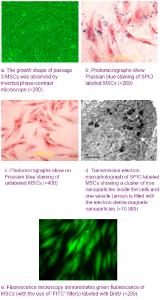
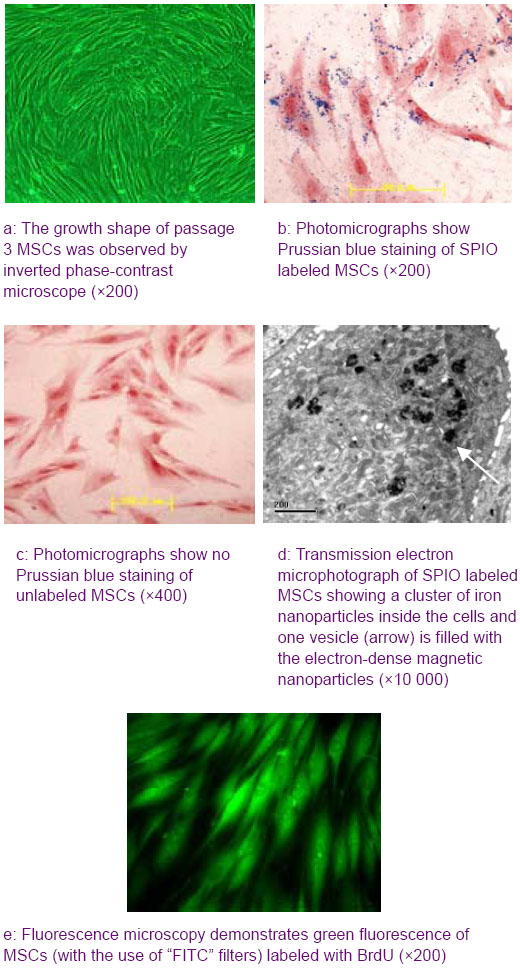
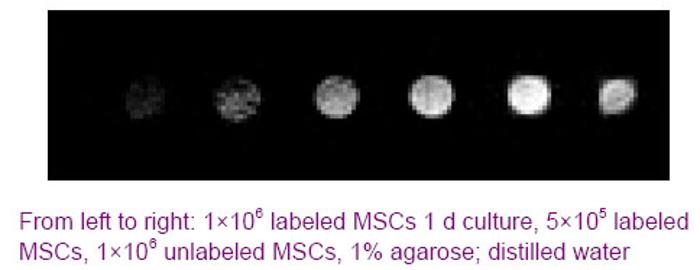
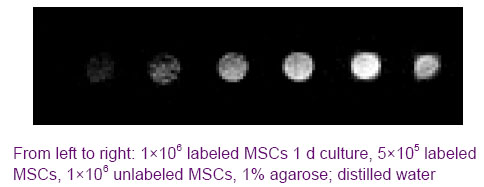
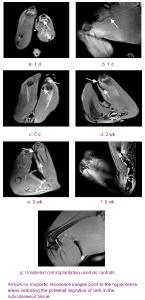
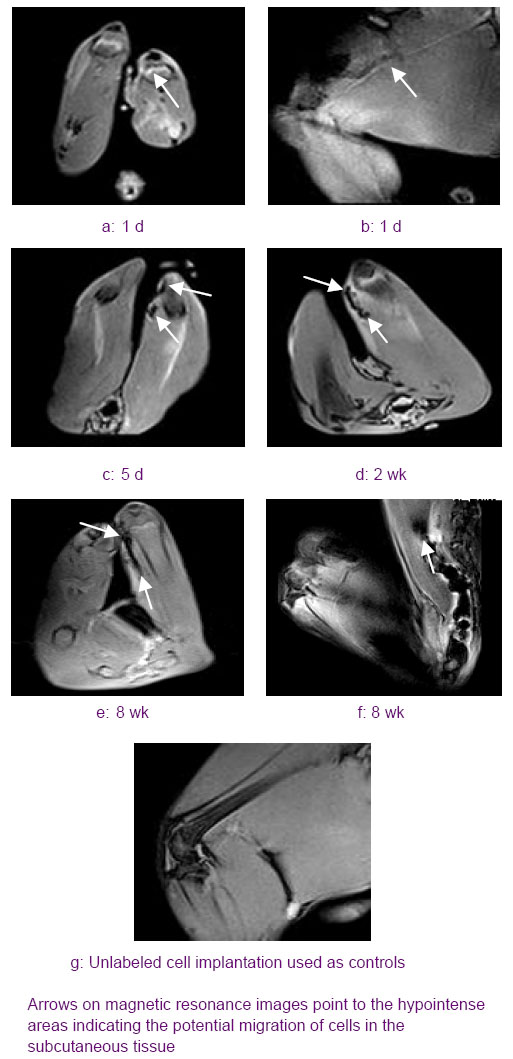
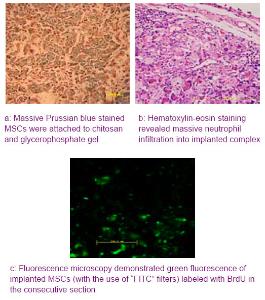
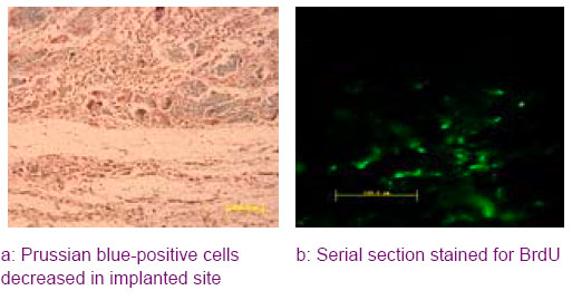
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9201-9208.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
In vivo magnetic resonance imaging tracking of superparamagnetic iron oxide labeled rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after subcutaneoustransplantation
Jin Xu-hong1, Zhang Shou1, Yang Liu 2, Wen Ya-ming2, Duan Xiao-jun2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Haikou Hospital Affiliated to Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China; 2Center of Joint Surgery, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing 400038, China
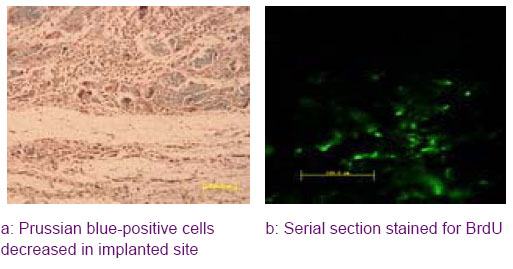
-
Received:2011-02-14Revised:2012-03-27Online:2012-12-02Published:2013-01-16 -
About author:Jin Xu-hong, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Haikou Hospital Affiliated to Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China jxh53@yahoo.cn -
Supported by:Key Science and Technology Planning Program of Haikou, No. 2010-168*, 2009-049-11*; Natural Science Foundation of Haikou, No. 309107*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jin Xu-hong, Zhang Shou, Yang Liu,Wen Ya-ming, Duan Xiao-jun. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging tracking of superparamagnetic iron oxide labeled rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after subcutaneoustransplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(49): 9201-9208.
share this article
| [1] Kuroda R, Ishida K, Matsumoto T, et al. Treatment of a full-thickness articular cartilage defect in the femoral condyle of an athlete with autologous bone-marrow stromal cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(2):226-231. [2] Zhou G, Liu W, Cui L, et al. Repair of porcine articular osteochondral defects in non-weightbearing areas with autologous bone marrow stromal cells. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(11):3209-3221. [3] Kidd S, Spaeth E, Dembinski JL, et al. Direct evidence of mesenchymal stem cell tropism for tumor and wounding microenvironments using in vivo bioluminescent imaging. Stem Cells. 2009;27(10):2614-2623. [4] Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, et al. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science. 1994; 263(5148):802-805. [5] Duan X, Yang L, Dong S, et al. Characterization of EGFP-labeled mesenchymal stem cells and redistribution of allogeneic cells after subcutaneous implantation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(7):751-759. [6] Lee RH, Pulin AA, Seo MJ, et al. Intravenous hMSCs improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(1): 54-63.[7] Pittenger MF, Martin BJ. Mesenchymal stem cells and their potential as cardiac therapeutics. Circ Res. 2004;95(1): 9-20. [8] Rüster B, Göttig S, Ludwig RJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells display coordinated rolling and adhesion behavior on endothelial cells. Blood. 2006;108(12):3938-3944.[9] Runnels JM, Zamiri P, Spencer JA, et al. Imaging molecular expression on vascular endothelial cells by in vivo immunofluorescence microscopy. Mol Imaging. 2006;5(1): 31-40. [10] Yoon YS, Park JS, Tkebuchava T, et al. Unexpected severe calcification after transplantation of bone marrow cells in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;109(25): 3154-3157. [11] Rochefort GY, Vaudin P, Bonnet N, et al. Influence of hypoxia on the domiciliation of mesenchymal stem cells after infusion into rats: possibilities of targeting pulmonary artery remodeling via cells therapies? Respir Res. 2005;6:125.[12] Arbab AS, Bashaw LA, Miller BR, et al. Intracytoplasmic tagging of cells with ferumoxides and transfection agent for cellular magnetic resonance imaging after cell transplantation: methods and techniques. Transplantation. 2003;76(7):1123-1130. [13] Farrell E, Wielopolski P, Pavljasevic P, et al. Effects of iron oxide incorporation for long term cell tracking on MSC differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;369(4):1076-1081.[14] Elgort DR, Duerk JL. A review of technical advances in interventional magnetic resonance imaging. Acad Radiol. 2005;12(9):1089-1099. [15] Ejbjerg BJ, Narvestad E, Jacobsen S, et al. Optimised, low cost, low field dedicated extremity MRI is highly specific and sensitive for synovitis and bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis wrist and finger joints: comparison with conventional high field MRI and radiography. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(9):1280-1287. [16] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.[17] Jing XH, Yang L, Duan XJ, et al. In vivo MR imaging tracking of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle labeled, engineered, autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells following intra-articular injection. Joint Bone Spine. 2008;75(4):432-438.[18] Arbab AS, Yocum GT, Kalish H, et al. Efficient magnetic cell labeling with protamine sulfate complexed to ferumoxides for cellular MRI. Blood. 2004;104(4):1217-1223. [19] Zhang Z, van den Bos EJ, Wielopolski PA, et al. In vitro imaging of single living human umbilical vein endothelial cells with a clinical 3.0-T MRI scanner. Magma. 2005;18(4):175-185. [20] Hsieh CH, Lee MC, Tsai-Wu JJ, et al. Deleterious effects of MRI on chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(3): 343-351. [21] Tallheden T, Nannmark U, Lorentzon M, et al. In vivo MR imaging of magnetically labeled human embryonic stem cells. Life Sci. 2006;79(10):999-1006.[22] Østergaard M, Ejbjerg B, Szkudlarek M. Imaging in early rheumatoid arthritis: roles of magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasonography, conventional radiography and computed tomography. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2005;19(1): 91-116. [23] Schirmer C, Scheel AK, Althoff CE, et al. Diagnostic quality and scoring of synovitis, tenosynovitis and erosions in low-field MRI of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with conventional MRI. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66(4):522-559.[24] Arbab AS, Bashaw LA, Miller BR, et al. Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging. Radiology. 2003;229(3):838-846.[25] Frank JA, Miller BR, Arbab AS, et al. Clinically applicable labeling of mammalian and stem cells by combining superparamagnetic iron oxides and transfection agents. Radiology. 2003;228(2):480-487.[26] Suh JS, Lee JY, Choi YS, et al. Efficient labeling of mesenchymal stem cells using cell permeable magnetic nanoparticles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009; 379(3):669-675. [27] Farrell E, Wielopolski P, Pavljasevic P, et al. Cell labelling with superparamagnetic iron oxide has no effect on chondrocyte behaviour. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(7):961-967. [28] Ju S, Teng G, Zhang Y, et al. In vitro labeling and MRI of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood. Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24(5):611-617. [29] Bulte JWM. Magnetic nanoparticles as markers for cellular MR imaging. J Magnetism Magnetic Materials. 2005;289: 423-427.[30] Arbab AS, Pandit SD, Anderson SA, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and confocal microscopy studies of magnetically labeled endothelial progenitor cells trafficking to sites of tumor angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):671- 678. [31] George AJT, Bhakoo KK, Haskard, DO, et al. Imaging Molecular and Cellular Events in Implantation. Implantation. 2006;82:1124-1129.[32] Magnitsky S, Watson DJ, Walton RM, et al. In vivo and ex vivo MRI detection of localized and disseminated neural stem cell grafts in the mouse brain. Neuroimage. 2005; 26(3):744-754.[33] Ding W, Bai J, Zhang J, et al. In vivo tracking of implanted stem cells using radio-labeled transferrin scintigraphy. Nucl Med Biol. 2004;31(6):719-725. [34] Bulte JW, Zhang S, van Gelderen P, et al. Neurotransplantation of magnetically labeled oligodendrocyte progenitors: magnetic resonance tracking of cell migration and myelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(26):15256-15261. [35] Jendelová P, Herynek V, DeCroos J, et al. Imaging the fate of implanted bone marrow stromal cells labeled with superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Magn Reson Med. 2003;50(4):767-776. |
| [1] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [2] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Liu Xun, Ouyang Hougan, Pan Rongbin, Wang Zi, Yang Fen, Tian Jiaxuan . Optimal parameters for physical interventions in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6727-6732. |
| [4] | Lin Meiyu, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Zhao Jing, Ruan Guangping. Action mechanism and progress of stem cells against ovarian granulosa cell senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5414-5421. |
| [5] | Hu Enxi, He Wenying, Tao Xiang, Du Peijing, Wang Libin. Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5374-5381. |
| [6] | Tian Zhenli, Zhang Xiaoxu, Fang Xingyan, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on lipid metabolism in human hepatocytes and regulatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4956-4964. |
| [7] | Han Fang, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Electrotactic migration and mechanisms of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4984-4992. |
| [8] | Hu Chen, Jiang Ying, Chen Jia, Qiao Guangwei, Dong Wen, Ma Jian. Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4720-4730. |
| [9] | Yang Chao, Luo Zongping. Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2648-2654. |
| [10] | Li Xiaofeng, Zhao Duo, Ouyang Qin, Pang Zixiang, Li Yuquan, Chen Qianfen. Protective effect of mangiferin on oxidative stress injury in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2669-2674. |
| [11] | Hu Zezun, Yang Fanlei, Xu Hao, Luo Zongping. Effect of surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under stretching conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1981-1989. |
| [12] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [13] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [14] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [15] | Zhou Shijie, Li Muzhe, Yun Li, Zhang Tianchi, Niu Yuanyuan, Zhu Yihua, Zhou Qinfeng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Wang Lining. Effect of Wenshen Tongluo Zhitong formula on mouse H-type bone microvascular endothelial cell/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||