Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 14-14.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Changes in serum levels of fibroblast growth factor-2, hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with avascular necrosis of femoral head treated by enriched autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation combined with core decompression
Zhang Jingyi, Hai Guodong, Yang Haofei, Fan Congliang, Yan Lei, Zhang Chunlei, Dou Junfeng, Ma Hailong
- Zhengzhou Orthopedics Hospital, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2019-06-19Revised:2019-06-21Accepted:2019-08-01Online:2020-01-08Published:2019-12-10 -
Contact:Hai Guodong, Master, Chief physician, Zhengzhou Orthopedics Hospital, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jingyi, Master, Attending physician, Zhengzhou Orthopedics Hospital, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Research & Development Project of Henan Province in 2018, No. 182102310475
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jingyi, Hai Guodong, Yang Haofei, Fan Congliang, Yan Lei, Zhang Chunlei, Dou Junfeng, Ma Hailong. Changes in serum levels of fibroblast growth factor-2, hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with avascular necrosis of femoral head treated by enriched autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation combined with core decompression[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 14-14.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
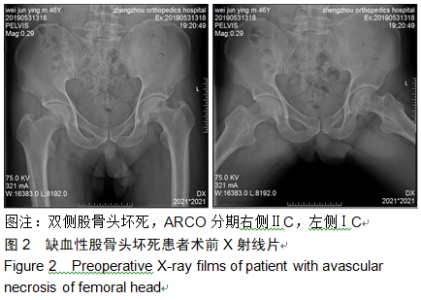
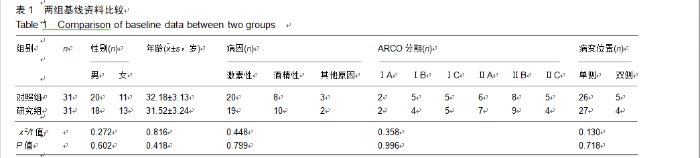
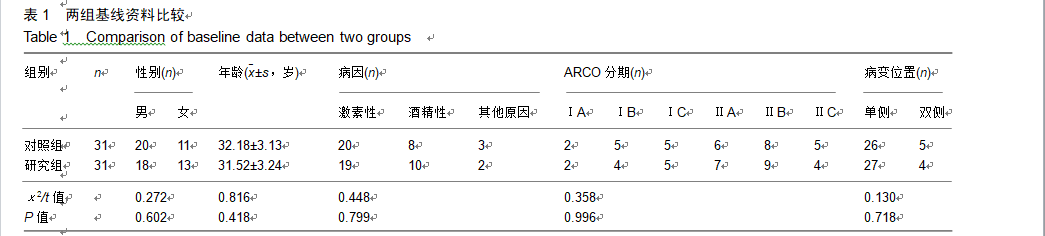
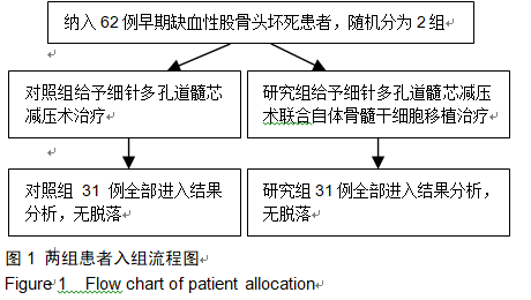
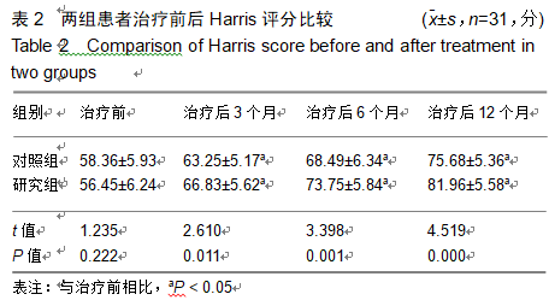
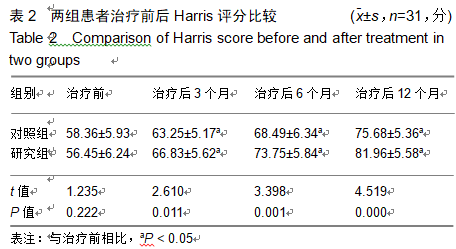
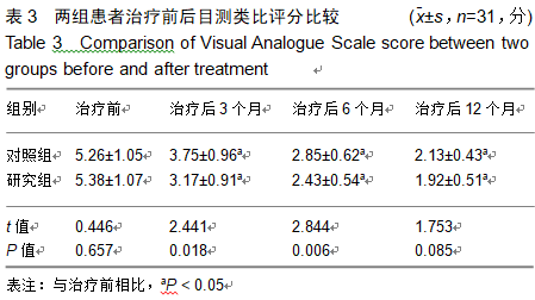
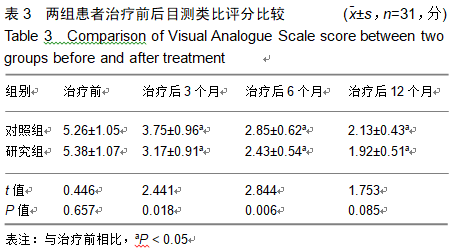
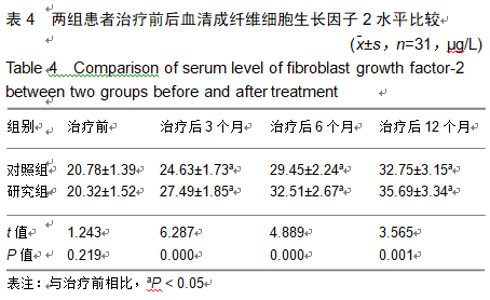
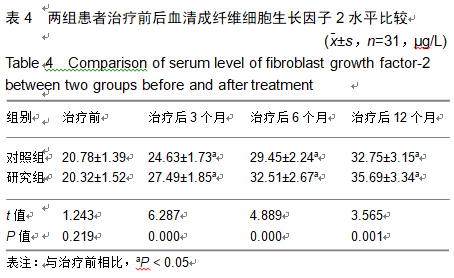
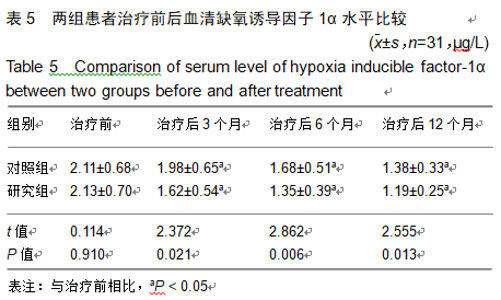
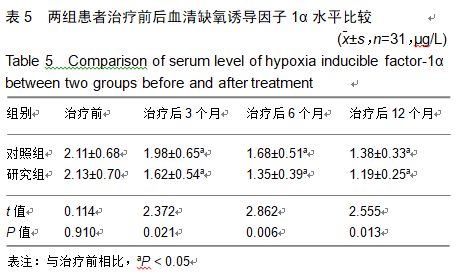
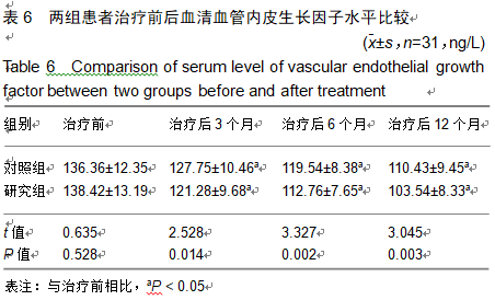
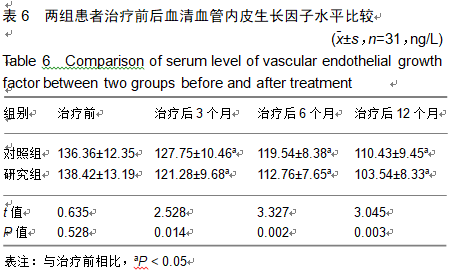
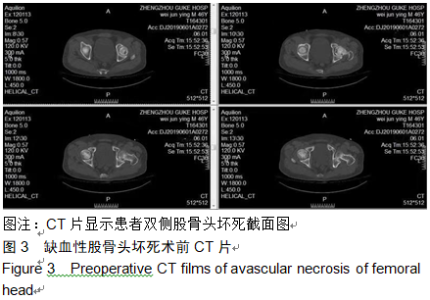
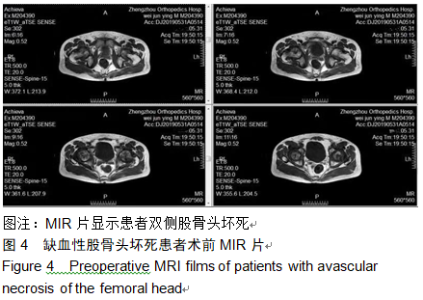
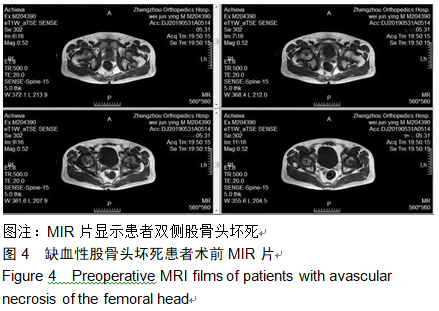
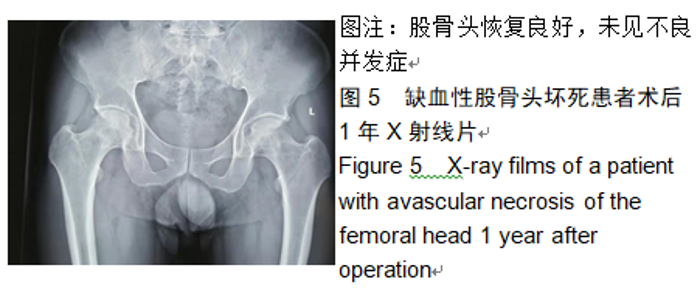
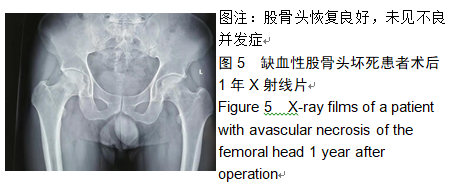
2.9 两组治疗后不良反应发生情况比较 治疗后随访1年,研究组出现切口感染1例,股骨头周围感染1例,不良反应发生率为6%(2/31);对照组出现股骨头塌陷1例,股骨头周围感染3例,不良反应发生率为13%(4/31)。股骨头塌陷患者给予关节置换,股骨头周围感染患者进行局部及全身消炎处理,感染得以控制,未影响髋关节功能。两组不良反应发生率比较差异无显著性意义(χ2=0.185,P=0.668)。 2.10 典型病例 患者男,46岁,双侧股骨头坏死,ARCO分期右侧ⅡC,左侧ⅠC,左侧股骨头坏死行钻孔减压术,术后减少负重行走7个月,经患者同意进行自体骨髓干细胞移植联合细针多孔道髓芯减压术治疗,右侧股骨头坏死行自体骨髓干细胞移植联合细针多孔道髓芯减压术治疗,术后1年半,现恢复良好,左髋部疼痛及活动受限消失。术后X射线检查股骨头恢复良好,未见不良并发症,见图2-6。 "
|
[1]GUERADO E, CASO E. The physiopathology of
avascular necrosis of the femoral head: an update. Injury. 2016;47 Suppl 6: S16-S26.
[2]NARAYANAN A, KHANCHANDANI P, BORKAR RM, et
al. Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head: A Metabolomic, Biophysical,
Biochemical, Electron Microscopic and Histopathological Characterization. Sci
Rep. 2017;7(1):10721.
[3]PYDA M, KOCZY B, WIDUCHOWSKI W, et al. Hip
resurfacing arthroplasty in treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral
head. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:304-309.
[4]常再平,王林,李龙,等.髋关节置换术对股骨头坏死患者髋关节Harris评分及运动功能的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(11): 2116-2118.
[5]LI X, XU X, WU W. Comparison of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells and core decompression in treatment of osteonecrosis of
the femoral head: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7(8):5024-5030.
[6]王得胜,侯毅,刘腾,等.超选择血管介入联合髓芯减压植骨术治疗早中期股骨头缺血性坏死的效果观察[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2019, 33(1): 35-36.
[7]朱孟国,张玉梅,王厚义,等.自拟骨愈方联合急诊手术对跟骨SandersⅡ~Ⅲ型闭合骨折HIF-1α及VEGF表达的影响[J].中国中医急症, 2018,27(2):230-232.
[8]仝晓阳,李慧,张苗,等.VEGF和EGFL在骨血管生成中的作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2017, 39(11):1461-1464.
[9]章坚林,于博,刘柱同.胫骨骨折髓内钉固定围术期血清FGF-2和IGF-1水平联合预测其术后骨不连的价值[J].广东医学,2018, 39(1): 122-125.
[10]张晓军,刘健,万磊,等.佐剂关节炎大鼠滑膜组织HIF-1α和VEGF及CD34表达上调促进血管新生[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2015, 31(8):1053-1056.
[11]KURODA Y, ASADA R, SO K, et al. A pilot study
of regenerative therapy using controlled release of recombinant human
fibroblast growth factor for patients with pre-collapse osteonecrosis of the
femoral head. Int Orthop. 2016;40(8):1747-1754.
[12]李子荣.股骨头坏死临床诊疗规范[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2015, 24(1):97-100.
[13]HARRIS WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip
after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An
end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
1969;51(4):737-755.
[14]严广斌.
视觉模拟评分法[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014, 8(2): 125-128.
[15]LIAO Y, SU R, ZHANG P, et al. Cortisol
inhibits mTOR signaling in avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop
Surg Res. 2017; 12(1):154.
[16]MONT MA, CHERIAN JJ, SIERRA RJ, et al.
Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A Ten-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg
Am.2015;97(19): 1604-1627.
[17]余燕娜,汤水福.中医辨证预防肾病综合征患者激素性股骨头坏死的回顾性分析[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2017,18(10):910-911.
[18]LANDGRAEBER S, TRAN TN, CLAßEN T, et al.
Geometric analysis of an expandable reamer for treatment of avascular necrosis
of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015; 135(10):1357-1362.
[19]余振阳,蔡谞,谷旺.改良多孔道髓芯减压术与传统钻孔减压术治疗早期股骨头缺血坏死的疗效观察[J].解放军医学院学报, 2016, 37(11): 1148-1151.
[20]石卫青,付阳阳,邱依辉,等.多孔道细针髓芯减压预防性治疗0期股骨头坏死的手术配合[J].军事医学, 2016, 40(11):936-936.
[21]杨宾宾,刘耀升,刘蜀彬,等.多种髓芯减压术治疗股骨头坏死的有限元研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2017, 12(1):39-45.
[22]李冀,李众利,苏祥正,等.小直径多孔道髓芯减压联合髋关节镜清理治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017,31(9): 1025-1030.
[23]王秀利,王义生,吴学建,等.自体骨髓干细胞种植骨诱导活性材料移植联合髓芯减压术治疗早期股骨头坏死[J].中华显微外科杂志, 2017,40(2): 142-145.
[24]DALTRO G, FRANCO BA, FALEIRO TB, et al. Use
of autologous bone marrow stem cell implantation for osteonecrosis of the knee
in sickle cell disease: a preliminary report. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018; 19(1):158.
[25]HEO SH, PARK YS, KANG ES, et al. Early
Results of Clinical Application of Autologous Whole Bone Marrow Stem Cell
Transplantation for Critical Limb Ischemia with Buerger's Disease. Sci Rep.
2016;6:19690.
[26]YUAN HF, ZHANG J, GUO CA, et al. Clinical
outcomes of osteonecrosis of the femoral head after autologous bone marrow stem
cell implantation: a meta-analysis of seven case-control studies. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 2016;71(2):110-113.
[27]赵日光,刘宏滨,韩冰,等.髓芯减压联合自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的疗效观察[J].人民军医,2016,59(4):372-373.
[28]KANG JS, SUH YJ, MOON KH, et al. Clinical
efficiency of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell implantation for osteonecrosis
of the femoral head: a matched pair control study with simple core
decompression. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):274.
[29]张洋,王楠,杨立枫,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植联合髓芯减压植骨修复股骨头坏死[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(6):883-890.
[30]AWAN B, TURKOV D, SCHUMACHER C, et al. FGF2
Induces Migration of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells by Increasing Core
Fucosylations on N-Glycans of Integrins. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;11(2):325-333.
[31]YOON KA, SON Y, CHOI YJ, et al. Fibroblast
growth factor 2 supports osteoblastic niche
cells during hematopoietic homeostasis recovery after bone marrow
suppression. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15(1):25.
[32]HUANG G, ZHAO G, XIA J, et al. FGF2 and
FAM201A affect the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head after
femoral neck fracture. Gene. 2018;652:39-47.
[33]PRIETO-DOMÍNGUEZ N, MÉNDEZ-BLANCO C, CARBAJO-
PESCADOR S, et al. Melatonin enhances sorafenib actions in human
hepatocarcinoma cells by inhibiting mTORC1/p70S6K/ HIF-1α and hypoxia-mediated
mitophagy. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(53):91402-91414.
[34]XIAO B, WANG S, YANG G, et al. HIF-1α
contributes to hypoxia adaptation of the naked mole rat. Oncotarget.
2017;8(66): 109941-109951.
[35]ZHANG W, YUAN Z, PEI X, et al. In vivo and in
vitro characteristic of HIF-1α and relative genes in ischemic femoral head
necrosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(6):7210-7216.
[36]PALAZON A, TYRAKIS PA, MACIAS D, et al. An
HIF-1α/VEGF-A Axis in Cytotoxic T Cells Regulates Tumor Progression. Cancer
Cell. 2017;32(5):669-683.
[37]王秀芳,王莉,张艳丽,等.哮喘患儿血清mTOR、HIF-1α及VEGF的表达及意义[J].中国妇幼保健, 2017,32(6):1197-1199.
[38]牟青杰,赵月华,程丹丹,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对氧诱导视网膜病变新生大鼠视网膜新生血管的影响[J].中国当代儿科杂志, 2017, 19(11): 1202-1207.
[39]乔军杰,周萌,黄江,等.低氧诱导因子-1α促进骨折愈合机制的研究进展[J].北京医学, 2018, 40(2):141-143. |
| [1] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [2] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [3] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [4] | Sun Weixing, Zhao Yongchao, Zhao Ranzun. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of myocardial infarction: problems, crux and new breakthrough [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3103-3109. |
| [5] | Cao Linlin, Ding Kaiyang, Song Hao, Wu Guolin, Hu Maogui, Fan Dandan, Zhou Chenyang, Wang Cuicui, Feng Yuanyuan. Efficacy and influencing factors of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of malignant lymphoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1993-1998. |
| [6] | Zhang Wenjian, Ma Lingfu, Wang Zhimin, Mo Wenjian, Zhou Ruiqing. Muscle mass evaluation and influencing factors of sarcopenia in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1999-2004. |
| [7] |
Wang Tiantian, Wang Jianzhong.
Application and prospect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the
treatment of early femoral head necrosis |
| [8] | Cao Guolong, Tian Faming, Liu Jiayin. Lovastatin combined with insulin effects on fracture healing in rat models of bilateral ovariectomized type 2 diabetic mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 673-681. |
| [9] | Zhang Suping, Sun Ling, Wan Dingming, Cao Weijie, Li Li, Liu Changfeng, Liu Yufeng, Wang Dao, Guo Rong, Jiang Zhongxing, Xie Xinsheng. Effectiveness of unrelated peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4994-5001. |
| [10] | Liu Guoming, Wang Qinfen, Lin Kefeng, Zhou Shiguo, Chen Zuxing, Lin Shishui. Whole body application of nerve growth factor promotes early healing of tibial shaft fracture and improves expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4680-4685. |
| [11] | Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Shi Peisheng, Xue Yun, Huang Qiang, Li Chuangbing, Gao Qiuming. L-arginine promotes the survival of extended dorsal perforator skin flap through activating L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4632-4637. |
| [12] | Chen Dongdong, Hao Yangquan, Zhang Gaokui, Li Huanhuan, Wang Qiuxia, Lu Chao. Three-dimensional printed navigation template assisted core decompression and bone grafting for treatment of ARCO stage II non-traumatic femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4322-4327. |
| [13] |
Geng Kang, Ding Xiaobin, Tian Xinli, Wang Xue, Yang Yuting, Yan Hong.
Electrical stimulation promotes wound healing and angiogenesis in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4152-4156. |
| [14] |
Feng Yuan, Han Zhiqi, Zhou Nuo.
Endothelial progenitor cells promote vasculogenesis and osteogenesis in the repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4046-4053. |
| [15] | Wei Yuanfeng, Huang Dongping. Current status of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3093-3100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||