Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9168-9173.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of different oxygen tensions on gene expression profiling of human embryonic stem cells
Guo Li-yuan1,2,3, Liu Wei-qiang1,2,3, He Wen-zhi1,2,3, Li Qing1,2,3, Sun Xiao-fang1,2,3
- 1Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical College, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; 2Key Laboratory for Major Obstetric Diseases of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Reproduction and Genetics, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2012-02-22Revised:2012-04-05Online:2012-12-02Published:2013-01-16 -
Contact:Sun Xiao-fang, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical College, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; Key Laboratory for Major Obstetric Diseases of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Reproduction and Genetics, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China xiaofangsun@hotmail.com -
About author:Guo Li-yuan★, Studying for master’s degree, Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical College, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; Key Laboratory for Major Obstetric Diseases of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Reproduction and Genetics, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China Liyuan-guo@hotmail.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30871378*, U1132005*; Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. A2011280*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Li-yuan, Liu Wei-qiang, He Wen-zhi, Li Qing, Sun Xiao-fang. Effects of different oxygen tensions on gene expression profiling of human embryonic stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(49): 9168-9173.
share this article
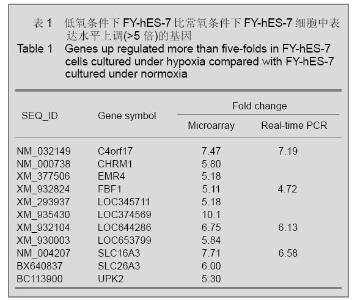
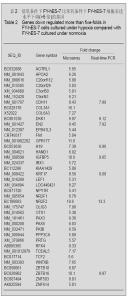
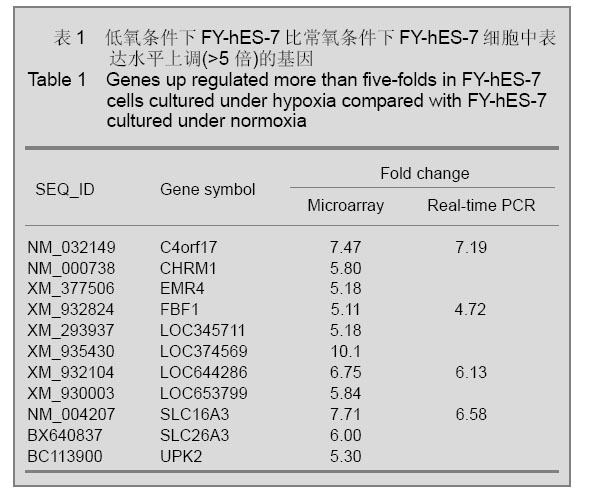
2.2 不同氧体积分数组FY-hES-7细胞的基因表达谱差异 实验利用Roche-NimbleGen Human Gene Expression Microarrays对不同氧体积分数组FY-hES-7细胞之间基因的表达情况进行对比分析,共发现低氧组比常氧组表达上调2倍以上基因1 840个,其中上调5倍以上者11个,见表1,而表达下调2倍以上基因1 676个,其中下调5倍以上者40个,见表2。 2.5 基因芯片结果的real-time PCR验证 验证结果表明基因C4orf17、LOC644286、FBF1、SLC16A3在低氧组中表达明显上调,而基因CDH11、DKK1、EN2、H19、IGFBP5、KRT17、NR2F2、ZBTB16表达明显下调,与芯片结果相似,见表1,2,由此可见实验获得的芯片结果比较可靠。"
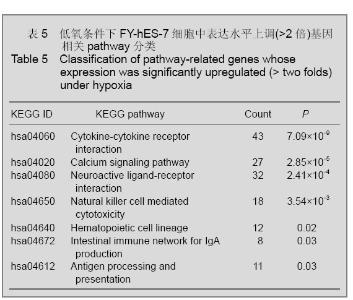
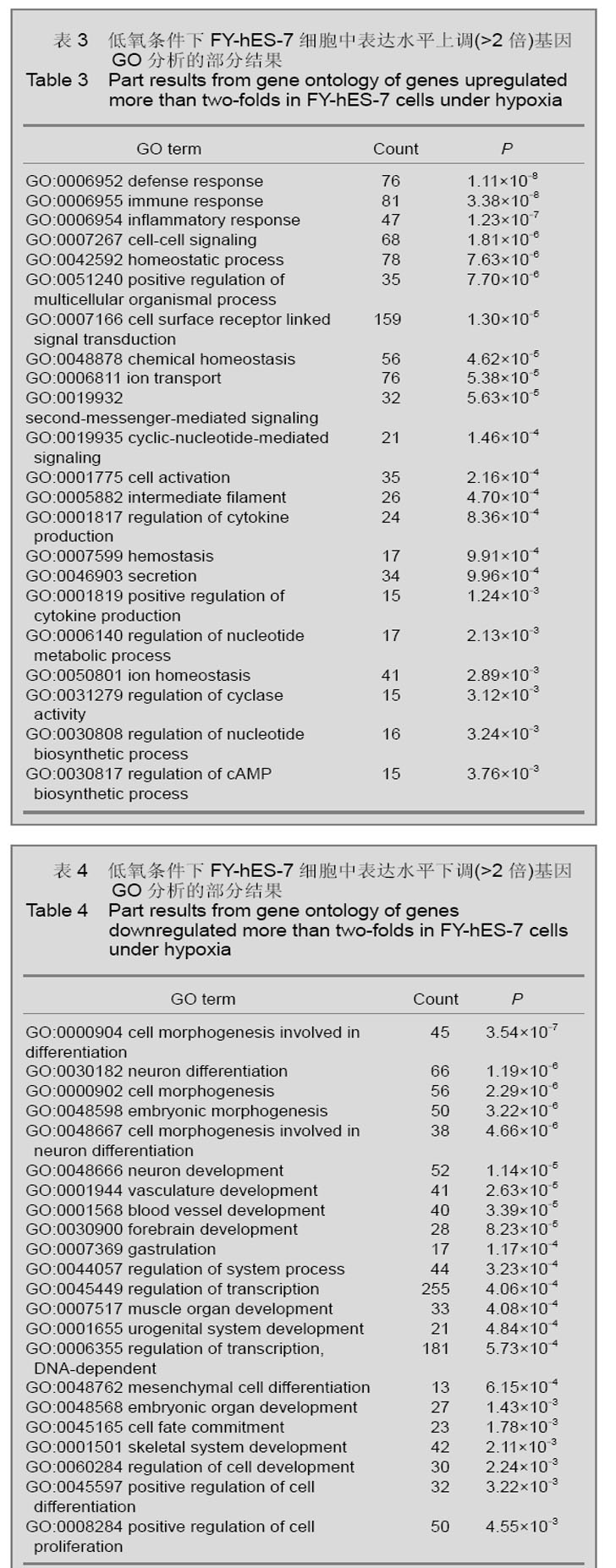
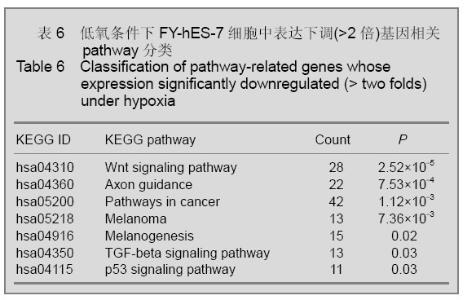
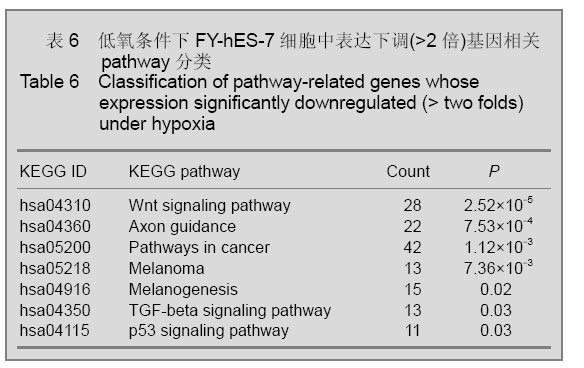
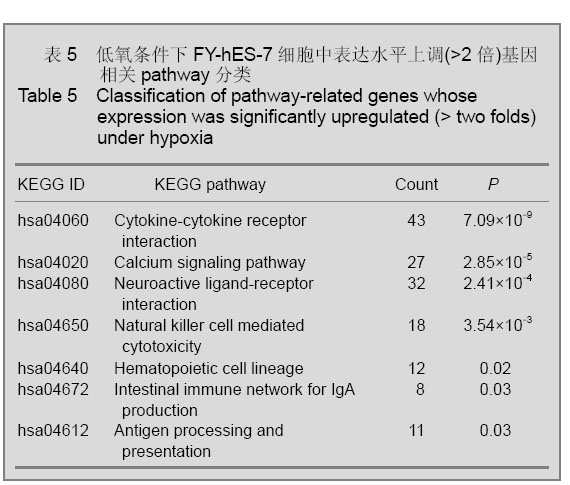
2.4 KEGG通路分析结果 通过对不同氧体积分数组差异表达(>2倍)基因的通路分析,发现对比常氧组,低氧组差异表达基因相关的细胞通路共有14条(P < 0.05),见表5,6。 表5,6可见低氧组中表达上调的基因与细胞因子受体的相互作用(cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction),免疫反应(intestinal immune network for IgA production;antigen processing and presentation)以及造血系统(hematopoietic cell lineage)等通路的改变相关,而表达下调基因则与胚胎发育(Wnt signaling pathway),肿瘤发生(pathways in cancer;Melanoma;Melanogenesis;TGF-beta signaling pathway;p53 signaling pathway)等通路改变相关。"
| [1] Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282(5391):1145-1147.[2] Westfall SD, Sachdev S, Das P, et al. Identification of oxygen-sensitive transcriptional programs in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(5):869-881.[3] Forristal CE, Wright KL, Hanley NA, et al. Hypoxia inducible factors regulate pluripotency and proliferation in human embryonic stem cells cultured at reduced oxygen tensions. Reproduction. 2010;139(1):85-97.[4] Cowan CA, Klimanskaya I, McMahon J, et al. Derivation of embryonic stem-cell lines from human blastocysts. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(13):1353-1356.[5] Forsyth NR, Musio A, Vezzoni P, et al. Physiologic oxygen enhances human embryonic stem cell clonal recovery and reduces chromosomal abnormalities. Cloning Stem Cells. 2006;8(1):16-23.[6] Lim HJ, Han J, Woo DH, et al. Biochemical and morphological effects of hypoxic environment on human embryonic stem cells in long-term culture and differentiating embryoid bodies. Mol Cells. 2011;31(2):123-132.[7] Millman JR, Tan JH, Colton CK. The effects of low oxygen on self-renewal and differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2009;14(6):694-700.[8] Zachar V, Prasad SM, Weli SC, et al. The effect of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) long-term normoxic and hypoxic cultures on the maintenance of pluripotency. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010;46(3-4):276-283.[9] Ezashi T, Das P, Roberts RM. Roberts, Low O2 tensions and the prevention of differentiation of hES cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(13):4783-4788.[10] Prasad SM, Czepiel M, Cetinkaya C, et al. Continuous hypoxic culturing maintains activation of Notch and allows long-term propagation of human embryonic stem cells without spontaneous differentiation. Cell Prolif. 2009;42(1):63-74.[11] Forsyth NR, Kay A, Hampson K, et al. Transcriptome alterations due to physiological normoxic (2% O2) culture of human embryonic stem cells. Regen Med. 2008;3(6): 817-833.[12] Simon MC, Keith B. The role of oxygen availability in embryonic development and stem cell function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(4):285-296.[13] Sun X, Long X, Yin Y, et al. Similar biological characteristics of human embryonic stem cell lines with normal and abnormal karyotypes. Hum Reprod. 2008;23(10):2185-2193.[14] Chen HF, Kuo HC, Chen W, et al. A reduced oxygen tension (5%) is not beneficial for maintaining human embryonic stem cells in the undifferentiated state with short splitting intervals. Hum Reprod. 2009;24(1):71-80.[15] Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44-57.[16] Moon SH, Kim SW, Kim JS, et al. Gene expression profiles in CHA3 and CHA4 human embryonic stem cells and embryoid bodies. Mol Cells. 2011;31(4):315-326.[17] Zhao M, Ren CP, Yang H, et al. Shengming Kexue Yanjiu. 2008;12(1):61-65.赵明,任彩萍,杨红,等.人胚胎干细胞和拟胚体基因表达谱的初步分析[J].生命科学研究,2008,12(1):61-65.[18] Rocha S. Gene regulation under low oxygen: holding your breath for transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32(8): 389-397. |
| [1] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [2] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Liu Xun, Ouyang Hougan, Pan Rongbin, Wang Zi, Yang Fen, Tian Jiaxuan . Optimal parameters for physical interventions in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6727-6732. |
| [4] | Hu Enxi, He Wenying, Tao Xiang, Du Peijing, Wang Libin. Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5374-5381. |
| [5] | Lin Meiyu, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Zhao Jing, Ruan Guangping. Action mechanism and progress of stem cells against ovarian granulosa cell senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5414-5421. |
| [6] | Tian Zhenli, Zhang Xiaoxu, Fang Xingyan, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on lipid metabolism in human hepatocytes and regulatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4956-4964. |
| [7] | Han Fang, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Electrotactic migration and mechanisms of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4984-4992. |
| [8] | Hu Chen, Jiang Ying, Chen Jia, Qiao Guangwei, Dong Wen, Ma Jian. Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4720-4730. |
| [9] | Yang Chao, Luo Zongping. Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2648-2654. |
| [10] | Li Xiaofeng, Zhao Duo, Ouyang Qin, Pang Zixiang, Li Yuquan, Chen Qianfen. Protective effect of mangiferin on oxidative stress injury in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2669-2674. |
| [11] | Hu Zezun, Yang Fanlei, Xu Hao, Luo Zongping. Effect of surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under stretching conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1981-1989. |
| [12] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [13] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [14] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [15] | Zhou Shijie, Li Muzhe, Yun Li, Zhang Tianchi, Niu Yuanyuan, Zhu Yihua, Zhou Qinfeng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Wang Lining. Effect of Wenshen Tongluo Zhitong formula on mouse H-type bone microvascular endothelial cell/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||