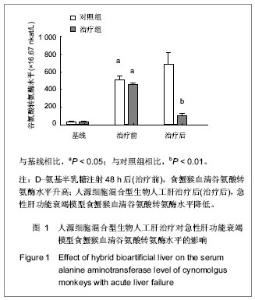
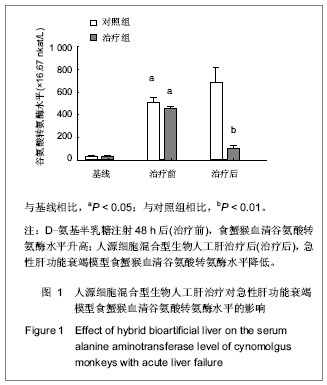
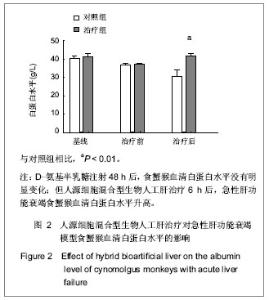
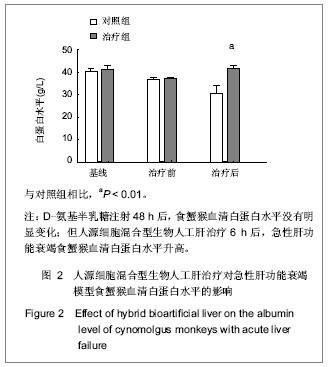
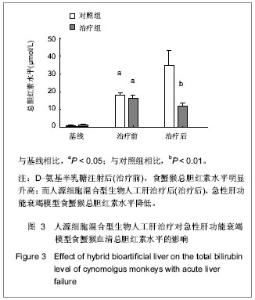
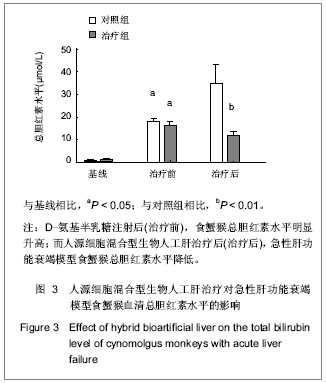
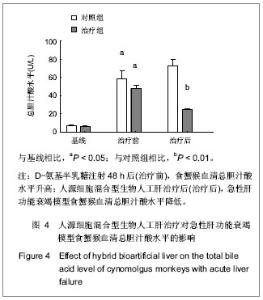
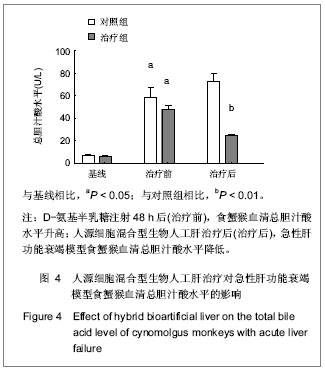
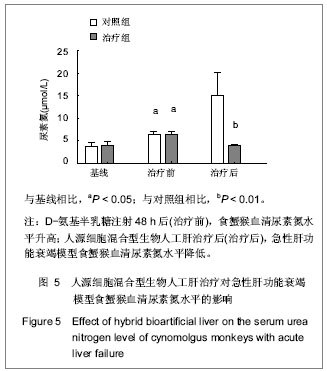
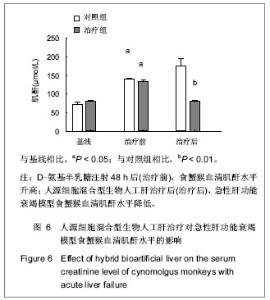
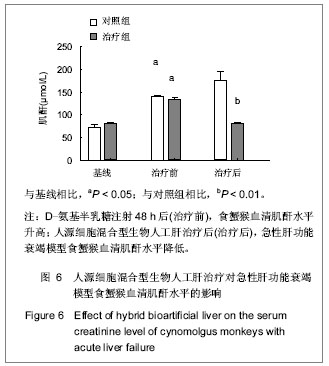
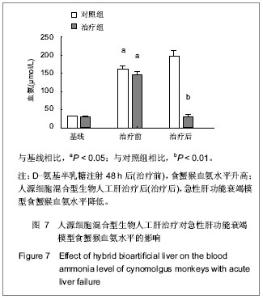
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (18): 3295-3302.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.18.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological metabolic function of the human liver cell line-1 used in bioartificial liver
Rao Xiao-hui, Jian Guo-deng, Zhang Zhi, Wang Yan, Pan Ming-xin, Gao Yi
- Second Department of Hepatology, Zhujang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2013-02-12Revised:2013-03-18Online:2013-04-30Published:2013-04-30 -
Contact:Pan Ming-xin, Doctor, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Professor, Second Department of Hepatology, Zhujang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China pmxwxy@sohu.com Gao Yi, Doctor, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Professor, Second Department of Hepatology, Zhujang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China gaoyi6164@163.com -
About author:Rao Xiao-hui★, Master, Second Department of Hepatology, Zhujang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China oulingjv@163.com -
Supported by:National High Technology Development Planning Project of China(863 Planning), No. 2006AA02A141
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Rao Xiao-hui, Jian Guo-deng, Zhang Zhi, Wang Yan, Pan Ming-xin, Gao Yi. Biological metabolic function of the human liver cell line-1 used in bioartificial liver[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(18): 3295-3302.
share this article
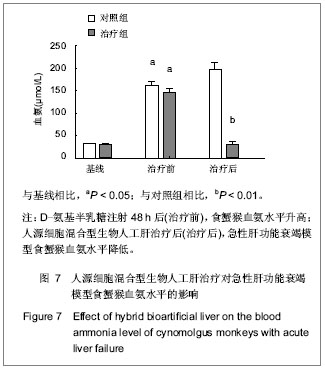
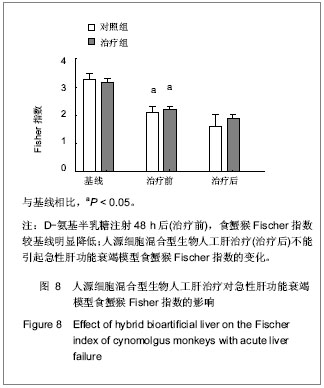
| [1] Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, et al. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2010;376(9736):190-201. [2] Bismuth H, Figueiro J, Samuel D. What should we expect from a bioartificial liver in fulminant hepatic failure? Artif Organs. 1998;22(1):26-31.[3] Xue YL, Zhao SF, Zhang ZY, et al. Effects of a bioartificial liver support system on acetaminophen induced acute liver failure canines. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5(4):308-311.[4] Rong YH, Liu HL, You SL, et al. Construction and experimental study on off-line hybrid bioartificial liver supporting system with human liver cell line. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2010;24(3): 193-195.[5] Shi XL, Zhang Y, Chu XH, et al. Evaluation of a novel hybrid bioartificial liver based on a multi-layer flat-plate bioreactor. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(28):3752-3760. [6] Pless G. Bioartificial liver support systems. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;640:511-523. [7] Miyoshi H, Ehashi T, Kawai H, et al. Three-dimensional perfusion cultures of mouse and pig fetal liver cells in a packed-bed reactor: effect of medium flow rate on cell numbers and hepatic functions. J Biotechnol. 2010;148(4): 226-232. [8] Dan YY, Yeoh GC. Liver stem cells: a scientific and clinical perspective. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23(5):687-698. [9] Schroeder IS, Wiese C, Truong TT, et al. Differentiation analysis of pluripotent mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells in vitro. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;530:219-250. [10] Fonsato V, Herrera MB, Buttiglieri S, et al. Use of a rotary bioartificial liver in the differentiation of human liver stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(1):123-132. [11] Tsiaoussis J, Newsome PN, Nelson LJ, et al. Which hepatocyte will it be? Hepatocyte choice for bioartificial liver support systems. Liver Transpl. 2001;7(1):2-10.[12] Nyberg SL, Remmel RP, Mann HJ, et al. Primary hepatocytes outperform Hep G2 cells as the source of biotransformation functions in a bioartificial liver. Ann Surg. 1994;220(1):59-67.[13] Nagaki M, Miki K, Kim YI, et al. Development and characterization of a hybrid bioartificial liver using primary hepatocytes entrapped in a basement membrane matrix. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46(5):1046-1056.[14] Dixit V. Development of a bioartificial liver using isolated hepatocytes. Artif Organs. 1994;18(5):371-384.[15] Rozga J, Morsiani E, Lepage E, et al. Isolated hepatocytes in a bioartificial liver: A single group view and experience. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1994;43(7):645-653.[16] Poyck PP, van Wijk AC, van der Hoeven TV, et al. Evaluation of a new immortalized human fetal liver cell line (cBAL111) for application in bioartificial liver. J Hepatol. 2008; 48(2):266-275. [17] Sivertsson L, Synnergren J, Jensen J, et al. Hepatic differentiation and maturation of human embryonic stem cells cultured in a perfused three-dimensional bioreactor. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(4):581-594. [18] Nyberg SL, Yagi T, Matsushita T, et al. Membrane barrier of a porcine hepatocyte bioartificial liver. Liver Transpl. 2003;9(3): 298-305.[19] Frühauf JH, Mertsching H, Giri S, et al. Porcine endogenous retrovirus released by a bioartificial liver infects primary human cells. Liver Int. 2009;29(10):1553-1561. [20] Di Nicuolo G, D'Alessandro A, Andria B, et al. Long-term absence of porcine endogenous retrovirus infection in chronically immunosuppressed patients after treatment with the porcine cell-based Academic Medical Center bioartificial liver. Xenotransplantation. 2010;17(6):431-439. [21] Yang Q, Liu F, Pan XP, et al. Fluidized-bed bioartificial liver assist devices (BLADs) based on microencapsulated primary porcine hepatocytes have risk of porcine endogenous retroviruses transmission. Hepatol Int. 2010;4 (4):757-761. [22] Kobayashi N. Life support of artificial liver: development of a bioartificial liver to treat liver failure. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009;16(2):113-117. [23] Sharma R, Greenhough S, Medine CN, et al. Three-dimensional culture of human embryonic stem cell derived hepatic endoderm and its role in bioartificial liver construction. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:236147. [24] Mizumoto H, Hayashi S, Matsumoto K, et al. Evaluation of a hybrid artificial liver module based on a spheroid culture system of embryonic stem cell-derived hepatic cells. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(2-3):421-428.[25] Greenhough S, Medine CN, Hay DC. Pluripotent stem cell derived hepatocyte like cells and their potential in toxicity screening. Toxicology. 2010;278(3):250-255. [26] Schmelzer E, Triolo F, Turner ME, et al. Three-dimensional perfusion bioreactor culture supports differentiation of human fetal liver cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6): 2007-2016. [27] Filippi C, Keatch SA, Rangar D, et al. Improvement of C3A cell metabolism for usage in bioartificial liver support systems. J Hepatol. 2004;41(4):599-605.[28] Harm S, Stroble K, Hartmann J, et al. Alginate-encapsulated human hepatoma C3A cells for use in a bioartificial liver device - the hybrid-MDS. Int J Artif Organs. 2009;32(11): 769-778.[29] Harimoto N, Taketomi A, Kitagawa D, et al. The newly established human hepatocyte cell line: application for the bioartificial liver. J Hepatol. 2005;42(4):557-564. [30] Hoekstra R, Nibourg GA, van der Hoeven TV, et al. The HepaRG cell line is suitable for bioartificial liver application. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43(10):1483-1489. [31] Jian GD, Zhang Z, Wang Y, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(12): 2129-2132.简国登,张志,汪艳,等.新型人源细胞混合型生物人工肝的安全性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(12):2129-2132.[32] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.中华人民共和国科学技术部. 关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[33] Xu YZ, Xue K, Gao Y, et al. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2010;18(19):1985-1989.徐玉振,薛琨,高毅,等.非人灵长类动物急性肝功能衰竭模型的建立[J].世界华人消化杂志,2010,18(19):1985-1989. [34] Shakil AO, Kramer D, Mazariegos GV, et al. Acute liver failure: clinical features, outcome analysis, and applicability of prognostic criteria. Liver Transpl. 2000;6(2):163-169.[35] Sass DA, Shakil AO. Fulminant hepatic failure. Liver Transpl. 2005;11(6):594-605.[36] Castaldo ET, Chari RS. Liver transplantation for acute hepatic failure. HPB (Oxford). 2006;8(1):29-34. [37] Chamuleau RA, Deurholt T, Hoekstra R. Which are the right cells to be used in a bioartificial liver? Metab Brain Dis. 2005; 20(4):327-335.[38] Ostapowicz G, Lee WM. Acute hepatic failure: a Western perspective. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15(5):480-488.[39] Pereira SP, McCarthy M, Ellis AJ, et al. Auxiliary partial orthotopic liver transplantation for acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 1997;26(5):1010-1017.[40] Goss JA, Shackleton CR, Maggard M, et al. Liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure in the pediatric patient. Arch Surg. 1998;133(8):839-846.[41] Esquivel CO, Keeffe EB, Garcia G, et al. Resection versus transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;14 Suppl:S37-41.[42] Lee KK, Kim DG, Moon IS, et al. Liver transplantation versus liver resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2010;101(1):47-53. [43] Chan SC. Liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure: as early as necessary and as late as possible. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(1):3-4. [44] Gómez Cabeza de Vaca V, Bernal Bellido C, Alamo Martínez JN, et al. Liver transplantation due to fulminant hepatic failure. Transplant Proc. 2012;44(7):2076-2077. [45] Lee WM. Acute liver failure. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;33(1):36-45. [46] Lucidi V, Buggenhout A, Boon N, et al. Liver transplantation for acute liver failure in adults. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2008;54(1):49-55.[47] Ndraha S, Hasan I, Simadibrata M. The effect of L-ornithine L-aspartate and branch chain amino acids on encephalopathy and nutritional status in liver cirrhosis with malnutrition. Acta Med Indones. 2011;43(1):18-22.[48] Bajaj JS. Management options for minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 2(6):785-790. [49] Ortiz M, Jacas C, Córdoba J. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: diagnosis, clinical significance and recommendations. J Hepatol. 2005;42 Suppl(1):S45-53. [50] Kola I, Landis J. Can the pharmaceutical industry reduce attrition rates? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(8):711-715.[51] Gómez-Lechón MJ, Lahoz A, Castell JV, et al. Evaluation of cytochrome P450 activities in human hepatocytes in vitro. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;806:87-97. |
| [1] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [2] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [3] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [4] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [5] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [6] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [7] | Chen Song, He Yuanli, Xie Wenjia, Zhong Linna, Wang Jian. Advantages of calcium phosphate nanoparticles for drug delivery in bone tissue engineering research and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3565-3570. |
| [8] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [9] | Gan Zhoujie, Pei Xibo. Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles in tumor therapy: superiority of nanoparticles in accumulation and drug release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2562-2568. |
| [10] | Zhou Xiaohong, Li Bocun, Li Jia, Peng Rui. Relationship between joint function and circadian rhythm in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis undergoing acupuncture and moxibustion at acupoints selected based on liver theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2192-2198. |
| [11] | Li Liqiang, Jiao Longxing, Zhang Wu, Yan Wentao, Li Jian, Li Minghao. Effect of immature dendritic cells derived from bone marrow on rejection of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2025-2029. |
| [12] | Ye Quanying, Chen Qisheng, Li Yanwen, Wang Ting, Chen Xiaoyan, Yue Yun. Effect of cassia seed aqueous extract on blood pressure level in N-nitro-L-arginine-methyl ester induced hypertensive rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1705-1711. |
| [13] | Hu Sheng, Yuan Haiyan, Hu Meng, Jin Shanhu. Effects of moderate treadmill exercise on alpha-smooth muscle actin and type IV collagen in the liver of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1723-1727. |
| [14] | Ma Minghe, Niu Yi . Thymosin alpha1 protects against liver injury in rats with zymosan-induced multiple organ failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1753-1758. |
| [15] | Fan Xuemin, Fang Shanbao, Chen Zhixing, Mo Shuixue. Status and application prospects of nano-clay Laponite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1622-1627. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||