Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 931-937.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.05.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of complications following autologous iliac crest bone graft from donor site
Zou Sha-sha1, Chen Ting-ting1, Tian Ru-hui1, Chang Yan-yan2, Wang Ya-nan1, Li Zheng1, Hu Hong-liang1
- 1 Shanghai Human Sperm Bank, Sperm Development and Genetics Laboratory, Shanghai Institute of Andrology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200001, China
2 Department of Neurology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200127, China
-
Received:2012-07-20Revised:2012-08-24Online:2013-01-29Published:2013-01-29 -
Contact:Hu Hong-liang, Doctor, Master’s supervisor, Associate professor, Shanghai Human Sperm Bank, Sperm Development and Genetics Laboratory, Shanghai Institute of Andrology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200001, China hongliang_hu1115@hotmail.com -
About author:Zou Sha-sha★, Studying for master’s degree, Shanghai Human Sperm Bank, Sperm Development and Genetics Laboratory, Shanghai Institute of Andrology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200001, China zoushashash@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zou Sha-sha, Chen Ting-ting, Tian Ru-hui, Chang Yan-yan, Wang Ya-nan, Li Zheng, Hu Hong-liang. Meta-analysis of complications following autologous iliac crest bone graft from donor site[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(5): 931-937.
share this article
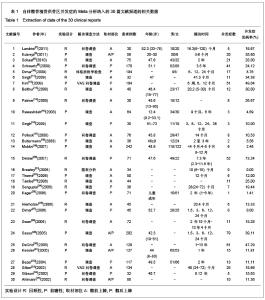
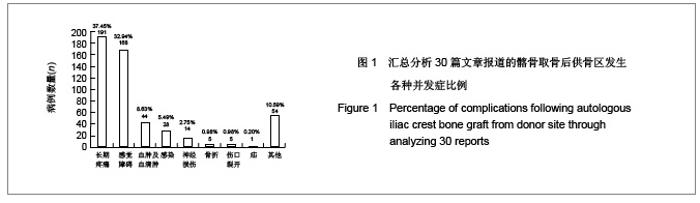
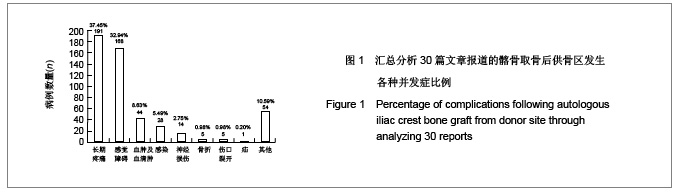
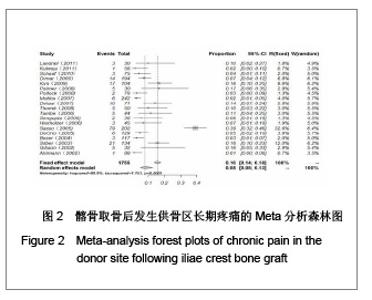
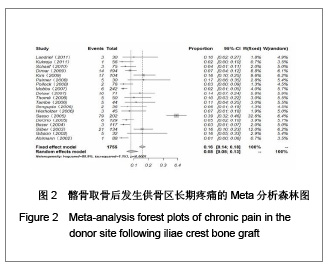
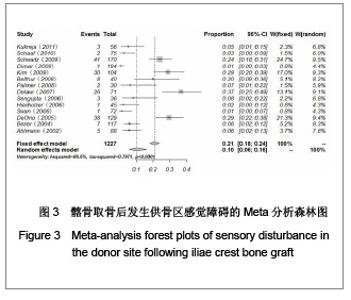
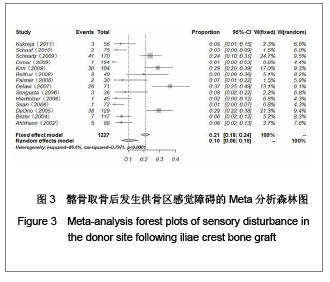
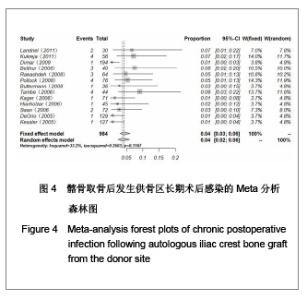
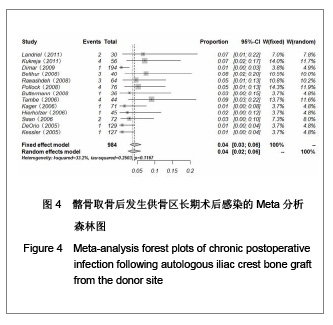
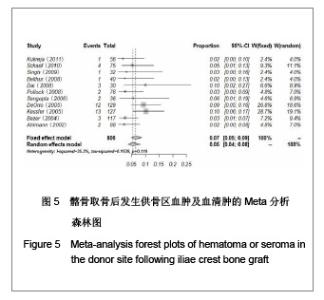
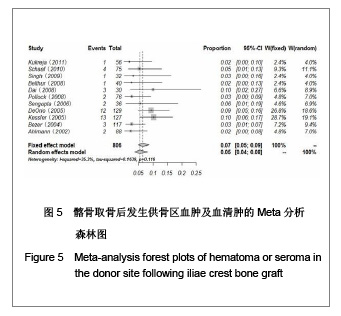
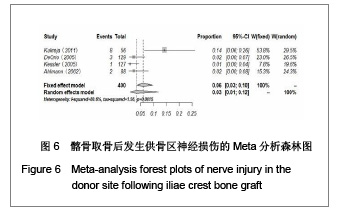
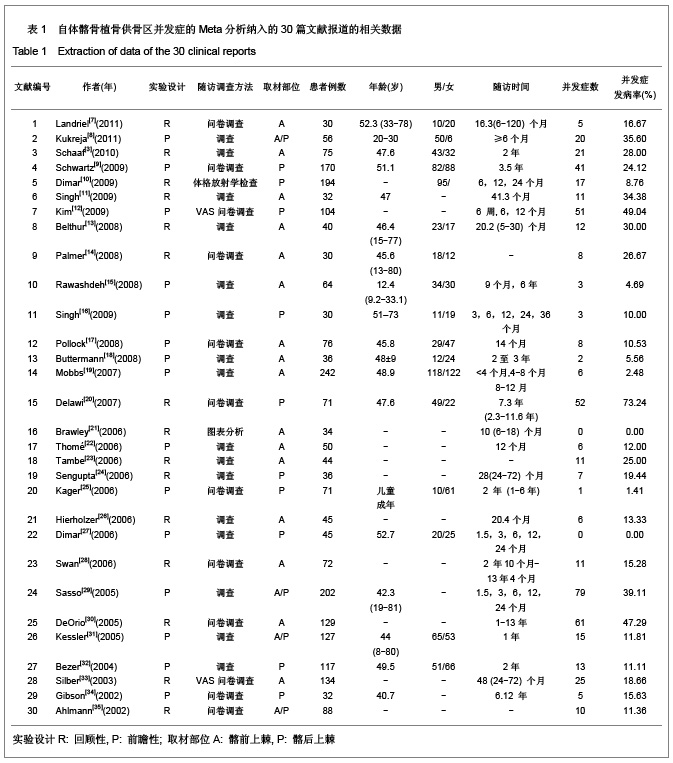
2.1 检索结果分析 按检索策略初步收集到文献共174篇,其中PubMed Medline 91篇,Ovid Medline 37篇,Cochrane Database 1篇,Embase Database 45篇。经过查阅文献标题、摘要,排除重复文献9篇及内容严重不符的文献120篇。再深入阅读全文,根据纳入标准选择文献,保留30篇英文文献进行归纳总结,其中15篇为回顾性临床研究,其余15篇为前瞻性临床研究。所有文献均采用图表分析发生并发症情况,12篇文献表明其采用了问卷调查的方式进行随访调查,结果见表1。30篇临床研究共计2 476例患者,并发症510例,即总发病率为20.6%(0%-73.24%)。 常见并发症包括:供骨区长期疼痛(191例)、感觉障碍(168例)、感染(28例)、血肿及血清肿(44例)、神经损伤(14例)。较少见的并发症包括最严重的供骨区疝形成(1例),供骨区骨折(5例),取骨切口裂开(5例)。其中所统计的其他并发症包含取骨后对患者生活质量的影响:即取骨后导致患者行走困难,影响其自理行为,妨碍其正常工作,伤疤处发痒及伤疤过大影响美观等,见图1和表2。 2.2 比较分析髂前上棘与髂后上棘供骨区并发症发生率 不同文献报道的取骨部位不一致,主要位置为髂前上棘(15篇)与髂后上棘(10篇),其中4篇文献在髂前上棘或髂后上棘处作切口进行取骨。经SPSS软件统计分析表明,1 133例髂前上棘供骨患者出现并发症196例(17.3%),870例髂后上棘供骨患者出现并发症190例(21.8%),二者差异无显著性意义(P=0.64)。 2.3 Meta分析森林图 对文献所报道的各种并发症进行数据统计,其中共有28篇研究报道了并发症:供骨区长期疼痛(19篇文献),感觉障碍(14篇文献),术后感染(13篇文献),血肿及血清肿(11篇文献),神经损伤(4篇文献)。 Meta分析森林图结果表明,长期疼痛为最常见的自体植骨并发症之一,其统计发生率为7.88%,95%可信区间为4.76%-12.79%。感觉障碍在供骨区也较常见,但不同研究对感觉障碍定义不一致,故其发生率变动较大,发生率均值为10.1%,95%可信区间为6.07%- 16.23%。供骨区感染(发生率=4.26%,95%可信区间为2.95%-6.12%),血肿及血清肿(发生率=6.55%,95%可信区间为4.90%-8.70%),神经损伤(发生率= 5.85%,95%可信区间为3.46%-9.71%),结果见图2-6。"
| [1] Miyazaki M, Tsumura H, Wang JC, et al. An update on bone substitutes for spinal fusion.Eur Spine J. 2009;18(6):783-799.[2] Giannoudis PV, Dinopoulos H, Tsiridis E. Bone substitutes: an update. Injury. 2005;36 Suppl 3:S20-27.[3] Schaaf H, Lendeckel S, Howaldt HP,et al. Donor site morbidity after bone harvesting from the anterior iliac crest.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(1):52-58.[4] Younger EM, Chapman MW. Morbidity at bone graft donor sites. J Orthop Trauma. 1989;3(3):192-195. [5] Summers BN, Eisenstein SM. Donor site pain from the ilium. A complication of lumbar spine fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71(4):677-680. [6] Missiuna PC, Gandhi HS, Farrokhyar F,et al. Anatomically safe and minimally invasive transcrestal technique for procurement of autogenous cancellous bone graft from the mid-iliac crest.Can J Surg. 2011;54(5):327-332.[7] Landriel FA, Hem S, Goldschmidt E,et al. Polyetheretherketone Interbody Cages Versus Autogenous Iliac Crest Bone Grafts With Anterior Fixation for Cervical Disc Disease. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011. [Epub ahead of print] [8] Kukreja S, Raza HKT, Agrawal AC. Iliac Crest Bone Graft Harvesting: Prospective Study Of Various Techniques And Donor Site Morbidity. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2011. [Epub ahead of print][9] Schwartz CE, Martha JF, Kowalski P,et al. Prospective evaluation of chronic pain associated with posterior autologous iliac crest bone graft harvest and its effect on postoperative outcome. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2009;7: 49.[10] Dimar JR 2nd, Glassman SD, Burkus JK,et al. Two-year fusion and clinical outcomes in 224 patients treated with a single-level instrumented posterolateral fusion with iliac crest bone graft. Spine J. 2009;9(11):880-885.[11] Singh JR, Nwosu U, Egol KA. Long-term functional outcome and donor-site morbidity associated with autogenous iliac crest bone grafts utilizing a modified anterior approach. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009;67(4):347-351.[12] Kim DH, Rhim R, Li L,et al. Prospective study of iliac crest bone graft harvest site pain and morbidity.Spine J. 2009; 9(11):886-892.[13] Belthur MV, Conway JD, Jindal G,et al. Bone graft harvest using a new intramedullary system.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(12):2973-2980.[14] Palmer W, Crawford-Sykes A, Rose RE. Donor site morbidity following iliac crest bone graft.West Indian Med J. 2008;57(5): 490-492. [15] Rawashdeh MA. Morbidity of iliac crest donor site following open bone harvesting in cleft lip and palate patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;37(3):223-227.[16] Ohtori S, Koshi T, Yamashita M,et al. Single-level instrumented posterolateral fusion versus non-instrumented anterior interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis: a prospective study with a 2-year follow-up.J Orthop Sci. 2011;16(4):352-358.[17] Pollock R, Alcelik I, Bhatia C,et al. Donor site morbidity following iliac crest bone harvesting for cervical fusion: a comparison between minimally invasive and open techniques. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(6):845-852.[18] Buttermann GR. Prospective nonrandomized comparison of an allograft with bone morphogenic protein versus an iliac-crest autograft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine J. 2008;8(3):426-435.[19] Mobbs RJ, Rao P, Chandran NK. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: analysis of surgical outcome with and without plating. J Clin Neurosci. 2007;14(7):639-642.[20] Delawi D, Dhert WJ, Castelein RM,et al. The incidence of donor site pain after bone graft harvesting from the posterior iliac crest may be overestimated: a study on spine fracture patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(17):1865-1868.[21] Brawley SC, Simpson RB. Results of an alternative autogenous iliac crest bone graft harvest method. Orthopedics. 2006;29(4):342-346.[22] Thomé C, Leheta O, Krauss JK,et al. A prospective randomized comparison of rectangular titanium cage fusion and iliac crest autograft fusion in patients undergoing anterior cervical discectomy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;4(1):1-9.[23] Tambe AD, Cutler L, Murali SR,et al. In scaphoid non-union, does the source of graft affect outcome? Iliac crest versus distal end of radius bone graft. J Hand Surg Br. 2006;31(1): 47-51.[24] Sengupta DK, Truumees E, Patel CK,et al. Outcome of local bone versus autogenous iliac crest bone graft in the instrumented posterolateral fusion of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(9):985-991.[25] Kager AN, Marks M, Bastrom T,et al. Morbidity of iliac crest bone graft harvesting in adolescent deformity surgery. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26(1):132-134.[26] Hierholzer C, Sama D, Toro JB,et al. Plate fixation of ununited humeral shaft fractures: effect of type of bone graft on healing.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(7):1442-1447.[27] Dimar JR, Glassman SD, Burkus KJ,et al. Clinical outcomes and fusion success at 2 years of single-level instrumented posterolateral fusions with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/compression resistant matrix versus iliac crest bone graft. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(22): 2534-2539.[28] Swan MC, Goodacre TE. Morbidity at the iliac crest donor site following bone grafting of the cleft alveolus. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;44(2):129-133.[29] Sasso RC, LeHuec JC, Shaffrey C,et al. Iliac crest bone graft donor site pain after anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a prospective patient satisfaction outcome assessment. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18 Suppl:S77-S81.[30] DeOrio JK, Farber DC. Morbidity associated with anterior iliac crest bone grafting in foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(2):147-151.[31] Kessler P, Thorwarth M, Bloch-Birkholz A,et al. Harvesting of bone from the iliac crest--comparison of the anterior and posterior sites. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;43(1):51-56.[32] Bezer M, Kocao?lu B, Aydin N,et al. Comparison of traditional and intrafascial iliac crest bone-graft harvesting in lumbar spinal surgery. Int Orthop. 2004;28(6):325-328. [33] Silber JS, Anderson DG, Daffner SD,et al. Donor site morbidity after anterior iliac crest bone harvest for single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(2):134-139.[34] Gibson S, McLeod I, Wardlaw D,et al. Allograft versus autograft in instrumented posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion: a randomized control trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27(15): 1599-1603.[35] Ahlmann E, Patzakis M, Roidis N,et al. Comparison of anterior and posterior iliac crest bone grafts in terms of harvest-site morbidity and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(5):716-720.[36] Zou SS,Hu HL. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(37):6991-6994. 邹沙沙,胡洪亮. Hedgehog信号通路与骨发育[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(37):6991-6994.[37] Hu H, Hilton MJ, Tu X,et al. Sequential roles of Hedgehog and Wnt signaling in osteoblast development. Development. 2005; 132(1):49-60. |
| [1] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [2] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [3] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [4] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [5] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [6] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [7] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [8] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [9] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [10] | Wu Gang, Chen Jianwen, Wang Shilong, Duan Xiaoran, Liu Haijun, Dong Jianfeng. Simple HyProCure subtalar stabilization in treatment of adolescent flexible flatfoot combined with painful accessory navicular bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| [11] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [12] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [13] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [14] | Li Quanxi, Shen Yu, Wan Wei, Sun Shanzhi. Changes of abdominal wall mechanics and pain after tension-free inguinal hernia repair with polypropylene mesh [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 548-552. |
| [15] | Ma Rui, Wang Jialin, Wu Mengjun, Ge Ying, Wang Wei, Wang Kunzheng. Relationship of pathogenic bacteria distribution with drug resistance and treatment cycle for periprosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 380-385. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||