Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9179-9185.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibit glioma growth
Liang Shuo1, 2, Jiao Hong-liang 3, Chi Lian-kai1, Shi Xin-yi1, Liang A-ming3, Tian Yi3, Han Jiao-ling1, Ma Shan-shan1, Yang Bo3, Guan Fang-xia1, 4
- 1Department of Bioengineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China; 2Biotherapy Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, Henan Province, China; 3Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China; 4Henan Academy of Medical Sciences, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2012-03-13Revised:2012-05-21Online:2012-12-02Published:2013-01-16 -
Contact:Guan Fang-xia, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Bioengineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001 -
About author:Liang Shuo★, Master, Department of Bioengineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China; Biotherapy Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, Henan Province, China shuoguo005@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Shuo, Jiao Hong-liang,Chi Lian-kai, Shi Xin-yi, Liang A-ming, Tian Yi, Han Jiao-ling, . Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibit glioma growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(49): 9179-9185.
share this article
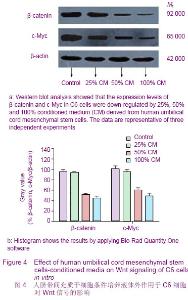
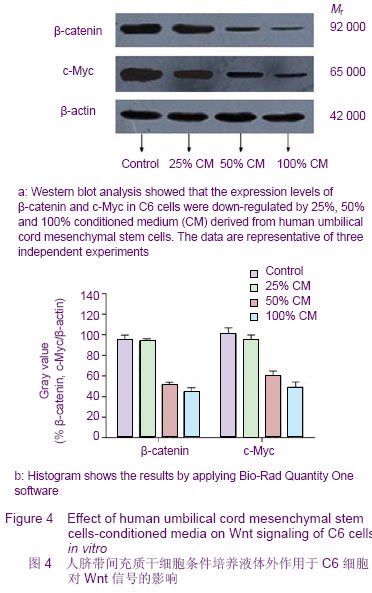
2.5 hUC-MSCs对C6细胞Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路蛋白表达的影响 Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号转导途径在肿瘤的发生发展中起着至关重要的作用[19-20]。Western blotting结果显示,在hUC-MSCs条件培养液作用下,C6细胞中β-连环蛋白和c-Myc蛋白表达水平下调,见图 4。尽管25%CM组β-连环蛋白和c-Myc表达水平有减小的趋势,但与对照组相比没有明显的变化。然而,随着条件培养液浓度的增加,50%和100% CM组中β-连环蛋白和c-Myc蛋白表达明显下降。因此,结果说明,hUC-MSCs条件培养液中的一些可溶性因子可能参与了抑制C6细胞中Wnt信号途径的过程。"
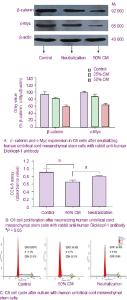
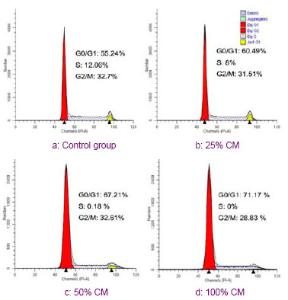
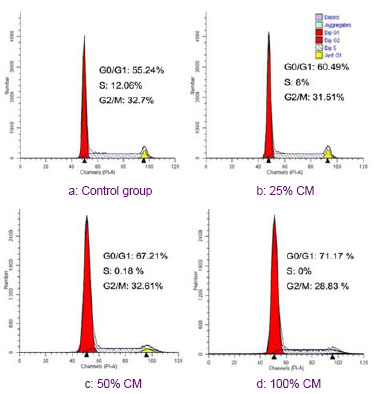
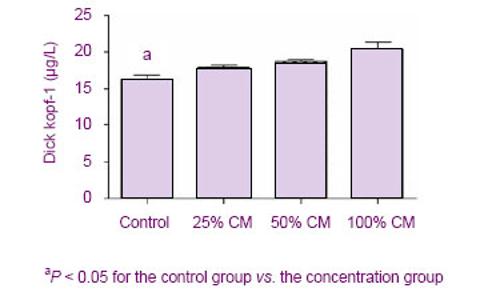
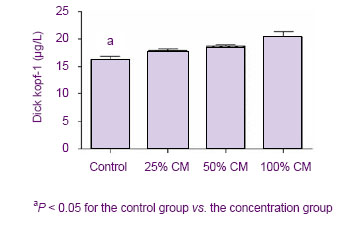
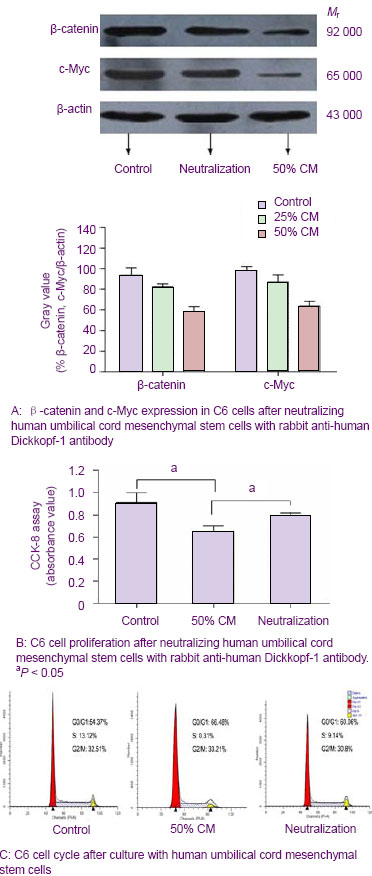
结果显示,Dickkopf-1蛋白的分泌水平与hUC-MSCs条件培养液的浓度呈正相关。随着条件培养液浓度的增加,Dickkopf-1的分泌量逐渐增多。 2.7 抗体中和效应 见图6。为了进一步证实Dickkopf-1是间充质干细胞抑制细胞增殖的一个关键因子,实验使用了抗Dickkopf-1的抗体来中和hUCMSCs-CM,然后用于处理C6细胞。结果发现,用兔抗人Dickkopf-1多克隆抗体预处理的hUCMSCs-CM失去了下调C6细胞中β-连环蛋白和 c-Myc表达水平的能力,见图6A。同时,CCK-8结果显示,Dickkopf-1中和部分地减弱了hUCMSCs-CM抑制C6细胞增殖的能力,见图6B。流式细胞仪结果显示用hUCMSCs-CM处理的C6细胞在G0/G1期的百分比由54.37%增加到66.48%,见图6C。然而,当Dickkopf-1的活性被抗Dickkopf-1的抗体部分中和后,C6细胞在G0/G1期的百分比由66.48%减少到60.06%,见图6C。这些数据说明,Dickkopf-1的中和作用部分地减弱了hUCMSCs-CM对C6细胞生长的抑制作用,提示了hUCMSCs-CM中的Dickkopf-1具有抑制C6细胞生长的作用。"
| [1] Donato V, Papaleo A, Castrichino A, et al. Prognostic implication of clinical and pathologic features in patients with glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide. Tumori. 2007;93(3):248-256.[2] Kang SG, Kim JH, Nam DH,et al. Clinical and radiological prognostic factors of anaplastic oligodendroglioma treated by combined therapy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2005; 45(5): 232-238. [3] Scheda A, Finjap JK, Tuettenberg J, et al. Ef?cacy of different regimens of adjuvant radiochemotherapy for treatment of glioblastoma. Tumori.2007; 93(1):31-36.[4] Fagioli F, Berger M, Braeh del Preyer A, et al.Regression of metastatic oateosmcoma following non-myeloab]ative stem cell transplantation.Haenmtologiea. 2003; 88(5):16.[5] Omuro Y, Matsumote G, Sasaki T, et al.Regression of nunresectable pancreatic tumor following nonmyeloablative allogeneic peripheral-blood stem-cell transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant.2003; 31(10):943-945.[6] Kim S K, Cargioll TG, Machluf Mt, et al.PEX-Producing human neural stem cells inhibit tumor growth in a mouse g1ioma model.Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11(16):5965-5970.[7] Khakoo AY, Pati S, Anderson SA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells exert potent antitumorigenic effects in a model of Kaposi’s sarcoma.J Exp Med.2006; 203(5):1235-1247.[8] Jiao HL, Guan FX, Yang B,et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit C6 glioma via downregulation of cyclin D1. Neurology India.2011; 59(2): 241-247.[9] Yang F, Zeng Q, Yu G,et al.Wnt/beta-catenin signaling inhibits death receptor-mediated apoptosis and promotes invasive growth of HNSCC. Cell Signal.2006; 18(2):679-687.[10] Baek SH, Kioussi C, Briata P. Regulated subset of G1 growth-control genes in response to derepression by the Wnt pathway. Proc Natl Acad USA.2003;100(6): 3245-3250.[11] Brott BK, Sokol SY. Regulation of Wnt/LRP signaling by distinct domains of Dickkopf proteins. Mol Cell Biol.2002; 22(17):6100-6110.[12] Chen G, Shukeir N, Potti A, et al. Up-regulation of Wnt-1 and beta-catenin production in patients with advanced metastatic prostate carcinoma: potential pathogenetic and prognosticimplications. Cancer. 2004; 101(6):1345-1356.[13] Byun T, Karimi M, Marsh JL, et al. Expression of secreted Wnt antagonists in gastrointestinal tissues: potential role in stem cell homeostasis. J Clin Pathol. 2005; 58(5):515-519.[14] Mao B, Wu W, Li Y, et al. LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature.2001; 411(6835): 321-325.[15] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E, et al. Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells.2007; 25(2) :319-331.[16] Livraghi T, Meloni F, Frosi A, et al. Treatment with stem cell differentiation stage factors of intermediate-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Res. 2005;15(7/8):399-408.[17] Lu YR, Yuan Y, Wang XJ,et al. The growth inhibitory effect of mesenchymal stem cells on tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008; 7(2):245-251.[18] Qiao L, Xu ZL, Zhao TJ,et al. Dkk-1 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells inhibits growth of breast cancer cells via depression of Wnt signaling. Cancer Lett. 2008; 269(1): 67-77.[19] Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV,et al. Wnt and β-catenin signalling: diseases and therapies.Nat Rev Genet. 2004; 5(9): 691-701.[20] Fodde R, Brabletz T. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007; 19(2):150-158.[21] Glennie S, Soeiro I, Dyson PJ,et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells. Blood. 2005; 105(7): 2821-2827. [22] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006; 107(1): 367-372.[23] Sotiropoulou PA, Perez SA, Gritzapis AD,et al. Interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and natural killer cells. Stem Cells.2006; 24(1): 74-85.[24] Zhu Y, Sun Z, Han Q, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit cancer cell proliferation by secreting DKK-1. Leukemia. 2009; 23(5):925-933.[25] Meisel R, Zibert A, Laryea M,et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells inhibit allogeneic T-cell responses by indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase-mediated tryptophan degradation. Blood.2004; 103(12): 4619-4621.[26] Qiao L, Xu ZL, Zhao TJ, et al. Suppression of tumorigenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells in a hepatoma model. Cell Res. 2008;18(12): 500-507. [27] Ramasamy R, Lam EF, Soeiro I, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation and apoptosis of tumor cells: impact on in vivo tumor growth. Leukemia.2007; 21(2):304–310.[28] Zhu W, Xu W, Jiang R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow favor tumor cell growth in vivo. Exp Mol Pathol.2006; 80(3): 267-274.[29] Ma Y, Hao XM, Zhang S,et al. The in vitro and in vivo effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on the growth of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.2011; 80(1): 267-274.[30] Studeny M, Marini FC, Dembinski JL.Mesenchymal stem cells: potential precursors for tumor stroma and targeted-delivery vehicles for anticancer agents, J. Natl. Cancer Inst.2004; 96 (21):1593–1603. |
| [1] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [2] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Liu Xun, Ouyang Hougan, Pan Rongbin, Wang Zi, Yang Fen, Tian Jiaxuan . Optimal parameters for physical interventions in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6727-6732. |
| [4] | Hu Enxi, He Wenying, Tao Xiang, Du Peijing, Wang Libin. Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5374-5381. |
| [5] | Lin Meiyu, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Zhao Jing, Ruan Guangping. Action mechanism and progress of stem cells against ovarian granulosa cell senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5414-5421. |
| [6] | Tian Zhenli, Zhang Xiaoxu, Fang Xingyan, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on lipid metabolism in human hepatocytes and regulatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4956-4964. |
| [7] | Han Fang, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Electrotactic migration and mechanisms of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4984-4992. |
| [8] | Hu Chen, Jiang Ying, Chen Jia, Qiao Guangwei, Dong Wen, Ma Jian. Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4720-4730. |
| [9] | Yang Chao, Luo Zongping. Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2648-2654. |
| [10] | Li Xiaofeng, Zhao Duo, Ouyang Qin, Pang Zixiang, Li Yuquan, Chen Qianfen. Protective effect of mangiferin on oxidative stress injury in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2669-2674. |
| [11] | Hu Zezun, Yang Fanlei, Xu Hao, Luo Zongping. Effect of surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under stretching conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1981-1989. |
| [12] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [13] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [14] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [15] | Zhou Shijie, Li Muzhe, Yun Li, Zhang Tianchi, Niu Yuanyuan, Zhu Yihua, Zhou Qinfeng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Wang Lining. Effect of Wenshen Tongluo Zhitong formula on mouse H-type bone microvascular endothelial cell/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||