为局限性腰背疼痛,9%为腰背痛伴四肢放射痛,10%腰背痛伴带状痛,4%腰背痛伴麻木感,10%不仅腰背痛,而且伴有四肢麻木和屈伸腰背时出现肋间神经痛和无力感。若胸腰椎发生骨质疏松性压缩骨折,则可出现急性疼痛,体位改变时尤为明显;该骨折部位相应的棘突出现叩击痛,经过两三周后逐渐减轻,但一部分患者会转化为慢性疼痛[4]。骨质疏松性慢性疼痛在疼痛初期,由安静状态开始活动时出现腰背痛,此后逐渐发展到持续性疼痛;在日常活动如用手向上持物、绊倒、用力开窗等情况下疼痛诱发或加剧;疼痛常在久坐、久立等长时间保持固定姿势时加剧,有时可伴有四肢放射性痛和麻木感[5]。 骨质疏松性疼痛表现为全身性骨痛,严重时不能入睡,运用降钙素等制剂治疗能有效缓解疼痛[6]。当重度骨质疏松症发生椎体骨折时,椎体压缩变形严重,椎体高度丢失较多,可造成椎间孔缩小压迫神经根造成下肢麻木无力,感觉运动功能障碍,容易误认为是椎间盘原因;或是高位椎间孔受压造成胸段脊神经根受压致胸壁疼痛不适等相应神经症状,类似心绞痛,上腹部疼痛类似急腹症,合并冠心病时容易造成误诊。 2.2 骨质疏松性慢性疼痛的发病机制 2.2.1 淤血机制 近年来有中医学者提出瘀血与骨痛关系密切,并且采用活血祛瘀疗法取得了明显的疗效[7-9]。淤血有血瘀发展而来,血瘀指血行速度滞缓变慢、血液黏稠度增高等病理状态。这种状态血液仍在脉络中运行,并没有凝结成死血,血液营养物质吸收利用障碍;病情由浅入深,血瘀证日久渐进,凝滞不散,便发展成淤血。通过对骨质疏松患者骨组织形态测量比较[10],发现患者骨小梁内有微血管的改变,钙及营养物质不能正常的通过哈弗斯系统进入骨骼,骨小梁变细,数目减少,造成残存骨小梁负荷加重,降低了骨小梁强度,一旦超过了其承重限度,就会使骨小梁折断,出现显微骨折;骨小梁折断使微血管破裂,形成血窦,而成瘀血,骨骼内部压力增高。骨骼内发生淤血,血瘀证,微循环及新陈代谢障碍,营养物质利用率降低,代谢废物堆积,内部血窦压力增高,局部组织缺血缺氧,痛觉神经受到激惹等正是骨质疏松症慢性疼痛的主要作用机制。 2.2.2 细胞因子及乳酸堆积 细胞因子通过自分泌、旁分泌和细胞黏附,在骨代谢过程中发挥重要作用。白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞抑制因子、白细胞介素11、巨噬细胞集落刺激因子、粒单细胞集落刺激因子等细胞因子促进破骨细胞生成,增强骨吸收。肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1是目前为止发现的刺激骨吸收作用最强的细胞因子[11]。绝经后女性雌激素分泌明显减少,失去了骨代谢中的骨吸收抑制作用,导致单核细胞产生过量的骨吸收性细胞因子,以致破骨细胞活动加强、骨骼钙质大量流失,骨质疏松和慢性骨痛[12]。 陈柏龄等[13]利用小鼠探究肿瘤坏死因子α在骨质疏松慢性疼痛中的作用,认为肿瘤坏死因子α在绝经后骨质疏松疼痛中发挥重要作用,并可能通过作用于背根神经节引起痛觉敏感;而抑制肿瘤坏死因子α的合成可缓解绝经后骨质疏松性疼痛。调查表明,当人体骨量流失超过12%时即可出现骨痛,骨质疏松症患者因脊柱椎体骨小梁萎缩减少,椎体缩短变形,脊柱前屈、胸腰背部肌肉为维持机体重心平衡,纠正过度前屈,肌肉收缩加剧,肌张力增加,肌肉血液微循环瘀滞,新陈代谢降低,易导致肌肉疲劳甚至痉挛,日积月累造成乳酸堆积而出现持续反复的慢性疼痛[14]。 2.2.3 其他 林秋喜等[15]认为骨质疏松性疼痛的产生是多方面的,考虑与如下因素有关:①破骨细胞溶骨导致,以夜间疼痛为主要表现。②机械应力导致微骨折,以劳累后疼痛为主要表现。③骨骼畸形所致的肌肉韧带受力异常。④严重的低骨量衰竭,长期卧床、制动所致。另外,有人也认为骨痛主要是由于骨转换过快,骨吸收增加所致。骨的痛觉神经广泛分布于骨外膜、骨内膜、骨小梁、皮质骨及内部哈弗斯系统,若椎体、骨盆及胸廓发生骨质疏松性显微骨折,骨小梁及部分皮质骨被吸收,骨骼内部结构发生显微变形及理化性质的改变,痛觉神经的外在支持结构受到破坏而遭受物理压迫及化学物质的刺激,进而出现反复慢性疼痛。但有关骨质疏松慢性骨痛的确切发病机制如生化信号转导途径尚不明确,仍需更多的基础性研究进行探讨和证实。 2.3 骨质疏松性慢性疼痛的治疗 2.3.1 药物治疗 降钙素:治疗骨质疏松性慢性疼痛的降钙素常用的有:鲑鱼降钙素和鳗鱼降钙素。杜瑞琴等[16]选入210例骨质疏松伴有慢性疼痛的患者,给予鲑鱼降钙素50 IU/d,治疗2周观察鲑鱼降钙素对骨质疏松性骨痛的疗效,199例患者完成治疗,80%以上的患者骨痛症状完全消失或明显减轻。有研究在两组随机双盲试验中发现降钙素能明显缓解骨质疏松性疼痛,早期改善患有椎体压缩骨折患者的日常活动[17]。降钙素治疗骨痛的机制可能有[18]:①有广泛骨吸收的骨痛,局部氢离子浓度增加,降钙素通过抑制骨吸收间接降低氢离子浓度,减轻骨痛。②骨痛与前列腺素类物质有关,而体外实验研究已证实降钙素可抑制前列腺素的合成。③中枢性镇痛作用:动物性实验证实降钙素可使动物痛阈提高。④应用降钙素后血浆β-内啡肽浓度明显提高,β-内啡肽可与阿片受体特异性结合而起到镇痛作用。 二膦酸盐:二膦酸盐是一类人工合成化合物,理化性质十分稳定,不能被酶水解,一经吸收,迅速进入骨组织,吸附于羟磷灰石晶体表面,抑制磷酸钙结晶的形成、聚集和溶解,并抑制软组织的异位钙化。主要药理作用是抑制破骨细胞生成及其活性,抑制骨吸收,常用的二膦酸盐有依替膦酸二钠、帕米膦酸钠、阿仑膦酸钠、利塞膦酸钠和唑来膦酸钠等。包丽华等[19]将患有骨痛的202例绝经后骨质疏松患者简单随机分为3组,阿仑膦酸钠组65例,依替二膦酸钠组67例和钙尔奇D组70例,治疗1年,结果前两组患者经治疗后骨痛症状明显改善,阿仑膦酸钠组平均改善时间为7-10 d,依替二膦酸钠组约为2周,钙剂组疼痛变化不明显,认为二膦酸盐能明显改善骨质疏松性骨痛,显著提高骨密度,增加骨强度,预防骨质疏松性骨折的发生。丁远远等[20]静脉应用二膦酸盐治疗原发性骨质疏松性骨痛,治疗后患者疼痛强度明显降低(P < 0.05),骨密度略有增高,认为静脉应用二膦酸盐治疗原发性骨质疏松性疼痛有给药方便,依从性好,安全性高,起效快,疗效优等特点[21]。 其他:特立帕肽、阿法骨化醇以及中西医结合治疗骨质疏松性疼痛都有着一定的疗效[22-24]。国外一项研究选入1 085例患有椎体骨折的女性患者作为研究对象,分为实验组和安慰剂对照组,给予特立帕肽20 μg/d,治疗19个月,发现在患有重度背痛的患者中57%可获得缓解[25];并和阿仑膦酸钠10 mg/d对照,给予特立帕肽20-40 μg/d进行治疗,中等到重度背痛患者中80%可获得缓解。陈大伟等[26]使用骨痹汤治疗80例原发性骨质疏松症腰背痛患者,疗效显著,并认为中药治疗骨质疏松症既可以缓解骨质疏松症导致的腰背痛,全身骨痛、乏力等临床症状,又可以提高性激素水平,降低骨钙的丢失,同时对衰老症状也有较大改善,提高中老年人的生活质量。 2.3.2 手术治疗 经皮椎体成形术:经皮椎体成形术是目前常用的一种脊柱微创技术,是指在影像技术介导下经皮穿刺后向骨折椎体内注入骨水泥填充剂,使骨折椎体的稳定性增强,椎体高度得到恢复,防止骨折进一步塌陷。自从1987年法国的Galibert等报道应用经皮椎体成形术治疗椎体血管瘤获得良好效果后,经皮椎体成形术得以广泛开展,并用于治疗骨质疏松脊柱压缩性骨折及脊柱良恶性肿瘤,能起到迅速止痛、稳定脊柱的目的[27]。 王晶等[28]采用经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松所致胸腰椎压缩性骨折患者91例,术后所有患者均获随访,随访时间12-24个月,术后早期疼痛得到完全或明显缓解,有效率为100%,由此认为经皮椎体成形术是一种能有效缓解骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折所致疼痛的方法。周华乔等[29]对确诊为骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的老年患者28例共34个椎体实施经皮椎体成形术与小针刀联合治疗,术后随访3-24个月,患者对疼痛缓解及功能改善均十分满意,由此认为经皮椎体成形术联合小针刀治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折疗效确切,能很好地改善椎体骨折引起的腰部疼痛,是一种简单、有效、安全、经济的治疗方法。李卉等[30]从不同角度分别证实了经皮椎体成形术治疗椎体压缩性骨折所致疼痛疗效确切,优于单纯的保守治疗[31-35]。研究认为,即使患者骨折持续时间长达1年,对经皮椎体成形术治疗仍有良好的反应[36],并受益于中期疼痛缓解和生活质量的提高。 经皮椎体成形术的止痛机制目前尚不明确,可能有以下几个方面[37]:①机械性,注入骨水泥能提高脊柱的生物力学性能,固定显微骨折,减少骨折断端的微小移动,从而减少对痛觉神经末梢的刺激。由于骨质疏松时椎体骨小梁间隙增宽,骨水泥能沿骨小梁间隙扩散至整个椎体,强化后对椎体具有支撑作用,能有效预防椎体塌陷和压缩性骨折的发生。②骨水泥的热效应,骨水泥在聚合反应时产生的热能峰值温度在52-93 ℃,可导致骨水泥周围的组织坏死,同时破坏组织内神经末梢,使疼痛消失或缓解。③化学性,骨水泥的细胞毒性作用本身对肿瘤细胞就具有毒性作用,可以杀死肿瘤组织。经皮椎体成形术主要并发症[38]分为术中并发症:骨水泥渗漏、栓塞、气胸、穿刺直接损伤神经根及脊髓、心血管系统反应;术后并发症:术后疼痛加重,邻近椎体骨折和穿刺处血肿形成及血肿压迫脊髓。尽管以上并发症时有发生,但只要正确掌握其适应症并积极采取相应有效的预防措施,这些并发症是可以预防和避免的。 经皮椎体后凸成形术:经皮椎体后凸成形术类似于经皮椎体成形术,是指在向伤椎注入骨水泥等填充剂之前,先通过导管装置向椎体置入可充气球囊,向球囊充气撑开受压变形椎体,然后退出球囊,向球囊撑开的椎体空间注入骨水泥,从而完全或部分恢复椎体丢失高度,纠正后凸畸形,增加椎体稳定性,缓解疼痛。自从Reiley等于1999年首先运用经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗脊柱椎体压缩骨折获得良好疗效后,经皮椎体后凸成形术是在经皮椎体成形术基础上发展完善并得到广泛的应用,它不仅能很好地缓解患者的疼痛症状,而且能将压缩的骨折椎体复位到一定的高度,从而获得后凸畸形的矫正[39]。 方秀统等[40]对76例(87个骨折椎体)老年性骨质疏松性脊柱压缩骨折患者采用经皮椎体后凸成形术进行治疗,平均随访时间2.1年,对患者骨密度、术前术后目测类比(VAS)疼痛评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数等指标进行统计分析,认为经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年性椎体骨质疏松压缩性骨折简单、安全、有效,不仅能够迅速完全或部分缓解患者的疼痛,提高患者脊柱功能活动和恢复骨折椎体的高度避免骨折椎体高度进一步丢失;还能同时降低患者合并症的发生率,改善患者的生活质量。经皮椎体后凸成形术的止痛机制及手术并发症类似于经皮椎体成形术。陈升浩等[41]采用经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗50例老年性骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折,随访时间12-28个月,通过疼痛评分、后凸角度的改善发现经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折是一种安全、可靠,止痛效果确切的脊柱微创技术。大量临床资料均显示经皮椎体后凸成形术不仅可以缓解疼痛[42-43],改善患者生活质量,而且还能降低再发骨折、椎体高度丢失、脊柱后凸进展以及慢性背痛的风险 (图1)[44]。Eck等[45]针对经皮椎体后凸成形术对疼痛控制和并发症的一项荟萃分析表明,与经皮椎体成形术相比较,经皮椎体后凸成形术能更明显地改善目测类比评分疼痛评分,但存在更大的骨水泥渗漏和造成新的骨折的风险。故积极有效的预防手术并发症至关重要。 2.3.3 其他 除了药物治疗和手术治疗外,脊柱支具、物理治疗,运动疗法、中医中药疗法以及心理疏导,患者健康教育等都有着不可低估的作用。通过严格的试验审查和患者反馈,Spinomed脊柱支具被证实能够有效增强腹"
| [1] Maddigan SL, Majumdar SR, Toth EL,et al. Health-related quality of life deficits associated with varying degrees of disease severity in type 2 diabetes. Health and quality of life outcomes.2003;1:78. [2] Hayashi Y. Bone diseases with Pain. Osteoporosis. Clinical calcium.2007;17(4):606-612. [3] 中国人骨质疏松症建议诊断标准(第二稿)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2000,6(1):1-3. [4] Malmros B, Jensen MB, Charles P,et al.Effect of specific physiotherapy on chronic pain, functional level and quality of life in osteoporosis. A prospective randomized single-blind placebo-controlled study. Ugeskrift for laegerl.1999;161(33): 4636-4641. [5] 周谋望.骨质疏松性骨痛的治疗[C].南京:中华医学会第九次全国物理医学与康复学学术会议论,2007. [6] 夏仁云,李光辉.重视骨质疏松性骨痛的治疗与研究(一)[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2011,17(10):577. [7] 邓伟民,邵玉.瘀血学说在原发性骨质疏松症治疗中的指导作用[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(23):164-165. [8] 王晓磊,别还兵.补肾健脾、养胃活血法治疗原发性骨质疏松性骨痛33例[J].中国中医急症, 2013,22(4):623-624. [9] 陈希,何铭涛,梁祖建,等.补肾健脾活血方治疗骨质疏松性腰痛的体会[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2008,14(9):683-683. [10] Gruber H, Farley S, Baylink D. Predictions on future diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis: results and discussion of a recent opinion poll. Calcified tissue international. 1995;57(2): 83-85. [11] Feng X. Regulatory roles and molecular signaling of TNF family members in osteoclasts. Gene.2005;350(1):1-13. [12] Luoma K, Riihimaki H, Luukkonen R,et al. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine. 2000;25(4): 487-492. [13] 陈柏龄,黎艺强,谢登辉. TNF-α在骨质疏松性疼痛中的作用[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(10):1931-1935. [14] Uebelhart B, Rizzoli R. Osteoporosis and pain or is osteoporosis painful? Revue Medicale Suisse. 2005;1(25): 1662-1665. [15] 林秋喜.质疏松的药物治疗[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版, 2006, 23(z1):163-164. [16] 杜瑞琴,詹志伟,胡肇衡,等.鲑鱼降钙素(考克)治疗骨质疏松性骨痛的疗效评价[J].中国新药杂志, 2005,14(10):1221-1224. [17] Lyritis GP, Paspati I, Karachalios T, et al. Pain relief from nasal salmon calcitonin in osteoporotic vertebral crush fractures. A double blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl.1997;275:112-114. [18] 彭松云,易洪城,唐良华.鲑鱼降钙素,仙灵骨葆联合干扰电流治疗骨质疏松性疼痛26例[J].中国老年学杂志, 2013,33(16): 4023-4024. [19] 包丽华,林华,李建华,等.二膦酸盐治疗对骨质疏松性骨痛、骨密度、骨强度的疗效及安全性评价[J].中华老年医学杂志, 2003, 22(11):659-662. [20] 丁远远,崔健君,周凤华.静脉应用双膦酸盐治疗原发骨质疏松痛[J].实用药物与临床, 2010,13(2):109-110. [21] Black DM, Delmas PD, Eastell R, et al. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2007 ;356(18):1809-1822. [22] Francis RM, Aspray TJ, Hide G, et al. Back pain in osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA. 2008;19(7):895-903. [23] 朱秀英,张延桥,裴丽春,等.钙三醇、依替膦酸二钠、枸橼酸钙联合应用对骨质疏松性脊椎骨折患者骨痛及骨密度的影响[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(24):5182-5183. [24] 宰衷静.固邦联合金乌骨通胶囊治疗骨质疏松性腰背疼痛[J].中医正骨,2009,21(5):53-54. [25] Genant HK, Halse J, Briney WG,et al. The effects of teriparatide on the incidence of back pain in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2005;21(7): 1027-1034. [26] 陈大伟,熊昌源.骨痹汤治疗原发性骨质疏松症腰背痛疗效观察[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2011,17(11):656-657,669. [27] 王卫平,刘志松.经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松压缩性骨折缓解疼痛的观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2007,22(1):65-66. [28] 王晶,李贵涛,孙鸿涛,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折疼痛疗效分析[J].国际骨科学杂志,2012,33(6):410-412. [29] 周华乔,谢光明,李亮,等.经皮椎体成形术与小针刀联合治疗老年骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折疼痛的临床研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2013,22(10):1092-1093. [30] 李卉,顾一峰,李永东,等.比较经皮椎体成形术与保守治疗对慢性疼痛性骨质疏松性椎体骨折患者疗效的非随机前瞻性试验[J]. 介入放射学杂志,2012,21(11):921-926. [31] 韩松辉,胡沛.经皮椎体成形术改善骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者的疼痛症状[J].中国临床康复, 2003,7(32):4423-4423. [32] 俞国成,李坚,谢垒,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折所致腰背部疼痛疗效分析[J].中国医师进修杂志, 2009,32(5): 4-6. [33] 王海蛟,王齐超,李玉伟,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗老年性骨质疏松性椎体骨折所致腰背疼痛[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2003,13(6): 361-363. [34] 刘宏建,杜靖远,韩松辉,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗疼痛性骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2004,33(4): 481-484. [35] 甄建壮,黄向东,乔颖.经皮椎体成形术治疗中老年性椎体骨折所致疼痛的临床探讨[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2007,25(4):473- 475. [36] Shen WJ, Shen YS. Nonsurgical treatment of three-column thoracolumbar junction burst fractures without neurologic deficit. Spine.1999;24(4):412-415. [37] 倪才方,吴春根,杨惠林.脊柱介入诊疗学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2009:146-148. [38] 阮良峰,陈源,马俭凡,等.经皮椎体成形术与经皮椎体后凸成形术相关并发症的防治探讨[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(11):32-34. [39] Ledlie JT, Renfro MB. Kyphoplasty treatment of vertebral fractures: 2-year outcomes show sustained benefits. Spine. 2006;31(1):57-64. [40] 方秀统,于方,付胜良,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年人骨质疏松性脊柱压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中华医学杂志,2013,93(33): 2654-2658. [41] 陈升浩,彭昊.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].临床外科杂志, 2014,22(3):192-194. [42] Wardlaw D, Cummings SR, Van Meirhaeghe J, et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet.2009;373(9668):1016-1024. [43] Klazen CA, Lohle PN, de Vries J, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet.2010;376(9746):1085-1092. [44] Wong CC, McGirt MJ. Vertebral compression fractures: a review of current management and multimodal therapy. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2013;6:205-214. [45] Eck JC, Nachtigall D, Humphreys SC, et al.Comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the literature. Spine J. 2008;8(3):488-497. [46] Pfeifer M, Begerow B, Minne HW. Effects of a new spinal orthosis on posture, trunk strength, and quality of life in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized trial. American journal of physical medicine & rehabilitation. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;83(3):177-186. [47] 高堪达,俞永林,蒯大禹,等.低频脉冲电磁场对原发性骨质疏松症患者骨痛、骨密度及骨代谢指标的影响[J].中国临床康复, 2004, 8(27):5913-5915. [48] 邵礼仙.低强度脉冲电磁场治疗骨质疏松症患者的疗效观察及护理[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2006,15(17):2418-2419. [49] 谢小波,崔红岩,庞丽云,等.脉冲电磁场用于治疗骨质疏松性疼痛的疗效评估及分析[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2011,34(2): 107-110. |
| [1] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [2] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [3] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [6] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [7] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [8] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [9] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [10] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [11] | Wu Gang, Chen Jianwen, Wang Shilong, Duan Xiaoran, Liu Haijun, Dong Jianfeng. Simple HyProCure subtalar stabilization in treatment of adolescent flexible flatfoot combined with painful accessory navicular bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| [12] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [13] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [14] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [15] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||