Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (17): 3184-3191.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.17.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Friction interface characteristics of ceramic-on-ceramic artificial hip joint
Li Qiang
- Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
-
Received:2012-12-29Revised:2013-03-05Online:2013-04-23Published:2013-04-23 -
About author:Li Qiang, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China chasli@139.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Qiang. Friction interface characteristics of ceramic-on-ceramic artificial hip joint[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(17): 3184-3191.
share this article

3 金属对超高分子量聚乙烯人工髋关节的摩擦界面 金属对超高分子量聚乙烯人工髋关节是目前应用最为广泛的髋关节材料,钴铬钼合金和超高分子量聚乙烯组成具有摩擦因数低、生物相容性好等优点,使用寿命在15-25年[11],存留率大于90%,长期的临床应用结果表明,其稳定性良好。由于超高分子量聚乙烯具有无毒、耐腐蚀、体内不易降解等优点,被作为人工髋关节材料在临床上使用[12],超高分子量聚乙烯内衬的可塑性是金属对金属和陶瓷对陶瓷髋关节假体很难达到的。但超高分子量聚乙烯作为摩擦界面的主要缺点是抗磨损性能较差,使磨损颗粒进入关节和周围组织,造成骨溶解和松动,直接影响人工髋关节假体的远期寿命。聚乙烯磨损颗粒产生的原因有多向摩擦、微接触下疲劳磨损、聚乙烯退变和表面裂纹等。 影响金属对超高分子量聚乙烯人工髋关节假体磨损性能的研究中发现,聚乙烯在与空气接触的条件下消毒产生的自由基会使聚乙烯产生老化现象,γ射线照射或电子束辐射会破坏聚乙烯分子内的碳-碳键或碳-氢键,使主链断裂,与体内的氧分子相互作用使聚乙烯氧化变性,磨损性能降低。而在无氧条件下,γ射线照射或电子束辐射可以引起分子间的交联作用,对抗分子间移动,有效抵抗垂直于分子主链轴平面的形变和磨损,明显提高聚乙烯的抗磨损性能。并且聚乙烯分子的交联和氧化过程之间存在竞争反应,交联作用增加时氧化反应减少,氧化反应增加时交联作用减少。为解决聚乙烯交联和氧化问题,可以通过在惰性环境应用γ射线消毒等方法增加交联率,热熔处理降低自由基残留,可明显提高抗磨损和抗老化性能。射线强度越大交联率越高,耐磨损性能越好,常用的γ射线照射强度为(20-40) kGy,使聚乙烯耐磨性能提高30%-50%,大于50 kGy的射线强度可使耐磨性能提高到85%以上,但过大的射线照射强度会导致材料力学性能的下降,尤其是疲劳强度和抗破裂硬度的下降,因此,对聚乙烯的最佳交联率还存在争议。 4 金属对金属人工髋关节的摩擦界面 由于超高分子量聚乙烯的高磨损率导致的骨溶解和远期松动问题,使金属对超高分子量聚乙烯人工髋关节在年轻患者或高活动量的患者中失败率较高,金属对金属人工髋关节得到重视,并在临床得以越来越广泛的应用。 金属对金属人工髋关节假体的润滑机制主要是混合润滑,润滑液膜的厚度决定了关节的磨损率。摩擦间隙越小,液膜的厚度越大,则摩擦界面的直接接触面越小,磨损也越低,但摩擦间隙太小容易出现边缘接触增加摩擦转矩,结果使磨损增加。摩擦间隙太大则液膜厚度不足以分离摩擦面,易出现点状接触应力从而增加磨损。不同直径的球头,其最合适的摩擦间隙也不一致。金属人工髋关节假体具有良好的润滑性能和极低的磨损率,并不是因为润滑液膜厚度的增加,而是由于制造工艺的改进,使摩擦面的光洁度有了非常大的提高。这种低磨损率使金属对金属人工髋关节允许更薄的金属臼杯,从而可以使用更大的股骨头。而且,金属对金属人工髋关节假体还具有自抛光特性,假体植入体内后,可在日常运动中将各种原因导致的表面刮痕重新抛光,从而具有摩擦界面自行修复的特征。 临床研究结果发现,快速磨损期内金属对金属假体的线性磨损率为25-35 μm/年,进入稳态磨损后,磨损率降低到5 μm/年,容积磨损率为0.3 mm3/百万周期,比传统的金属对聚乙烯人工髋关节假体低100倍,骨溶解的发生率也非常少。但是金属对金属假体产生的磨损颗粒平均粒径为0.05 μm,按其容积磨损率计算,每年产生的颗粒数为(6.7×1012)-(2.5×1014),磨损颗粒可散布于体内各脏器和体液中,使血液和尿液中的金属离子含量迅速升高,容易引起金属离子浓聚、金属过敏、介导免疫反应、金属肾毒性和金属致畸等发生。"

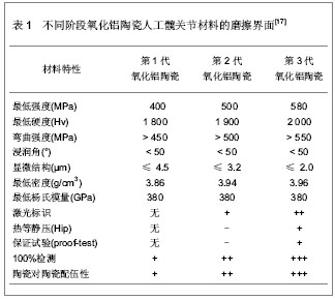
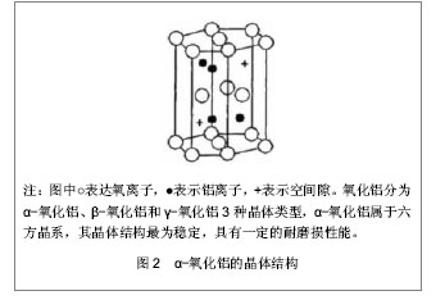
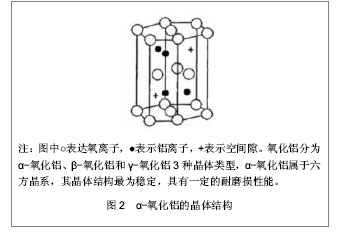
5 陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节的摩擦界面 陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体的设计和固定是经过一系列改进的无机非金属材料,可以分为惰性生物陶瓷和活性生物陶瓷,惰性生物陶瓷是指对机体几乎不发生反应或极小发生反应的陶瓷材料,如氧化铝陶瓷、氧化锆陶瓷等[13],活性生物陶瓷是指与组织界面发生作用,使化学键结合,并诱导骨结合的材料,如羟基磷灰石陶瓷、生物活性玻璃等。根据美国在2005年10月至2006年12月的研究数据表明,在112 095例人工髋关节假体置换的患者中,陶瓷对陶瓷界面的人工髋关节置换占14%,患者以年轻人居多,小于55岁的患者占总人数的24.5%,并且年轻患者中有25.7%应用的是陶瓷对陶瓷界面的人工髋关节[14]。陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体使用至今已有40余年,产品材料纯度更高,密度更佳,晶体颗粒更小,质量控制更加严格。 5.1 氧化铝陶瓷人工髋关节假体的磨损特点 氧化铝陶瓷在1970年由法国学者Boutin[15]首次作为人工髋关节材料界面植入到人体,Mittelmeier等[16]又设计氧化铝陶瓷作为关节界面,在临床治疗中获得大量应用。氧化铝陶瓷人工髋关节的应用历程大致可以分为4个阶段,每个阶段氧化铝陶瓷材料的磨擦界面都有各自的特点,见表1。"
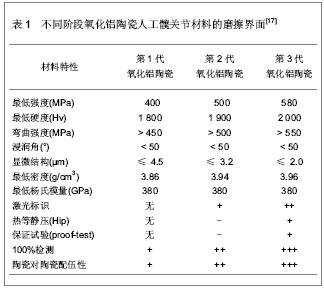
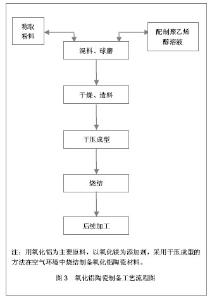
第4代氧化铝陶瓷其材料密度、强度、韧性均较氧化铝和氧化锆更大,生物相容性及耐磨损性等性能也更优异,因加入氧化锶而呈粉红色,又被称为粉陶。粉陶人工髋关节假体的出现成为髋关节疾病患者的新选择,在临床上的应用也有上升趋势。粉陶人工髋关节的材料具有耐磨损的特征,使用寿命长,避免金属磨屑的不良反应,还具有硬度大等优点。同时,粉陶人工髋关节的抗裂性能有明显提高,可以制成更薄的内衬,使用更大直径的股骨头假体,降低股骨头脱位的发生率,使患者能够获得最大范围的关节活动度,置换后功能恢复良好,可使疼痛得到明显的缓解,经过一段时间的功能锻炼可以恢复正常人的活动范围。因此,第4代粉陶人工髋关节假体是目前国际上最先进的人工髋关节材料。陶瓷-陶瓷组合已被证实是目前最耐磨损的假体组合,并且是年轻髋关节病变患者、对髋关节功能和使用寿命要求较高患者的最佳选择,极大提高了患者治疗后的生活质量。 5.2 氧化铝陶瓷人工髋关节假体的制备工艺 近年来,对陶瓷人工髋关节假体进行改造,制备工艺也有所改进[18],见图3。"
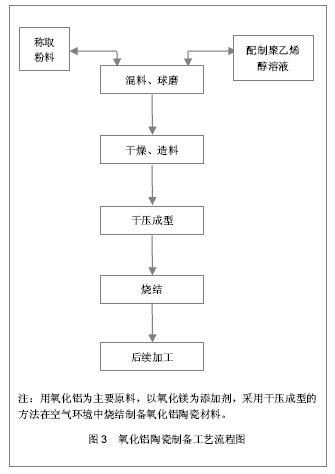
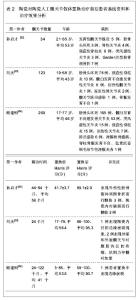
陶瓷人工髋关节假体的先进制备工艺可以得到高度抛光的表面,从而达到球头内衬之间最佳间隙,抛弃球头的裙边设计和严格控制球窝的锥度。被放行的陶瓷与金属部件需要通过严格的破碎实验,破碎载荷达到55-110 kN,相当于5-10倍人体髋关节活动所需承受的应力,而且每个陶瓷部件在出厂前要通过100%的超载无损试验[19]。 陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体的主要问题在于股骨头易碎裂、断裂强度以及抗张强度低[20-21]。经过优选材料、制备工艺以及人工假体设计的改进,28 mm陶瓷头的破碎率为0.01%,32 mm陶瓷头的破碎率仅为0.004%,而且,这些破碎多与人工假体安放的位置不良或创伤有关。内衬植入时或假体置换后撞击导致臼杯边缘的破损是较为常见的,不同设计的假体发生率为1.0%-2.6%,采用髋臼杯比内衬稍大的设计可以减少其发生率。此外,正确的操作技术对人工假体的寿命非常重要,陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体对安装位置要求更高,位置不良极易导致假体撞击,是加速磨损的主要原因。 5.3 影响陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体磨擦界面的因素 5.3.1 患者因素 临床上摩擦副的选择主要考虑患者因素,包括患者的年龄、身体状况、活动水平、预期寿命和经济状况等因素。年龄在60岁以上,活动量不大的患者,金属对超高分子量聚乙烯人工髋关节假体仍属首选。对于年轻的患者,由于活动量大、预期寿命长,则应优先考虑更耐磨损的陶瓷对陶瓷或金属对金属人工髋关节假体,以期获得较佳的远期效果。在选择金属对金属摩擦副人工髋关节假体时,还必须排除金属过敏和肾功能损害的患者。由于陶瓷人工髋假体尚缺乏国际标准,在陶瓷对陶瓷假体选用时,禁忌混用不同品牌的产品,禁止陶瓷头与金属部件作摩擦副,在假体安装时要保持假体表面状态完好,植入前彻底清洗假体接触面,安装陶瓷头时先轻拧到位再以配套工具轻轻敲击,不能以金属工具直接敲击陶瓷部件。 5.3.2 操作因素 人工髋关节假体安装和使用也是影响摩擦界面寿命的重要因素。陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体对安装位置非常敏感,安装位置不良,可以出现假体撞击,由此产生的磨损率高于常规磨损率数倍至数10倍。人工全髋关节假体对线不良,可产生假体撞击和异常的假体受力模式,引起线性磨损的明显增加。置换后高活动量和体育运动均可加速假体磨损,对于陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体摩擦副还可能增加假体破碎概率。因此,重视安装质量和置换后控制适量运动所产生的作用可能超过选择更优良的假体摩擦副。 5.4 陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体治疗后效果 5.4.1 陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体置换治疗前后患者基线资料和治疗效果 见表2。"

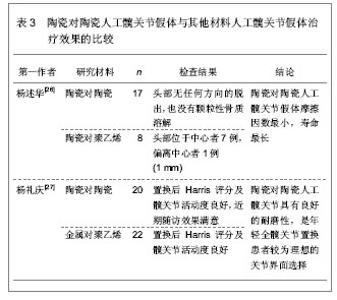
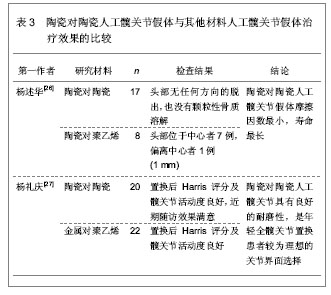
蔡友治等[25]回顾分析第三代氧化铝陶瓷全髋关节置换在中青年患者中的中期临床疗效,收集2001年5月至2006年5月98例行全陶人工髋关节置换患者的临床资料,共获得有效随访患者82例,共89例髋,其中男43例(48髋),女39例(41髋),平均年龄47.6岁,平均随访时间101.9个月(66-120个月),对有效随访的患者均进行临床和影像学检查评估疗效。结果患者置换前Harris评分(49.8±8.0)分(36-65分),置换后末次随访(92.3±2.6)分(86-97分)(P < 0.05)。随访均未见假体破裂,未发生假体周围感染,无翻修病例。1例置换后出现脱位,1例出现关节异响现象,均在非手术治疗后消失。置换后影像学均无可观察到的磨损和骨溶解,无明显异位骨化,无假体松动。研究结果显示第三代氧化铝全陶髋关节假体用于中青年患者初次全髋关节置换,中期临床随访结果满意,是一种良好的治疗选择。 5.4.2 陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节假体与其他材料人工髋关节假体治疗效果的比较 见表3。"
| [1] 华子恺,张建华.人工关节模拟实验机发展状况[C].哈尔滨:中国机械工程学会,2006:73-76.[2] Matsoukas G, Willing R, Kim IY.Total hip wear assessment: a comparison between computational and in vitro wear assessment techniques using ISO 14242 loading and kinematics.J Biomech Eng.2009;131(4):041011.[3] 周银生.陶瓷人工关节的跑合褐摩擦性能研究[J].摩擦学学报, 1998,18(2):103-107.[4] 周银生. 氮化硅陶瓷作为人工髋关节材料的摩擦试验研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2001,20(4):326-329.[5] 华子恺. 人工关节润滑技术与摩擦学测试研究[D].上海:上海大学,2011:6-8.[6] Saikko V.A hip wear simulator with 100 test stations. Proc Inst Mech Eng H.2005;219(5):309-318.[7] 向定汉,潘青林,姚正军.聚四氟乙烯自润滑编织复合材料关节轴承的摆动摩擦磨损性能研究[J].摩擦学学报,2003,23(1):72 -75.[8] 高新蕾.Schiff碱铜络合物改性超高分子量聚乙烯及润滑油的摩擦学研究[D].北京:机械科学研究总院,2006:8-11.[9] 中国知网. 中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2012-08-10. https://www.cnki.net[10] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2012-08-10.http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl[11] 许杰,马若凡, 董文武,等.数字化术前计划在人工髋关节翻修髋臼重建术中的初步应用评估[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012, 6(2):29-32.[12] 刘广建.超高分子量聚乙烯[M].化学工业出版社,2001:9-11.[13] Brown GD, Swanson EA, Nercessian OA.Neurologic injuries after total hip arthroplasty.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2008;37(4):191-197.[14] Bozic KJ, Kurtz S, Lau E, et al.The epidemiology of bearing surface usage in total hip arthroplasty in the United States.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91(7):1614-1620.[15] Boutin P.Total arthroplasty of the hip by fritted aluminum prosthesis. Experimental study and 1st clinical applications.Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1972;58(3):229-246.[16] Mittelmeier H, Heisel J.Sixteen-years' experience with ceramic hip prostheses.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1992;(282): 64-72.[17] Heros RJ, Willman G. Ceramic in total hip arthroplasty: history,mechanical properties,clinical results,and current manufacturing state of the art.Seminars Arthroplasty.1998; 9(3):114-122.[18] 童幸生,张静.氧化铝陶瓷摩擦磨损实验研究[J].江汉大学学报(自然科学版),2011,39(2):34-37.[19] 刘庆,张洪.惰性生物陶瓷在人工髋关节的应用[J].中国医疗器械信息,2006,13(2):5-7.[20] White TO, Dougall TW.Arthroplasty of the hip. Leg length is not important.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2002;84(3):335-338.[21] Knight JL, Atwater RD.Preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Quantitating its utility and precision.J Arthroplasty. 1992;7 Suppl:403-409.[22] 孙启才,王祥华,严世贵,等.陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节置换术治疗髋关节疾患[J].中医正骨,2013,25(1):43-46.[23] 刘庆,殷建华,周乙雄,等.陶瓷对陶瓷人工髋关节置换手术技巧及相关研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(14):1062-1064.[24] 顾建明,徐辉,刘庆,等.陶瓷对陶瓷全髋关节置换术的初步体会[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2010,4(3):310-315.[25] 蔡友治,严世贵,吴浩波,等.氧化铝全陶界面在中青年患者全髋关节置换术中的临床中期结果[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2011,5(5):42-44.[26] 杨述华,肖宝钧,李进,等.陶瓷头对陶瓷髋臼和陶瓷头对聚乙烯髋臼髋关节置换术临床应用观察[J].中国矩形外科杂志,2003, 11(6):370-372.[27] 杨礼庆,李希,付勤.陶瓷-陶瓷与金属-聚乙烯全髋关节置换后的早期效果比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2012,16(52): 9691-9696.[28] 钟会明.两种不同界面全髋关节置换治疗年龄小于55岁股骨头无菌性坏死患者的临床效果比较[D].浙江:浙江大学,2012:5-7. |
| [1] | Liu Pengran, Jiao Rui, Tao Jin, Chen Hui, Dai Jihang, Yan Lianqi. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty with different interface prostheses in the treatment of elderly hip diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2347-2351. |
| [2] | Jiang Jianhao, Li Peng, Du Gangqiang, Liu Hongzhi, Wang Hui, Zhang Kai, Yang Shangyou, Yang Shuye. Cobalt-chromium particles inducing preosteoblasts may aggravate periprosthetic inflammation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(26): 4101-4108. |
| [3] | Li Wei1, Zhang Hong, Cao Li-jun, Ren Guo-shan, Yan Zhan-ping, Zhao Chang-yi, Gao Zeng-min. Establishment of normal lumbar and osteoporosis three-dimensional finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1521-1526. |
| [4] | Zhang Xue-jun, Wang Chen. Digital templating alleviates leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1527-1534. |
| [5] | Li Guang-wei, Wang Hong-jun, Sun Xiao-zhi. Total knee arthroplasty for the treatment of severe knee disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1535-1542. |
| [6] | Wang Nian-hong, Yan Jun-tao, Sun Wu-quan, Hu Yong-shan, Xia Jun, Wei Li-cheng, Wu Yi, Jia Jie, Ouyang Gui-lin, He Yong, Guo Yan-ming, Xu Jie. Therapeutic effect of early Tuina rehabilitation treatment after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1543-1548. |
| [7] | Yang Peng, Bai Jian, Wang Xin-ran, Geng Yan-li. Intelligent prosthetic ankle based on the finite state machine control [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1549-1554. |
| [8] | Ao Jun, Wan Lei, Liao Wen-bo, Xue Zhong-lin, Yu Bo, Jin An-min. Screw stress features of the posterior asymmetric or symmetric fixation of transforaminal lumbar fusion based on a three-dimensional finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1555-1562. |
| [9] | Ni Wei-feng, Xu Jian-guang, Xue Feng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of in situ and reductive interbody fusion of lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1563-1570. |
| [10] | Xue Jian, Jin An-min, Sun Xiao-ping, Wang Yan-bin, Xie Wei-yong. Clinical outcomes of unilateral lumbar pedicle screw combined with translamina facet screw fixation versus bilateral fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1571-1578. |
| [11] | Zhang Qi-wei, Zhang Yao-nan, Sun Chang-tai, Xu Hong-bing. Computer-assisted versus free-hand pedicle screw implantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1579-1585. |
| [12] | Yi Guo-liang, Song Xi-zheng, Wang Wen-jun, Yao Nü-zhao. Biomechanical testing of adjacent double segment lumbar fractures treated with the spinal external fixator [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1586-1591. |
| [13] | Jia Ting-ting, Zhang Yun-tao, Liu Shun-zhen, Sun Xin, Hou Yu-dong. Chemokin CXC motif receptor 4 expression in bone tissue surrounding anode-oxidized implants during early implantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1592-1597. |
| [14] | Liu Yue, Zheng Shi-wei, Wu Liang, Zhang Yan, Yang Tie-yi. Femoral neck shortening after fracture fixation with cannulated screws [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1598-1604. |
| [15] | Xu Ke-lin, Yin Qu-dong, Gu San-jun, Sun Zhen-zhong, Shou Kui-shui. Absorbable screw internal fixation: Complications and prevention measures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1605-1610. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||