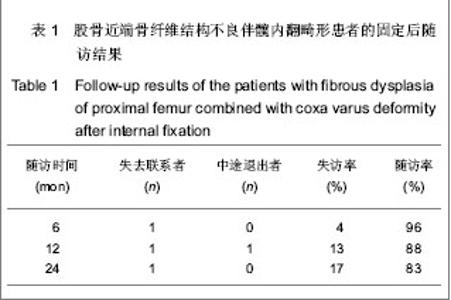
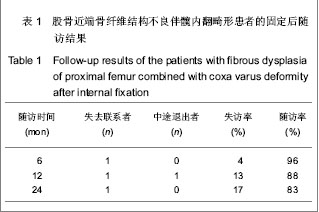
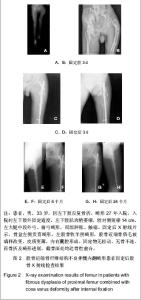
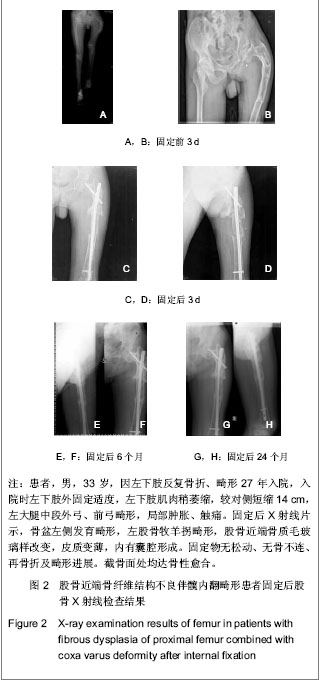
| [1] Stanton RP. Surgery for fibrous dysplasia. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21(Suppl 2):P105-109. [2] Stanton RP, Diamond L. Surgical management of fibrous dysplasia in McCune-Albright syndrome. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2007;4(Suppl 4):446-452.[3] Corsi A, Collins MT, Riminucci M , et al. Osteomalacic and hyperparathyroid changes in fibrous dysplasia of bone:core biopsy studies and clinical correlation. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(7):1235-1246.[4] Chapurlat RD, Delmas PD, Liens D, et al. Long-term effects of intravenous pamidronate in fibrous dysplasia of bone. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12(10):1746-1752.[5] Kelly MH, Brillante B, Collins MT. Pain in fibrous dysplasia of bone: age-related changes and the anatomical distribution of skeletal lesions. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19(1):57-63.[6] Chapurlat RD, Hugueny P, Delmas PD, et al. Treatment of fibrous dysplasia of bone with intravenous pamidronate: long-term effectiveness and evaluation of predictors of response to treatment. Bone. 2004;35(1):235-242.[7] Chapurlat RD, Gensburger D, Jimenez-Andrade JM, et al. Pathophysiology and medical treatment of pain in fibrous dysplasia of bone. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012;7(Suppl 1):S3.[8] Plotkin H, Rauch F, Zeitlin L, et al. Effect of pamidronate treatment in children with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(10):4569-4575.[9] Stanton RP, Ippolito E, Springfield D, et al. The surgical management of fibrous dysplasia of bone. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012,7(Suppl 1):S1.[10] Lppolito E, Bray EW, Corsi A, et al. Natural history and treatment of fibrous dysplasia of bone: a multicenter clinicopathologic study promoted by the European Pediatric Orthopaedic Society. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2003;12(3): 155-177.[11] Muller ME, Allgower M. Guke Neiguding. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House. 1998.[12] Ozaki T, Hillmann A, Bettin D, et al. Intramedullary, antibioticloaded cemented, massive allografts for skelet al reconstruction. 26 cases compared with 19 uncemented allografts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1997;68(4):387-391.[13] Guille JT, Kumar SJ, MacEwen GD. Fibrous dysplasia of the proximal part of the femur. Long-term results of curettage and bone-grafting and mechanical realignment. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1998;80(5):648-658.[14] Niu XH, Wang Z, Huang YT, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 1998;5(4):329.牛晓辉,王臻,黄耀添,等.98例四肢骨纤维结构不良临床分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,1998,5(4):329.[15] Fu L, Jia JF, Cui XH. Linchuang he Shiyan Yixue Zazhi. 2010; 9(24):1878-1879.傅磊,贾俊峰,崔晓虎.交锁髓内针加自体骨移植治疗股骨骨纤维结构不良27例[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2010,9(24):1878-1879.[16] Zhonghua Yixuehui. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House. 2009.中华医学会.临床诊疗指南-骨科分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2009.[17] Xu ST, Ge BF, Xu YK. Beijing: People's Military Medical Press. 2012.胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].第4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2012.[18] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01.[19] Cui Y, Liu JG, Li SQ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(10):1905.崔岩,刘建国,李叔强,等.骨纤维结构不良的诊断和治疗进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(10):1905.[20] Zhang TH, Liao GQ. Zhonghua Kouqiang Yixue Yanjiu Zazhi (Dian Zi Ban). 2008;2(5):531.张同韩,廖贵清.骨纤维异常增殖症的研究进展[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2008;2(5):531.[21] Lu CZ. Zhonghua Yixuehui Diliuci Quanguo Guzhi Shusonghe Gukuangyan Jibing Xueshu Huiyi lunwen Huibian. Shumian Jiaoliu. 2011.鹿存芝.核素骨显像在骨纤维结构不良诊断中价值探讨[C].中华医学会第六次全国骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病学术会议论文汇编.书面交流.2011.[22] Di Caprio MR, Enneking WF. Fibrous dysplasia. Pathophysiology, evaluation and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(8):1848-1864.[23] Li T, Xing BB, Duan H, et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2009;(3):261-263.李涛,行斌斌,段宏,等.股骨近端骨纤维结构不良的外科治疗[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,(3):261-263. [24] Xu DF, Deng H. Jilin Yixue Zazhi. 2011;32(6):1164.许多富,邓珩,王礼.小儿骨纤维结构不良治疗体会[J].吉林医学, 2011,32(6):1164.[25] Meng P, Bi XY, Huang XJ. Shiyong Guke Zazhi. 2012; 18(2): 180-182.孟朋,毕晓英,黄相杰.降钙素和阿仑膦酸钠治疗骨纤维异常增殖症[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(2):180-182.[26] Li GD, Ogose A, Hotta T, et al. Long-term efficacy of oral alendronate therapy in an elderly patient with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia: A case report. Oncol Lett. 2011;2(6): 1239-1242.[27] Hai GD, Guo W, Ji T, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2010;18(1):26-29.海国栋,郭卫,姬涛,等.股骨近端骨纤维结构不良的外科治疗-一种分区方法[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(1):26-29.[28] Xu ST, Zhang LH, Zhu B, et al. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 2002; 40(7):555.胥少汀,张龙海,朱兵,等.肋骨移植治疗长骨纤维异样增殖症[J].中华外科杂志,2002,40(7):555. [29] Qiu GX, Dai KR. 3rd ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House. 2005.邱贵兴,戴克戎.骨科手术学[M].第3版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2005.[30] Zhang LH, Xu ST, Zhu B, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2002;10(11):1054-1056.张龙海,胥少汀,朱兵,等.四肢骨纤维异样增殖症的固定治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,10(11):1054-1056.[31] Xing BB, Tu CQ, Duan H, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2007;15(1):24-26.行斌斌,屠重棋,段宏,等.股骨纤维结构不良伴重度内翻畸形的外科治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(1):24-26.[32] Tong ZC, Wang KZ, Jiao N, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2011; 24(4):345-348.同志超,王坤正,焦宁,等.股骨近端纤维结构不良的固定治疗[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(4):345-348.[33] Zhu M, Fan DB, Wang X, et al. Zhongguo Guzhongliu Gubing. 2006;5(5):293-295.朱敏,凡道斌,王欣,等.股骨近端骨的纤维结构不良伴严重弯曲畸形的治疗方法探讨[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2006,5(5):293-295.[34] Leet AI, Collins MT. Current approach to fibrous dysplasia of bone and McCune–Albright syndrome. J Child Orthop. 2007; 1(1):3-17.[35] Shi W, Miao XM, Liu SC, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2010;18(2):100.石伟,苗旭漫,刘绍臣,等.经皮股骨近端交锁髓内针内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折(附180例报道)[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010, 18(2):100. |