Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (22): 3597-3602.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.22.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Telemedicine in orthopedics: a Web of Science-based literature analysis
Zhai Yun-kai1, 2, Zhu Wei-jun1, Sun Dong-xu1, 2, Zhao Jie1
- 1The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Engineering Research Center of Digital Medicine, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-02-17Online:2014-05-28Published:2014-05-28 -
Contact:Zhao Jie, Doctor, Professor, Master’s supervisor, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhai Yun-kai, Doctor, Associate professor, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China; Henan Engineering Research Center of Digital Medicine, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the "Huimin Project" Special Funds from Ministry of Science and Technology of China, No. 2013GS410101; the Science and Technology Major Projects of Henan Province, No.121100111100
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhai Yun-kai, Zhu Wei-jun, Sun Dong-xu, Zhao Jie. Telemedicine in orthopedics: a Web of Science-based literature analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(22): 3597-3602.
share this article
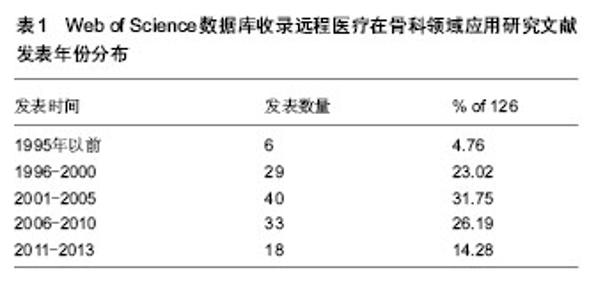
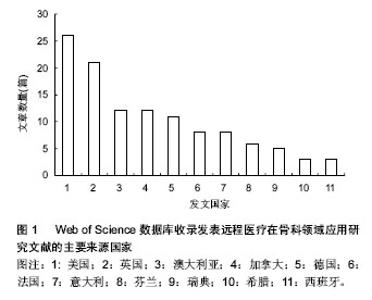
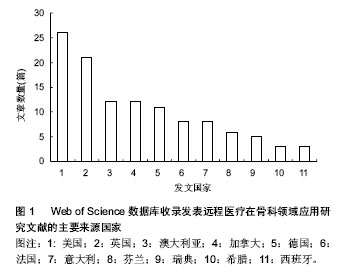
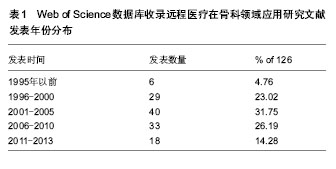
2.1 Web of Science数据库收录远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究文献的数量分析 在165篇远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究的文献中,研究原著126篇,会议录29篇,书评6篇,综述5篇,笔记2篇,会议摘要2篇,其他2篇。其中,研究原著所占的比例较大,占文献总数的76.36%,远远多于其他类型的文献,其次是会议录,占文献总数的18.18% (因有会议记录可能作为研究原著发表再次收录,所以文献类型的文献总量大于检索到的文献总量)。 2.2 Web of Science数据库收录远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究文献发表年份分布 见表1。 在SCI数据库检索到远程医疗在骨科领域的应用最早的文献发表于1993年,表明其是一个新兴的领域。到了21世纪以后,随着计算机网络的飞速发展,远程医疗的稿件也大量增加,在21世纪最初的10年间,远程医疗在骨科领域发表了73篇文献,约占总发表文献量的60%。说明远程医疗在骨科领域的研究已得到广泛的认识。 2.3 Web of Science数据库收录远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究文献的来源国家情况 见图1。 远程医疗在骨科领域的研究分布国家较广,从数量来看,美国的研究文献篇数最多,为26篇,占总文献量的20.63%,其次为英国及澳大利亚和加拿大。在排名前10位的远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究文献中,没有亚洲国家发表的稿件。"
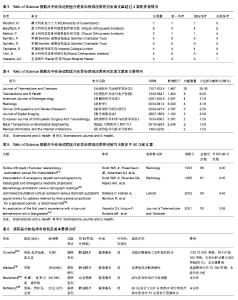
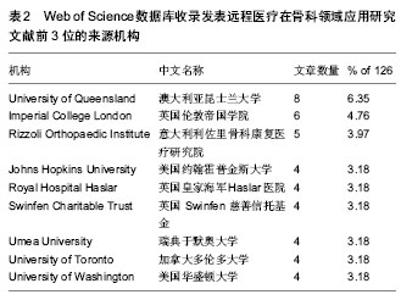
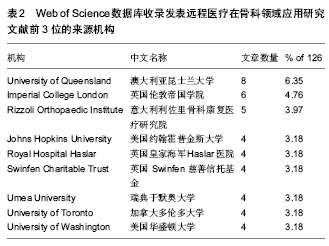
2.5 Web of Science数据库收录远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究的作者数量分析 见表3。 在126篇文献中,澳大利亚昆士兰大学(University of Queensland)的Wootton R,意大利利佐里骨科康复医疗研究院 (Rizzoli Orthopaedic Institute)的Baruffaldi F及Mattioli P作者发表文献以7篇,6篇,5篇分别列于前3位。 其中,意大利利佐里骨科康复医疗研究院创建于1896年,是世界著名的骨科专科医院,也是最早提供骨科远程会诊的医院之一。远程会诊服务是由医院信息管理系统负责提供,以信息技术为基础建立的外部远距外科网络,该服务受限于国民医疗保健制度(包括保健站,医院及门诊诊所),涉及范围几乎囊括意大利全境。医院信息管理系统还提供国际联络服务,以使必要的远程会诊设备功能得以实现。患者需要提前在远程会诊系统进行预约,预约成功的患者可通过视频联系医师,该医师会向患者展示检查流程,并与患者直接交流。医师还会提供一份附有治疗建议的报告。 Swinfen慈善信托基金的远程医疗网络将发展中国家的卫生保健工作者与国际的咨询专家池连接起来。该网络总部设在英国,由完全的志愿者组织Swinfen慈善信托(SCT)运营管理。自从1999 年第一个远程医疗链接起,这个网络处于持续发展状态,至今已拥有60多个国家的193所转诊医院和诊所。Swinfen慈善信托网络每年接收大约250例转诊,转诊卫生保健工作者初始发布和咨询医生第一次响应之间的平均间隔时间为19-24 h。 2.6 Web of Science数据库中收录远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究的出版文献来源期刊分析 见表4。 2.7 Web of Science数据库中收录远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究的出版文献单篇论文被引情况分析 见表5。 2.8 Web of Science数据库中收录远程医疗在骨科领域应用研究的临床有效性及成本费用分析 见表6。"

| [1] WHO. A health telematics policy in support of WHO’s Health-For-All strategy for global health development: report of the WHO group consultation on health telematics, 11–16 December, Geneva, 1997. Geneva, World Health Organization, 1998. [2] Einthoven W. Le télécardiogramme [The telecardiogram]. Arch Int Physiol, 1906;4:132-164. [3] Craig J, Patterson V. Introduction to the practice of telemedicine. J Telemed Telecare. 2005;11(1):3-9. [4] Currell R, Urquhart C, Wainwright P, et al. Telemedicine versus face to face patient care: effects on professional practice and health care outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD002098. [5] Clayman RV. Transatlantic robot-assisted telesurgery. J Urol. 2002;168(2):873-874. [6] Froehlich W, Seitaboth S, Chanpheaktra N, et al. Case report: an example of international telemedicine success. J Telemed Telecare. 2009;15(4):208-210. [7] Mukundan S Jr, Vydareny K, Vassallo DJ, et al. Trial telemedicine system for supporting medical students on elective in the developing world. Acad Radiol. 2003;10(7): 794-797. [8] Viñals F1, Mandujano L, Vargas G, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease using four-dimensional spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC) telemedicine via an Internet link: a pilot study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005; 25(1):25-31. [9] Heinzelmann PJ, Jacques G, Kvedar JC. Telemedicine by email in remote Cambodia. J Telemed Telecare. 2005;11 Suppl 2:S44-47. [10] Latifi R, Merrell RC, Doarn CR, et al. "Initiate-build- operate-transfer"--a strategy for establishing sustainable telemedicine programs in developing countries: initial lessons from the balkans. Telemed J E Health. 2009;15(10):956-969. [11] Chanussot-Deprez C1, Contreras-Ruiz J. Telemedicine in wound care. Int Wound J. 2008;5(5):651-654. [12] Vassallo DJ, Hoque F, Roberts MF, et al. An evaluation of the first year's experience with a low-cost telemedicine link in Bangladesh. J Telemed Telecare. 2001;7(3):125-138. [13] Vassallo DJ, Swinfen P, Swinfen R, et al. Experience with a low-cost telemedicine system in three developing countries. J Telemed Telecare. 2001;7 Suppl 1:56-58. [14] Wallace DL, Jones SM, Milroy C, et al. Telemedicine for acute plastic surgical trauma and burns. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61(1):31-36. [15] Jones SM, Milroy C, Pickford MA. Telemedicine in acute plastic surgical trauma and burns. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2004; 86(4):239-242. [16] Gardiner S, Hartzell TL. Telemedicine and plastic surgery: a review of its applications, limitations and legal pitfalls. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65(3):e47-53. [17] Roa L, Gómez-Cía T, Acha B, Serrano C. Digital imaging in remote diagnosis of burns. Burns. 1999;25(7):617-623. [18] Knobloch K, Rennekampff HO, Vogt PM. Cell-phone based multimedia messaging service (MMS) and burn injuries. Burns. 2009;35(8):1191-1193. [19] Saffle JR, Edelman L, Theurer L, et al. Telemedicine evaluation of acute burns is accurate and cost-effective. J Trauma. 2009;67(2):358-365. [20] Warshaw EM, Lederle FA, Grill JP, et al. Accuracy of teledermatology for pigmented neoplasms. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61(5):753-765. [21] Scott WW Jr, Rosenbaum JE, Ackerman SJ, et al. Subtle orthopedic fractures: teleradiology workstation versus film interpretation. Radiology. 1993;187(3):811-815. [22] Scott WW Jr, Bluemke DA, Mysko WK, et al. Interpretation of emergency department radiographs by radiologists and emergency medicine physicians: teleradiology workstation versus radiograph readings. Radiology. 1995;195(1):223-229. [23] Wallace P, Haines A, Harrison R, et al. Joint teleconsultations (virtual outreach) versus standard outpatient appointments for patients referred by their general practitioner for a specialist opinion: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359(9322):1961- 1968. [24] Vassallo DJ, Hoque F, Roberts MF, et al. An evaluation of the first year's experience with a low-cost telemedicine link in Bangladesh. J Telemed Telecare. 2001;7(3):125-138. [25] Crowther JB, Poropatich R. Telemedicine in the U.S. Army: case reports from Somalia and Croatia. Telemed J. 1995;1(1): 73-80. [26] Wallace DL, Smith RW, Pickford MA. A cohort study of acute plastic surgery trauma and burn referrals using telemedicine. J Telemed Telecare. 2007;13(6):282-7. [27] Houtchens BA, Clemmer TP, Holloway HC, et al. Telemedicine and international disaster response. Medical consultation to Armenia and Russia via a Telemedicine Spacebridge. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1993;8(1):57-66. [28] McManus J, Salinas J, Morton M, et al. Teleconsultation program for deployed soldiers and healthcare professionals in remote and austere environments. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2008;23(3):210-6; discussion 217. [29] Scerri GV, Vassallo DJ. Initial plastic surgery experience with the first telemedicine links for the British Forces. Br J Plast Surg. 1999 Jun;52(4):294-8. [30] Tangtrakulwanich B, Kwunpiroj W, Chongsuvivatwong V, et al. Teleconsultation with digital camera images is useful for fracture care. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;449:308-312. [31] Syed TA,Sadiq Z, Shah YR, et al. Role of mobile multimedia messaging service (MMS) in trauma and orthopaedic telediagnosis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2007; 17: 603-607. [32] Bertani A, Launay F, Candoni P, et al. Teleconsultation in paediatric orthopaedics in Djibouti: evaluation of response performance. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(7): 803-807. [33] Archbold HA, Guha AR, Shyamsundar S, et al. The use of multi-media messaging in the referral of musculoskeletal limb injuries to a tertiary trauma unit using: a 1-month evaluation. Injury. 2005;36(4):560-566. [34] Jacobs MJ, Edmondson MJ, Lowry JC. Accuracy of diagnosis of fractures by maxillofacial and accident and emergency doctors using plain radiography compared with a telemedicine system: a prospective study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002 Apr;40(2):156-162. [35] Seemann R, Guevara G, Undt G, et al. Clinical evaluation of tele-endoscopy using UMTS cellphones. Surg Endosc. 2010 Nov;24(11):2855-2859. [36] Korim M, Soobrah R, Hull P. To admit or not: The use of a camera mobile phone in trauma and orthopaedics at night in a UK hospital. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2009;19:217-221. [37] 王军强,赵春鹏,胡磊,等.远程外科机器人辅助胫骨髓内钉内固定系统的初步应用[J].中华骨科杂志.2006;26(10):682-686. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||