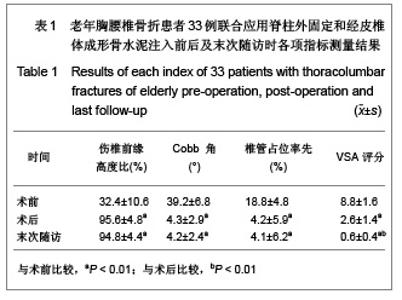
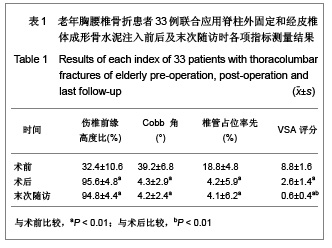
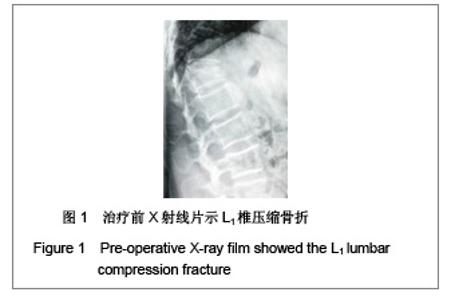
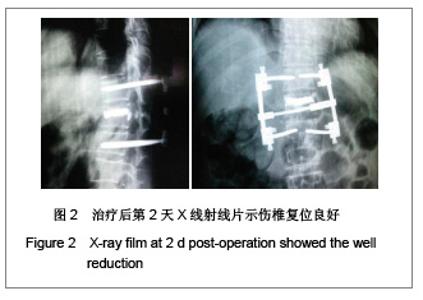
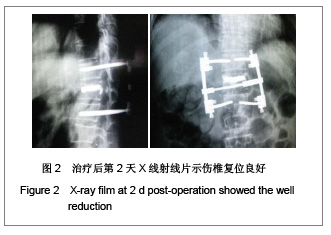
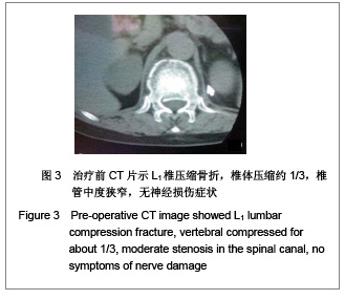
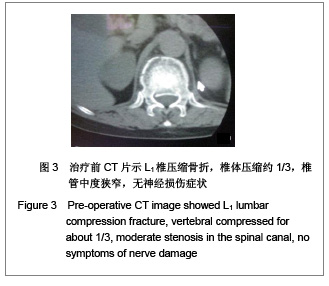
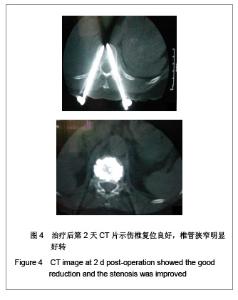
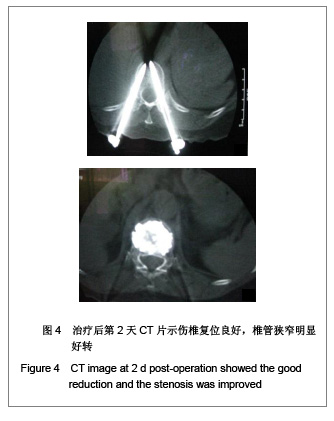
| [1] Liu H,Wang WJ,Song XZ,et al. Yixue Linchuang Yanjiu. 2006; 23(2):148-150. 刘洪,王文军,宋西正,等.新型脊柱外固定器的研制和生物力学测试[J].医学临床研究, 2006,23(2):148-150.[2] State council of the People’s Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution.1994-09-01. 中华人民共和国国务院.医疗机构管理条例.1994-09-01.[3] Wang WJ,Lu LY,Song XZ,et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2006;16(9):663-666. 王文军,陆凌云,宋西正,等.经皮椎弓根钉外固定系统联合椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(9): 663-666.[4] Peng XZ,Chen M,Wu ZG,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(8):1515-1518. 彭小忠,陈明,武振国,等.经皮椎体成形102例中22例骨水泥渗漏原因[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(8):1515-1518.[5] Hashimoto T, Kaneda K, Abumi K. Relationship between traumatic spinal canal stenosis and neurologic deficits in thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988; 13(11):1268-1272.[6] Xu JC,Bai JP, Xilin Baoleri,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(13):2366-2370. 徐建成,白靖平,锡林宝勒日,等. 注入骨水泥椎体成形与非手术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2366-2370.[7] Magerl F.External skeletal fixation of the lower thoracic and the lower spine. In Uhthoff HK(ed).Current concepts of external Fixation of fracture.Berlin:Heidelberg, Springer-verlag. 1982:353.[8] Olerud S, Sjöström L, Karlström G,et al. Spontaneous effect of increased stability of the lower lumbar spine in cases of severe chronic back pain. The answer of an external transpeduncular fixation test. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(203):67-74.[9] Xu YJ,Zheng ZG,Wang YJ,et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Shunshang Zazhi. 1994;4(4):152-156. 徐又佳,郑祖根,王以进,等.经椎弓根外固定器的设计和生物力学分析[J].中国脊柱损伤杂志,1994,4(4):152-156.[10] Jin ZS,Wang DX,Fan WM,et al. Jiangsu Yiyao. 2005;31(2): 102-105. 金正帅,王道新,范卫民,等.脊柱外固定复位器在胸腰椎骨折的应用[J].江苏医药, 2005,31(2):102-105.[11] Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P,et al. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie. 1987;33(2):166-168.[12] Paúl L, Santonja C, Izquierdo E. Complete necrosis of a spinal giant cell tumor after vertebroplasty. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17(4):727-731.[13] Jiang GQ,Ouyang J,Lu B,et al. Zhonghua Chuangshang Zazhi. 2009;25(2):131-133. 蒋国强,欧阳甲,卢斌,等. 经皮椎体成形术治疗重度骨质疏松性压缩骨折[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2009,25(2):131-133.[14] Song XZ,Wang XD,Wang WJ,et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2008;21(9):698-699. 宋西正,汪向东,王文军,等.脊柱外固定器的研制及其在胸腰椎骨折微创治疗中的临床应用[J].中国骨伤,2008,21(9):698-699.[15] Yin ZX,Ding HM,Song XZ,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(13):2423-2427. 尹知训,丁红梅,宋西正,等.经皮椎弓根植器械与新型脊柱外固定联合应用的力学评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(13):2423-2427.[16] Song XZ,Wang WJ,Song LZ,et al. Jizhu Waike Zazhi. 2012; 10(1):17-21. 宋西正,王文军,宋林章,等.外固定器联合经皮椎体植骨微创治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的影像学评价[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(1): 17-21.[17] Song XZ, Wang WJ, Wang D, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2009;22(10):791-792. 宋西正,王文军,王东,等.经皮椎弓根植骨联合脊柱外固定微创治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国骨伤,2009,22(10):791-792.[18] Yang CY,Luo H,Zhu J,et al. Jizhu Waike Zazhi. 2009; 7(1): 13-17. 杨长远,罗辉,朱军,等.新型脊柱外固定系统联合经皮椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].脊柱外科杂志,2009,7(1):13-17.[19] Zhang SD,Wang C,Jiang XJ,et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009;4(2):288-292. 张绍东,王宸,姜星杰,等.硫酸钙骨水泥在胸腰椎爆裂骨折椎体成形术中的生物力学性能[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,4(2): 288-292.[20] Perry A, Mahar A, Massie J,et al. Biomechanical evaluation of kyphoplasty with calcium sulfate cement in a cadaveric osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture model. Spine J. 2005;5(5):489-493.[21] Wilson DR, Myers ER, Mathis JM,et al. Effect of augmentation on the mechanics of vertebral wedge fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(2):158-165.[22] Song XZ,Yi GL,Wang WJ,et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2011;21(8):659-662. 宋西正,易国良,王文军,等.外固定器整复下经皮椎体成形术治疗伤椎后壁破损的骨质疏松性压缩骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011,21(8):659-662.[23] Chin DK, Kim YS, Cho YE,et al. Efficacy of postural reduction in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures followed by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Neurosurgery. 2006;58(4): 695-700.[24] Bedbrook GM.Treatment of thoracolumbar dislocation and fractures with paraplegia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975;(112): 27-43.[25] Knop C, Fabian HF, Bastian L,et al. Late results of thoracolumbar fractures after posterior instrumentation and transpedicular bone grafting.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26(1):88-99.[26] Yin QD,Zheng ZG,Dong QR,et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2004;7(4):408-409. 殷渠东,郑祖根,董启榕,等.椎弓根螺钉位置与手术效果的关系[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2004,7(4):408-409.[27] Phillips FM, Todd Wetzel F, Lieberman I,et al. An in vivo comparison of the potential for extravertebral cement leak after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(19):2173-2178.[28] Soini JR, Seitsalo SK. The external fixation test of the lumbar spine. 30 complications in 25 of 100 consecutive patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1993;64(2):147-149.[29] Huang QS,Peng MX,Lin Y,et al. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2005; 25(12):758-760. 黄其杉,彭茂秀,林焱,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华骨科杂志, 2005,25(12):758-760. |