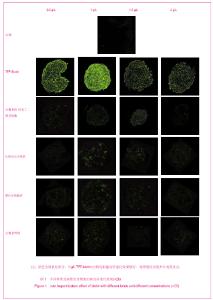
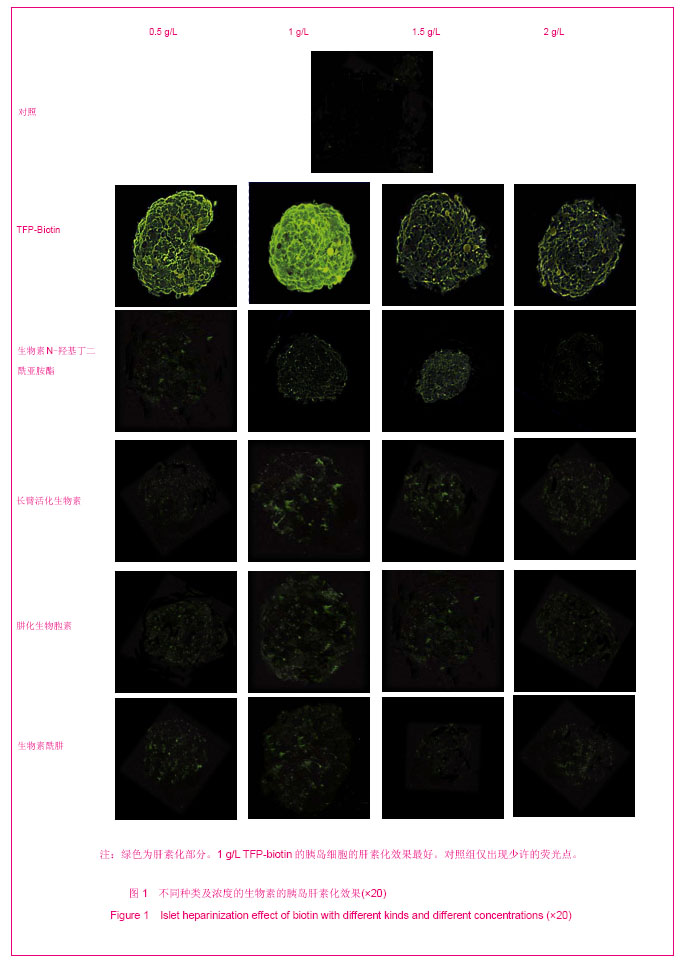
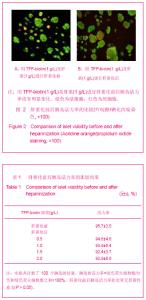
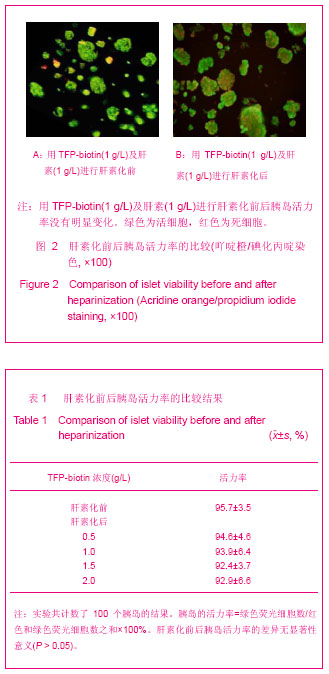
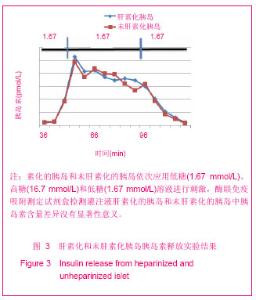
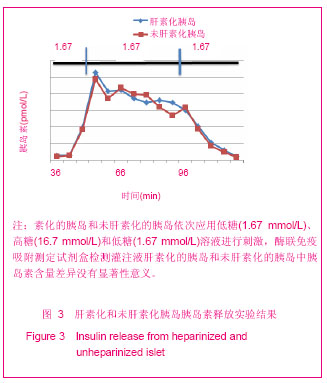
| [1] Brissova M, Powers AC. Revascularization of transplanted islets: can it be improved? Diabetes. 2008;57(9):2269-2271.[2] Hirsh J, Warkentin TE, Shaughnessy SG, et al. Heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin: mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, dosing, monitoring, efficacy, and safety. Chest. 2001;119(1 Suppl):64S-94S.[3] Kett WC, Osmond RI, Moe L, et al. Avidin is a heparin-binding protein. Affinity, specificity and structural analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1620(1-3):225-234.[4] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01. 中华人民共和国国务院.医疗机构管理条例. 1994-09-01.[5] Qi M, Barbaro B, Wang S, et al. Human pancreatic islet isolation: Part I: digestion and collection of pancreatic tissue. J Vis Exp. 2009;(27). pii: 1125. [6] Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(13):1318-1330. [7] Zwillich T. Diabetes research. Islet transplants not yet ready for prime time. Science. 2000;289(5479):531-533.[8] Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Paty BW, et al. Strategic opportunities in clinical islet transplantation. Transplantation. 2005;79(10): 1304-1307.[9] Trivedi N, Steil GM, Colton CK, et al. Improved vascularization of planar membrane diffusion devices following continuous infusion of vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell Transplant. 2000;9(1):115-124.[10] Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):669-676.[11] Schlessinger J, Plotnikov AN, Ibrahimi OA, et al. Crystal structure of a ternary FGF-FGFR-heparin complex reveals a dual role for heparin in FGFR binding and dimerization. Mol Cell. 2000;6(3):743-750.[12] Pellegrini L, Burke DF, von Delft F, et al. Crystal structure of fibroblast growth factor receptor ectodomain bound to ligand and heparin. Nature. 2000;407(6807):1029-1034. [13] Abelson JN, Simon MI, Wilchek M, et al. Avidin-Biotin Technology (Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 184). Waltham: Academic Press. 1990.[14] Askenasy N, Yolcu ES, Wang Z, et al. Display of Fas ligand protein on cardiac vasculature as a novel means of regulating allograft rejection. Circulation. 2003;107(11): 1525-1531.[15] He Z, Wang F, Kumagai-Braesch M, et al. Long-term gene expression and metabolic control exerted by lentivirus-transduced pancreatic islets. Xenotransplantation. 2006;13(3):195-203.[16] Zhang N, Schröppel B, Chen D, et al. Adenovirus transduction induces expression of multiple chemokines and chemokine receptors in murine beta cells and pancreatic islets. Am J Transplant. 2003;3(10):1230-1241.[17] Yang Y, Li Q, Ertl HC, et al. Cellular and humoral immune responses to viral antigens create barriers to lung-directed gene therapy with recombinant adenoviruses. J Virol. 1995; 69(4):2004-2015.[18] Chang TM. From artificial red blood cells, oxygen carriers, and oxygen therapeutics to artificial cells, nanomedicine, and beyond. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2012; 40 (3):197-199. [19] Kerby A, Bohman S, Westberg H, et al. Immunoisolation of islets in high guluronic acid barium-alginate microcapsules does not improve graft outcome at the subcutaneous site. Artif Organs. 2012;36(6):564-570. [20] Schneider S, Klein HH. Long-term graft function of cryostored alginate encapsulated rat islets. Eur J Med Res. 2011;16(9):396-400.[21] Vaithilingam V, Quayum N, Joglekar MV, et al. Effect of alginate encapsulation on the cellular transcriptome of human islets. Biomaterials. 2011;32(33):8416-8425. [22] Barkai U, Weir GC, Colton CK, et al. Enhanced Oxygen Supply Improves Islet Viability in a New Bioartificial Pancreas. Cell Transplant. 2012. in press.[23] Villiger P, Ryan EA, Owen R, et al. Prevention of bleeding after islet transplantation:lessons learned from a multivariate analysis of 132 cases at a single institution. Am J Transplant. 2005;5(12):2992-2998. |