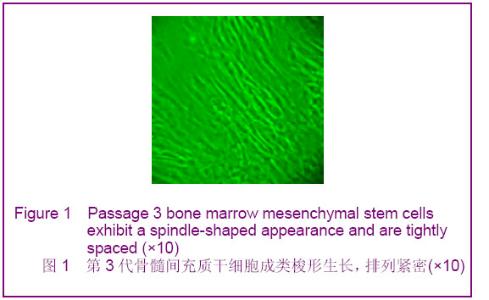
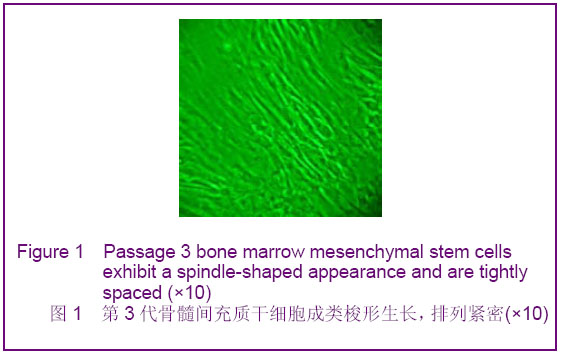
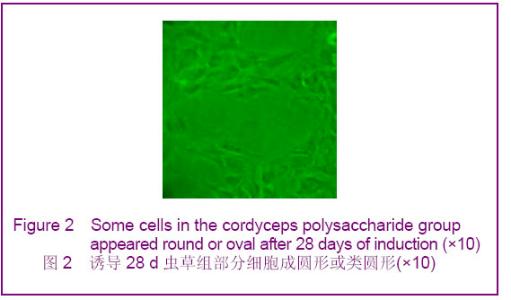
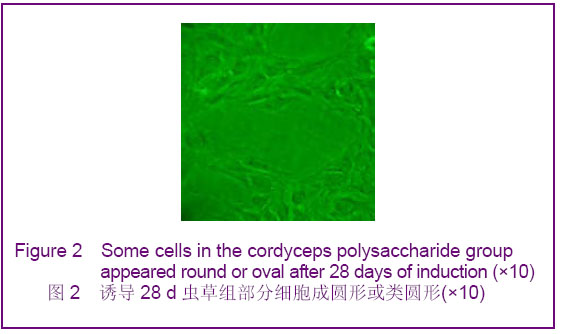
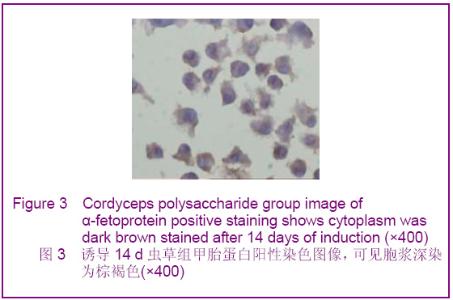
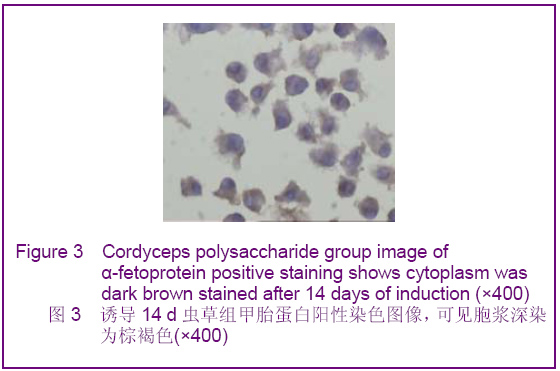
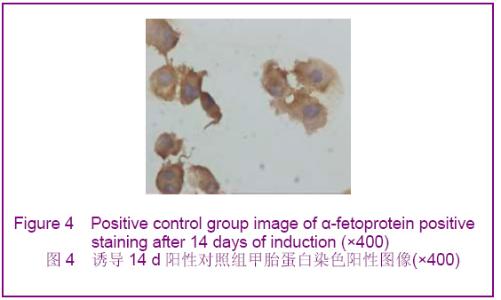
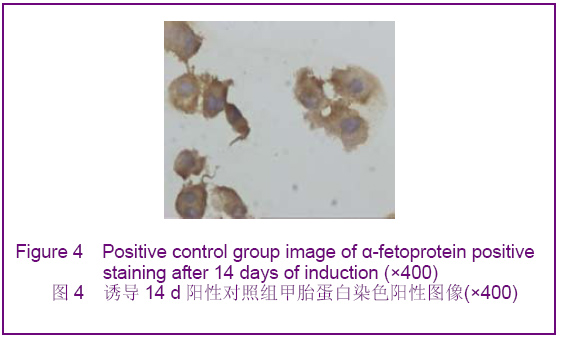
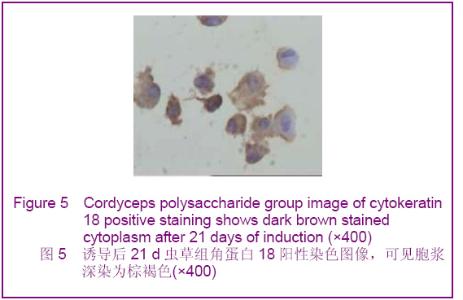
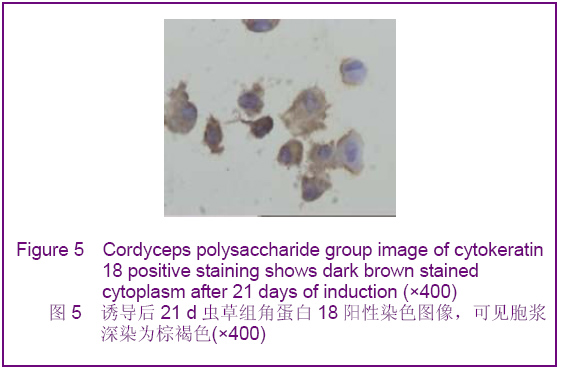
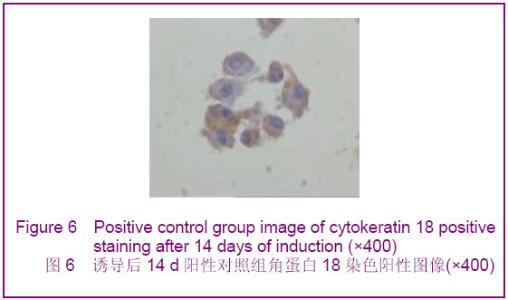
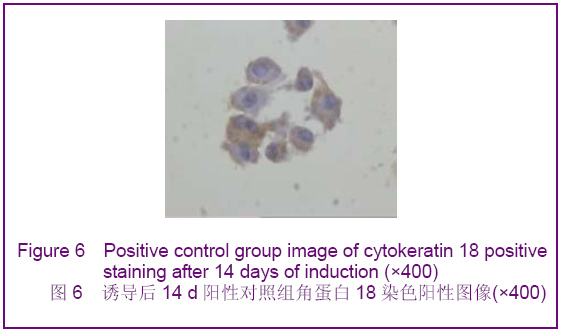
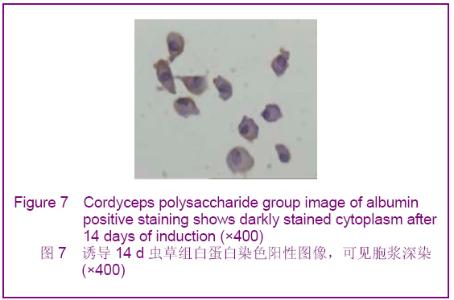
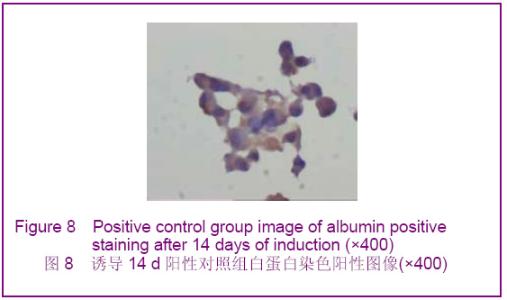
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9221-9225.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cordyceps polysaccharide induces differentiation of adult rat mesenchymal stem cells into a hepatocyte lineage in vitro
Liu Jiang-kai1, Song Ya-fang2, Liu You-zhang2, Yang Yu-chen2, Zhang Jiu-mei2
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450008, Henan Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2012-03-05Revised:2012-07-06Online:2012-12-02Published:2013-01-16 -
About author:Liu Jiang-kai☆, M.D., Attending physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450008, Henan Province, China ljk1008@yahoo.cn -
Supported by:Sceience and Technology Program of Guangdong Province, No. 2010B030700068*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Jiang-kai, Song Ya-fang, Liu You-zhang, Yang Yu-chen, Zhang Jiu-mei. Cordyceps polysaccharide induces differentiation of adult rat mesenchymal stem cells into a hepatocyte lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(49): 9221-9225.
share this article
| [1] Oh SH, Hatch HM, Petersen BE. Hepatic oval 'stem' cell in liver regeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13(6):405-409.[2] Fang SY,Yao HW,Li J,et al. Anhui Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2004; 39(3):201-203.方士英,姚宏伟,李俊,等.虫草多糖对小鼠化学性肝损伤的保护作用[J].安徽医科大学学报,2004,39(3):201-203.[3] Huang JM,Lu JH.Shandong Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao. 2010; 34(3):258-259.黄军民,卢建华.虫草多糖对肝损伤模型小鼠肝细胞胞外基质表达的影响[J].山东中医药大学学报,2010,34(3):258-259.[4] Zheng XL,Li YG,Zhong S,et al. Zhejiang Nongye Kexue. 2011 (3):702-705.郑贤林,李有贵,钟石,等.蚕蛹虫草多糖对氢化可的松致小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J].浙江农业科学,2011(3):702-705.[5] Oh SH, Miyazaki M, Kouchi H,et al. Hepatocyte growth factor induces differentiation of adult rat bone marrow cells into a hepatocyte lineage in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;279(2):500-504.[6] Avital I, Inderbitzin D, Aoki T,et al. Isolation, characterization, and transplantation of bone marrow-derived hepatocyte stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;288(1):156-164.[7] He ZJ,Fang CH,Ma JX,et al. Jiefangjun Yixue Zazhi. 2006; 31(5):446-449.何忠杰,方驰华,马俊勋,等. 肝细胞生长因子与表皮细胞生长因子联合诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为类肝细胞[J].解放军医学杂志,2006,31(5):446-449. |
| [1] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [2] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Liu Xun, Ouyang Hougan, Pan Rongbin, Wang Zi, Yang Fen, Tian Jiaxuan . Optimal parameters for physical interventions in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6727-6732. |
| [4] | Lin Meiyu, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Zhao Jing, Ruan Guangping. Action mechanism and progress of stem cells against ovarian granulosa cell senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5414-5421. |
| [5] | Hu Enxi, He Wenying, Tao Xiang, Du Peijing, Wang Libin. Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5374-5381. |
| [6] | Tian Zhenli, Zhang Xiaoxu, Fang Xingyan, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on lipid metabolism in human hepatocytes and regulatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4956-4964. |
| [7] | Han Fang, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Electrotactic migration and mechanisms of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4984-4992. |
| [8] | Hu Chen, Jiang Ying, Chen Jia, Qiao Guangwei, Dong Wen, Ma Jian. Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4720-4730. |
| [9] | Yang Chao, Luo Zongping. Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2648-2654. |
| [10] | Li Xiaofeng, Zhao Duo, Ouyang Qin, Pang Zixiang, Li Yuquan, Chen Qianfen. Protective effect of mangiferin on oxidative stress injury in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2669-2674. |
| [11] | Hu Zezun, Yang Fanlei, Xu Hao, Luo Zongping. Effect of surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under stretching conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1981-1989. |
| [12] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [13] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [14] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [15] | Zhou Shijie, Li Muzhe, Yun Li, Zhang Tianchi, Niu Yuanyuan, Zhu Yihua, Zhou Qinfeng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Wang Lining. Effect of Wenshen Tongluo Zhitong formula on mouse H-type bone microvascular endothelial cell/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||