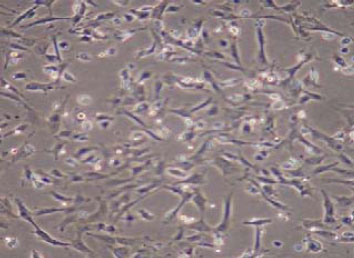
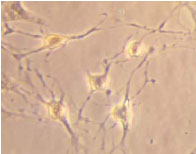
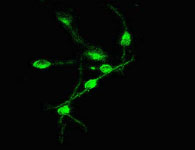
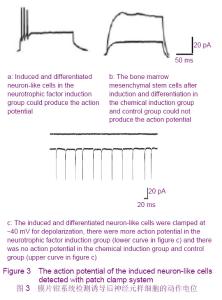
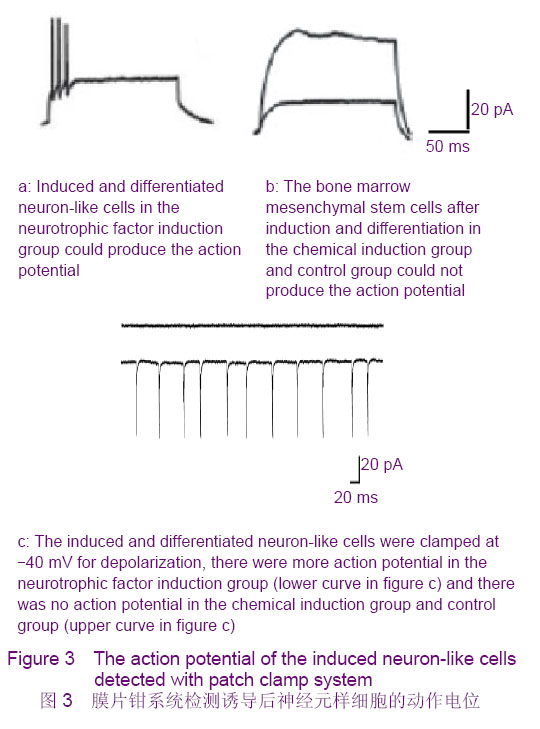
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9121-9127.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.001
Trans-differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into functional neurons
Huang Bao-sheng1, Wang Tian-lu1, Li Li-xin2, Xie Qing-song2, Tian He-ping2, Zhang Yin1
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, BenQ Medical Center, Nanjing Medical University, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing 210019, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2012-08-28Revised:2012-09-13Online:2012-12-02Published:2013-01-16 -
Contact:Wang Tian-lu, Chief physician, Department of Neurosurgery, BenQ Medical Center, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210019, Jiangsu Province, China timu.wang@benqhospital.com -
About author:Huang Bao-sheng★, Master, Attending neurosurgeon, Department of Neurosurgery, BenQ Medical Center, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210019, Jiangsu Province, China bosen.huang@benqhospital.com -
Supported by:Medical Technology Development Project of Nanjing Health Department, No.QKK10194*; Scientific Research Staring Foundation of Nanjing BenQ Medical Center, No.SRD20100008*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Bao-sheng, Wang Tian-lu, Li Li-xin, Xie Qing-song, Tian He-ping, Zhang Yin. Trans-differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into functional neurons[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(49): 9121-9127.
share this article
| [1] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255(5052):1707-1710.[2] Ferrari G, Cusella-De Angelis G, Coletta M, et al. Muscle regeneration by bone marrow-derived myogenic progenitors. Science. 1998;279(5356):1528-1530.[3] Grigorian AS, Gilerovich EG, Pavlichenko NN, et al. Effect of transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells on neuronal survival and formation of a glial scar in the brain of rats with severe traumatic brain injury. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2011;150(4): 551-555.[4] Nikitina VA, Chausheva AI, Zhanataev AK, et al. Assessment of DNA damage in human bone marrow cells and multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2011;151(4): 550-552.[5] Kim BJ, Seo JH, Bubien JK, et al. Differentiation of adult bone marrow stem cells into neuroprogenitor cells in vitro. Neuroreport. 2002;13(9):1185-1188.[6] Yang HJ, Xia YY, Wang L, et al. A novel role for neural cell adhesion molecule in modulating insulin signaling and adipocyte differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 15):2552-2560.[7] Wu YX, Wang Y, Ben XM. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(1):11-14.吴玉新,王燕,贲晓明.表皮生长因子干预小鼠非黏附骨髓间充质干细胞成纤维细胞集落形成及向神经元样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(1):11-14.[8] Shakhbazau AV, Petyovka NV, Kosmacheva SM, et al. Neurogenic induction of human mesenchymal stem cells in fibrin 3D matrix. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2011;150(4):547-550.[9] Li XF, Zhao JM, Su W, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(10):1721-1725.李晓峰,赵劲民,苏伟,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(10):1721-1725.[10] Ba YC, Tang JZ, Fan Y, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(6):1050-1055.巴迎春,唐建中,范艳,等.脊髓损伤亚急性期移植神经干细胞:损伤脊髓5-羟色胺的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(6): 1050-1055.[11] Iwanami A, Kaneko S, Nakamura M, et al. Transplantation of human neural stem cells for spinal cord injury in primates. J Neurosci Res. 2005;80(2):182-190.[12] He XY, Shen HY, Xiang P, et al. Zhongguo Yundong Yixue Zazhi. 2010;29(2):208-210.贺晓玉,沈慧勇,项鹏,等.人神经干细胞移植对脊髓损伤大鼠后肢运动功能恢复的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(2):208- 210.[13] Yang QG, Zhang Q, Chen YP, et al. Functional recovery of njured sciatic nerve by ntraperitoneal injection of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(7):505-509.[14] Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276(5309):71-74.[15] Rogers TB, Pati S, Gaa S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells stimulate protective genetic reprogramming of injured cardiac ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50(2):346-356. [16] Boxall SA, Jones E. Markers for characterization of bone marrow multipotential stromal cells. Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012: 975871.[17] Sher L. The role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the pathophysiology of adolescent suicidal behavior. Int J Adolesc Med Health. 2011;23(3):181-185.[18] Li L, Xu Q, Wu Y, et al. Combined therapy of methylprednisolone and brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes axonal regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. Chin Med J (Engl). 2003;116(3): 414-418.[19] Chen L, Zhang ZG, Chen B, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces neuron-like cellular differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood cells in vitro. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(13):972-977.[20] Fan CG, Zhang QJ, Han ZC. Zhonghua Shenjing Waike Zazhi. 2005;21(7):387-392.范存刚,张庆俊,韩忠朝.人脐带间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化的研究[J].中华神经外科杂志,2005,21(7):387-392. [21] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[22] Cronberg T, Rundgren M, Westhall E, et al. Neuron-specific enolase correlates with other prognostic markers after cardiac arrest. Neurology. 2011;77(7):623-630.[23] Guo Y, Gong HS, Zhang J, et al. Remarkable reduction of MAP2 in the brains of scrapie-infected rodents and human prion disease possibly correlated with the increase of calpain. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30163. [24] Zhou JY, Zhang QJ. Zhonghua Shenjing Waike Zazhi. 2008 ; 24(3):216-219.周剑云,张庆俊.人脐带间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化过程中ILK的表达变化及意义[J].中华神经外科杂志, 2008,24(3):216- 219.[25] Deng W, Obrocka M, Fischer I, et al. In vitro differentiation of human marrow stromal cells into early progenitors of neural cells by conditions that increase intracellular cyclic AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;282(1): 148-152. [26] Kuo YC, Chiu KH. Inverted colloidal crystal scaffolds with laminin-derived peptides for neuronal differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(3): 819-831. [27] Zeng R, Hu ZB, Guo WT, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(6):1030-1034.曾荣,胡资兵,郭伟韬,等.依达拉奉体外定向诱导人间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(6):1030-1034.[28] Wilkins A, Kemp K, Ginty M, et al. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor which promotes neuronal survival in vitro. Stem Cell Res. 2009;3(1):63-70. [29] Conforti E, Arrigoni E, Piccoli M, et al. Reversine increases multipotent human mesenchymal cells differentiation potential. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2011;25(2 Suppl):S25-33.[30] Honglin Q, Liu RL. Researches on application of stem cell therapy in exercise-induced spinal cord injury recovery. Adv Intell Soft Comput. 2012;119:95-101.[31] Park WB, Kim SY, Lee SH, et al. The effect of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on the recovery of bladder and hindlimb function after spinal cord contusion in rats. BMC Neurosci. 2010;11:119.[32] Guo ZY, Jiang XD, Xu RX, et al. Zhonghua Shenjing Yixue Zazhi. 2005;4(6):545-550.郭再玉,姜晓丹,徐如祥,等.骨髓基质细胞源性神经干细胞体外分化及电生理特性的研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2005,4(6): 545-550.[33] Mareschi K, Novara M, Rustichelli D, et al. Neural differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells: Evidence for expression of neural markers and eag K+ channel types. Exp Hematol. 2006;34(11):1563-1572. |
| [1] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [2] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Liu Xun, Ouyang Hougan, Pan Rongbin, Wang Zi, Yang Fen, Tian Jiaxuan . Optimal parameters for physical interventions in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6727-6732. |
| [4] | Hu Enxi, He Wenying, Tao Xiang, Du Peijing, Wang Libin. Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5374-5381. |
| [5] | Lin Meiyu, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Zhao Jing, Ruan Guangping. Action mechanism and progress of stem cells against ovarian granulosa cell senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5414-5421. |
| [6] | Tian Zhenli, Zhang Xiaoxu, Fang Xingyan, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on lipid metabolism in human hepatocytes and regulatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4956-4964. |
| [7] | Han Fang, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Electrotactic migration and mechanisms of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4984-4992. |
| [8] | Hu Chen, Jiang Ying, Chen Jia, Qiao Guangwei, Dong Wen, Ma Jian. Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4720-4730. |
| [9] | Yang Chao, Luo Zongping. Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2648-2654. |
| [10] | Li Xiaofeng, Zhao Duo, Ouyang Qin, Pang Zixiang, Li Yuquan, Chen Qianfen. Protective effect of mangiferin on oxidative stress injury in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2669-2674. |
| [11] | Hu Zezun, Yang Fanlei, Xu Hao, Luo Zongping. Effect of surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under stretching conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1981-1989. |
| [12] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [13] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [14] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [15] | Zhou Shijie, Li Muzhe, Yun Li, Zhang Tianchi, Niu Yuanyuan, Zhu Yihua, Zhou Qinfeng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Wang Lining. Effect of Wenshen Tongluo Zhitong formula on mouse H-type bone microvascular endothelial cell/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||