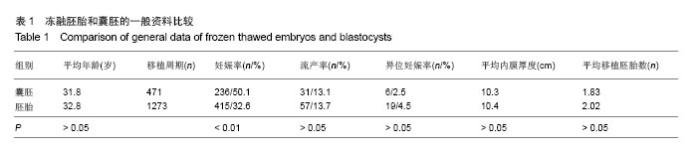
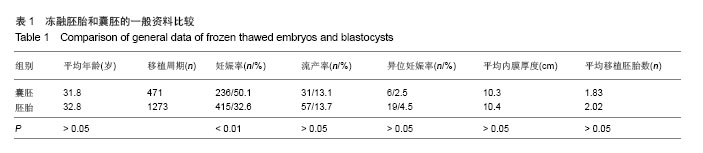
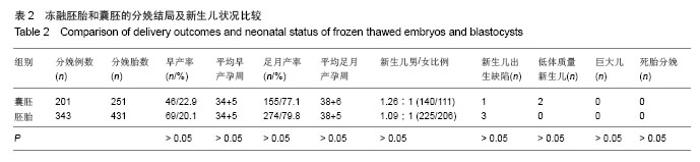
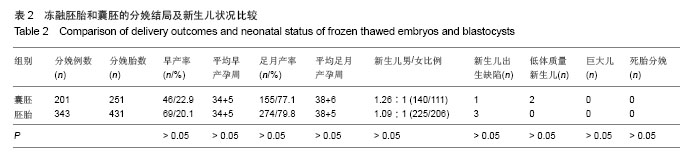
| [1]Trounson A,Mohr L.Human pregnancy following cryopreservation,thaw and transfer of an eight-cell embro. Nature. 1983;305(5936):707-709.
[2]Cohen J,Jones HW.How to avoid multiple pregnancies in assistive reproductive technologies.Semin Reprod Med. 2001; 19(3):269-278.
[3]Anderson AR,Wilkinson SS,Price S,et al. Reduction of high order multiples in frozen embryo transfers.Reprod Biomed Online.2005;0(3):402-405.
[4]Balaban B,Urman B,Ata B,et al.A randomized controlled study of human Day 3 embryo cryopresservation by slow freezing or vitrification :vitrification is associated with higher survival, metabolism and blastocyst formation.Hum Reprod.2008; 23(9): 1976-1982.
[5]冯贵雪,陈焕华,张波,等.玻璃化冷冻技术临床应用的安全性[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2014,(1):129-130.
[6]Thomas MR,Sparks AE,Ryan CL,et al.Clinical prediction of human blastocyst formation and pregnancy after extendedembryo culture and transfer.Fertil Steril.2010; 94(2): 543-548.
[7]Fanchin R,Ayoubi JM,Righini C,et al.Uterine contravtility decreases at the time of blastocyst transfers.Hum Reprod. 2001;16(6):105-109.
[8]Hartshome GM,Wick K,Elder K,et al.Effect of cell number at ferrzing upon survival and viability of cleaving embryos generated from stimulated IVF cycles. Hum Reprod.1990; 5(7):857-861.
[9]Archer J,Gook DA,Edgar DH.Blastocyst formation and cell numbers in human frozen-thawed embryos following extended culture. Hum Reprod.2003;18(8):1669-1673.
[10]Fanchin R,Ayoubi JM,Righini C,et al.Uterine contravtility decreases at the time of blastocyst transfers.Hum Reprod. 2001;16(6):105-109.
[11]周灿权. 诱发排卵与超排卵用药及监测[J].中国实用妇科与产科杂志,2001,17(1):78.
[12]Ku SY, Suh CS, Kim SH, et al. A pilot study of the use of low dose human menopausal gonadotropin in ovulation induction. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.2003; 109(1): 55-59.
[13]Filicori M, Cognigni GE, Pocognoli P, et al. Comparison of controlled ovarian stimulation with human menopausal gonadotropin or recombinant folliclestimulating hormone. Fertil Steril.2003;80(2):390-397.
[14]Kolibianakis E, Bourgain C, Albano C, et al. Effect of ovarian stimulation with recombinant folliclesimulating hormone, gonadotropin releasing hormone anragonists, and human chorionic gonadotropin on endometrial maturation on the day of oocyte pickup. Fertil Steril.2002; 78(5):1025-1029.
[15]Filicori M. Use of luteinizing hormone in the treatment of infertility: time for reassessment.Fertil Steril.2003;9(2): 253-255.
[16]Filicori M, Cognigni GE. Clinical review 126: roles and novel regiments of luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone in ovulation induction. Clin Endocrinol Metab.2001; 86(1):1437-1441.
[17]Davis OK, Rosenwaks Z. Superovulation strategies for assisted reproductive technologies. Semin Reprod Med.2001; 19(3):207-212.
[18]Hsieh Y, Tsai H, Chang C, et al. Comparison of a single halfdose, longacting form of gonadotropinreleasing hormone analog(GnRHa) and a shortacting form of GnRHafor pituitary suppression in a controlled ovarian hyperstimulation program. Fertil Steril.2010;73(4):817-820.
[19]龙晓林.辅助生育技术中的控制性超排卵[J].实用医学杂志, 2002, 18(3):224-226.
[20]孙捷,陈厚仰,黄志辉,等.126例梗阻性无精子症借助ICSI治疗的临床结局分析[J].中国医学创新,2011,8(23):7-9.
[21]唐文豪,姜辉,马潞林,等.男性不育患者精子形态学分析生殖激素关系的研究[J].中华男科学杂志,2012,18(3):243-247.
[22]田丰丰,张玲,周友泉.精子形态与活率及活力关系探讨[J].检验医学与临床,2009,6(21):1816-1818.
[23]周吉海.男性不育症治疗的研究进展[J].国外医学计划生育分册,1998,11(4):206-209.
[24]罗汉宏,杨建华.精液常规在男性不育诊断中的重要作用[J].中国男科学杂志,2001,15(3):214-216.
[25]Gardner DK,Lane M,Stevens J,et al.Blastocyst score affects implantion and pregnanccy outcome:towards a single blastocyst transfer.Fertil Steril.2000;73(6):1155-1158.
[26]Ma WH,Yang X,Liang XY.Obesity does not aggravate vitrification injury in mouse embryos: a prospective study. Reprod Bio Endocrin.2012;10(8):68-68.
[27]岳超敏,方丛,宫晓,等.囊胚解冻过夜培养后移植对妊娠结局的影响[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2013,34(3):415-421.
[28]Vajta G,Nagy ZP.Are progeammable freezers still needed in the embryo laboratory? Review on vitrification.Reprod Biomed Online.2006;12:779-796.
[29]夏凡,李青旺.哺乳动物胚胎冷冻技术研究进展[J].家畜生态, 2012, 25(3):50-53.
[30]Whittingham DG.Survival of mouse embryos frozen to -196℃ and -269℃.Science.1972;178-411.
[31]Willadsen SM.Factor affecting the survival of sheep embryos during deepfreezing and thawing.The Freezing of Mammalian Embryos.1977:175-200
[32]Rall WF,Fahy GM.Ice-free cryopreservation of mouse embryos at-196℃ by Vitrification.Nature.1985;313:573-575.
[33]徐勇,张嘉保.哺乳动物胚胎超低温冷冻保存的研究进展[J].黑龙江,黑龙江动物繁殖,2010,19(1):15-17.
[34]严云勤,李光鹏,郑小民.发育生物学原理与胚胎工程[M].哈尔滨:黑龙江科学出版社,1995.
[35]Obersrein,N.Cryopreservationofequineembryosbyopenpulledstraw.Cryoloop,or conven-tionalslowcoolingmetholds. Therigenology.2001;55:607-613.
[36]赵静,孟轲音,王宏志,等.哺乳动物胚胎冷冻保存研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2007,28(10):95-97.
[37]Kuwayama M.Highly efficient vitrification for cryopreservation of human oocytes and embryos:thecryotop method. Theriogenology.2007;67:73-80.
[38]Kumasako Y,Kumon JY,Gilbert L.Succesful pregnancy after the vitrification of zygotes using commercial vitrification solution and conventionalstraws to protect against infections in liquid nitrogen.J Assist Reprod Genet.2005;22:33-35.
[39]Zhu GJ,Jin L,Zhang HW,et al.Vitrification of human cleaved embryos in vitro fertilizaton-embryo transfer.Chinese Journal of Obstetetrics and Gynecology, 2005;40(10):682-684.
[40]Youssry M,Ozmen B,Zohni K,et al.Current aspects of blastocyst cryopreservation.Reprod Biomed Online.2008;16: 311-320.
[41]王宁怡,孙晓溪,鹿朱娣,等.影响冻融胚胎发育潜能及妊娠结局因素的探讨[J].生殖与避孕,2012,32(8):533-539.
[42]甑璟然,孙正怡,邓成艳,等.玻璃化冷冻囊胚复苏移植与新鲜胚胎移植的围产期状况比较[J].生殖医学杂志,2009,4(18):86-89.
[43]Takahashi K,Mukaida T,Goto T,et al.Perinatal outcome of blastocyst transfer with vitrification using cryoloop:a 4-year follow-up study.Fertil Steril.2005;84(1):88-91.
[44]Thomas MR,Sparks AE,Ryan CL,et al.Clinical prediction of human blastocyst formation and pregnancy after extendedembryo culture and transfer.Fertil Steril.2010;94(2): 543-548.
[45]Milki AA,Jun SH,Hinckley MD,et al.Comparison of the sex ratio with blastocyst transfer and cleavage stage transfer.J Assist Reprod Genet.2003;2098:323-326.
[46]王宇峰,于春梅,杨海燕,等.程序化冷冻与玻璃化冷冻卵裂期胚胎移植的母婴结局对照分析[J].生殖医学杂志,2014,23(1):11-15.
[47]甄璟然,王雪,孙正怡,等.复苏单囊胚移植周期中囊胚形态学评分对临床妊娠的影响[J].生殖医学杂志,2014,23(1):7-10.
[48]孙林,罗海娇,鄢磊,等.IVF/ICSI-ET技术中单卵双胎的发生及其相关因素[J].生殖与避孕,2014,34(1):27-35.
[49]耿洁,胡玉琴,刘兰兰,等.卵子玻璃化冷冻在体外受精-胚胎移植取精失败周期中的应用[J].实用医院临床杂志,2014,11(1): 156-157.
[50]杨静仪,黄赛君.辅助生殖技术出生儿的智能发育调查研究[J].中国妇幼保健,2014,29(6):913-914.
[51]王玮,曹金凤,滑天,等.两种内膜准备方案在多囊卵巢综合征患者冻融胚胎移植中的应用[J].中国妇幼保健,2014,29(1):94-96.
[52]王晓慧.胚胎干细胞的冻存复苏及其自发分化培养时上皮间质转化过程的研究[D].镇江:江苏大学,2013.
[53]曹森杨,李采霞,温开群,等.影响冷冻胚胎解冻后移植妊娠率的因素分析[J].医学信息,2014,13:507-508.
[54]王芳,陈绍威.体外受精-胚胎移植的助孕效果:胚胎体外培养和低温保存[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18):2939-2944.
[55]李城,李梅,马水英,等.不同发育天数冻融单囊胚移植的临床结局比较[J].现代妇产科进展,2014,23(2):121-123.
[56]侯艳琼,罗红.三维超声对人工周期冷冻胚胎复苏移植结局的预测价值[J].四川医学,2014,4:428-429,430.
[57]李游,伍琼芳,易迎春.超长方案降调节对多囊卵巢综合症不孕患者行IVF结局的影响[J].江西医药,2014,2:117-120. |