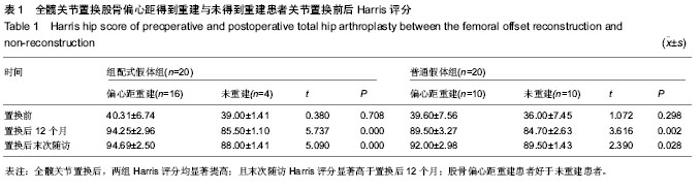
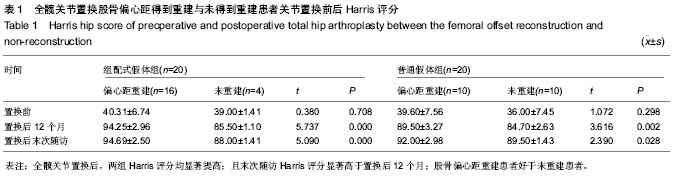
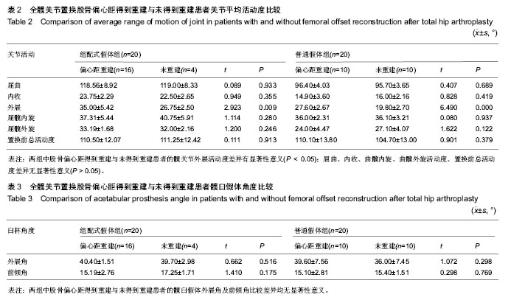
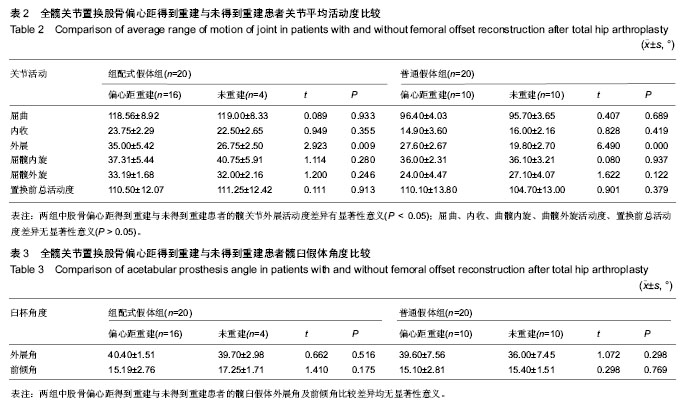
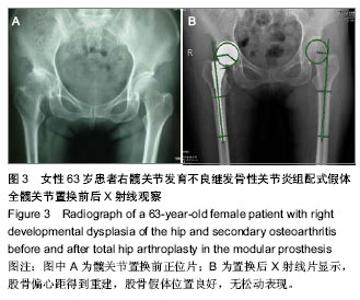
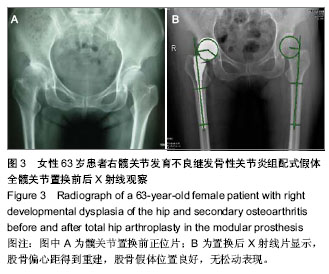
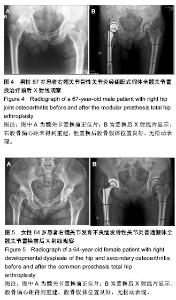
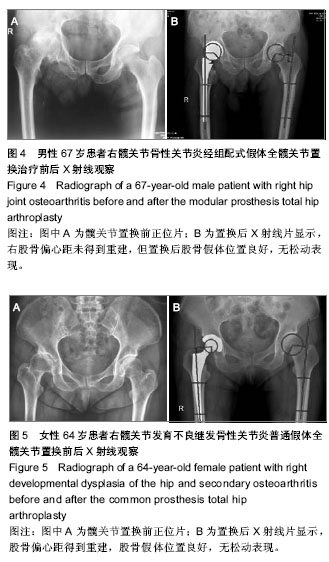
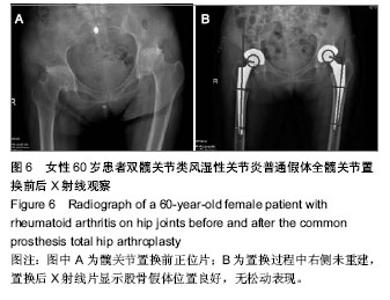
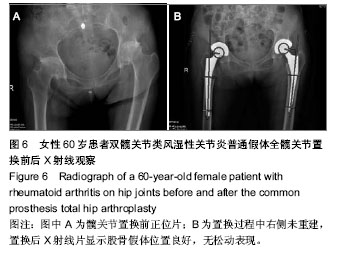
| [1] Jolles BM, Zangger P, Leyvraz PF. Factors predisposing to dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty :a multivariate analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(3):282-288. [2] Sakalkale DP, Sharkey PF, Eng K, et al. Effect of femoral component offset on polyethylene wear in total hip arthroplsty. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2001;388:125-134.[3] Dorr LD, Wan Z. Causes of and treatment protocal for instability of total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;355(6):144-151.[4] Barrack RL, BuraK C, Skinner HB. Concerns about ceramics in THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2004;429(4):73-79.[5] Cannestra VP, Berger RA, Quigley LR, et al.Hybrid total hip arthroplasty with a precoated offset stem. Four to nine-year results. J Bone Joint Surg AM.2000;82(9):1291-1299.[6] Kleemann RU, Heller MO, Stoeckle U, et al. THA loading arising from in creased femoral anterversion and offset m ay lead to critical cement stresses. J Orthop Res.2003; 21(5): 767-774.[7] Soong M,Rubash HE,Macaulay W.Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004;12(5):314-321.[8] Bourne BR, Rorabeck CH.Soft tissue balancing:the hip. J Arthroplasty.2002;17 (4Suppl):17-22.[9] 周一新.骨科标准新突破手术技术指导规范-《人工髋、膝关节置换术》解读[J].中国卫生标准管理,2011,2(04):72-74.[10] Conn KS, Clarke MT, Hallett JP.A simple guide to determine the magnification of radiographs and to improve the accuracy of preoperative templating. J Bone Joint Surg.2002;84(2): 269-272.[11] Nunn D, Freeman MAR, Hill PF, et al. The measurement of migration of the acetabular component of hip prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg. 1989;71(4):629-631.[12] Murray DW. The definition and measurement of acetabular orientation.J Bone Joint Surg . 1993;75(2):228-232.[13] Woo RY, Morrey BF. Dislocations after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg [Am].1982;64(9):1295-1306.[14] 张晖,裴福兴,杨静,等.混合型全髋关节置换术治疗股骨头缺血性坏死中期评估[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(8):590-595.[15] Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. The revision hip. Cemented stem revision: Less we forget. Orthopaedics.2003;26(9):933-934.[16] Sotereanos NG, Sauber TJ, Tupis TT. Modular femoral neck fracture after primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(1):196.e7-9.[17] Michael JA, Tamara C, Joshua C, et al.A Comparison of Two Implant Systems in Restoration of Hip Geometry in Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(2):443-446.[18] 史振才,李子荣,介国斌,等.全髋关节置换术的软组织平衡[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(4):306-309.[19] 史振才,李子荣,介国斌,等.全髋人工关节置换术的肢体不等长[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(3):177-180. [20] 胡弘,夏军. 偏心距重建对股骨颈骨折关节置换术后恢复的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(8):711-714.[21] Manish D, Lawrence D. Dorr, Rupesh T, et al.Hip Offset in Total Hip Arthroplasty: Quantitative Measurement with Navigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(2):429-436.[22] Bartz RL, Nobel PC, Kadakia NR, et al. The effect of femoral component head size on posterior dislocation of the artificial hip joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(9):1300-1307. [23] 汤宇,孙天胜.股骨偏心距与全髋关节置换术后假体功能及相关生物力学的变化[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(33):133-135. |