Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5227-5232.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1988
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cognition of degenerative lumbar scoliosis and its orthopedic fusion and fixation
Zhang Kefeng1, Liu Yang2, Zhang Cunxin1, Lü Chaoliang1
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272111, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Joint Surgery, Zhucheng People’s Hospital, Zhucheng 262200, Shandong Province, China
-
Online:2019-11-18Published:2019-11-18 -
Contact:Lü Chaoliang, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272111, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Kefeng, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272111, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Kefeng, Liu Yang, Zhang Cunxin, Lü Chaoliang. Cognition of degenerative lumbar scoliosis and its orthopedic fusion and fixation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5227-5232.
share this article
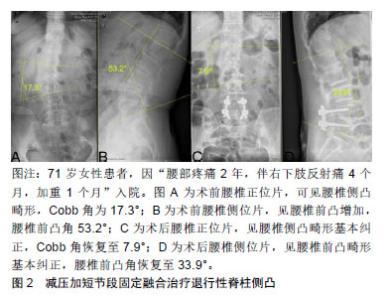
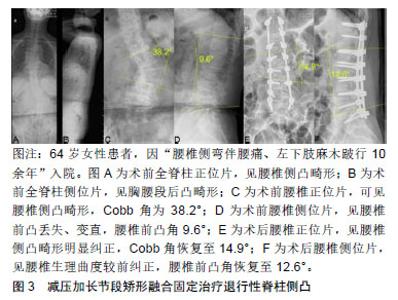
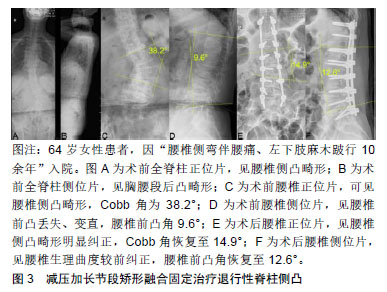
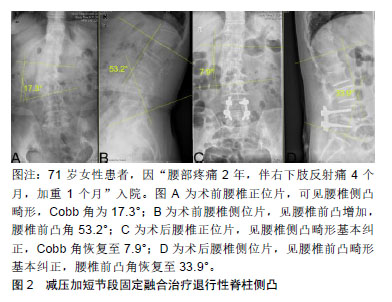
2.1 发病机制 尽管目前关于成人退变性脊柱侧凸的具体发病机制仍不十分清楚,但其病理生理学与脊柱的退行性改变密切相关。多数学者认为,椎间盘的退变是退变性脊柱侧凸的始动因素[6-7]。因椎间盘的退变,导致椎体两侧告退发生改变,或上下椎体发生旋转,导致椎间盘和关节突关节不对称,给脊柱两侧带来了不对称的负荷,从而导致了退行性脊柱侧凸的发生。 另一种理论认为绝经后骨质疏松症会导致退行性脊柱侧凸,因为骨质疏松症在50岁以上的女性中最为常见[7-8]。而退行性脊柱侧凸通常开始于50岁以后,其患病率随年龄的增长而增加,有研究报道绝经后患有骨质疏松症的妇女退变性脊柱侧凸的患病率明显高于正常的绝经妇女。此外非对称性椎间隙或椎体塌陷(如外伤骨折、姿势性侧弯、长期特殊体位等)可导致塌陷严重侧受力加大,产生骨小梁微骨折,进一步加重侧凸。 2.2 分型 2.2.1 脊柱侧凸研究学会分型 脊柱侧凸研究学会在2006年推出了成人脊柱畸形分类系统[8-9]。该系统参照青少年的King分型和Lenke分型,对脊柱侧凸的类型、区段、主侧凸等概念给与了明确的定义。该系统关注脊柱畸形的影像学特征,将局部畸形、冠状面及矢状面平衡、脊柱退行性变等因素全部纳入分型考虑范围之内,能够对脊柱侧凸和后凸进行综合分类,是目前比较全面的分型系统。然而,由于不考虑患者的症状和年龄,这种分型系统并不有助于选择手术方法或预测手术结果。而且该系统比较繁琐,不利于记忆,因此临床普及较差。 2.2.2 Abei分型 Aebi[10]根据畸形原因将成人脊柱侧凸分为3大类:Ⅰ型为原发性退变性脊柱侧凸,由椎间盘不对称和关节突关节退行性改变而引起;Ⅱ型为进行性特发性脊柱侧凸,由成年前开始的特发性脊柱侧凸进一步发展引起;Ⅲ型为继发性成人脊柱侧凸:Ⅲa型是由静止性脊柱侧凸或骨盆倾斜等原因引起,Ⅲb型是一种类似骨质疏松性骨折和脊柱侧凸畸形的骨代谢疾病,是由椎体骨质薄弱引起。Aebi分类是根据病因进行分类,帮助规划整体治疗,预测脊柱侧凸的自然进展。但该方法不能反映畸形的具体特征和大小,无法反映畸形的严重程度,不能帮助确定合适的手术方法。 2.2.3 Schwab分型 Schwab分型侧重于影像学表现与临床评价的关系[11],根据影像学表现对曲线顶端、腰椎前凸、椎体半脱位进行分类。研究发现,曲线的下端与前凸丧失相结合,导致与健康相关的生活质量较差。对于腰椎前凸减少、椎半脱位增高的患者,手术治疗更为常见。该系统的局限性在于虽然矢状面平衡是决定成人脊柱畸形患者临床疗效的重要因素,但它不能描述整体平衡。他修改了分类,将全脊柱平衡纳入矢状面[12]。然而,修订后的分类没有考虑影响矢状位平衡的脊柱-骨盆参数。 2.2.4 SRS-Schwab分型 SRS-Schwab分型于2012年发表,考虑了脊柱-骨盆参数与矢状位平衡之间的关系[13-14]。该系统由4部分组成:弯曲类型、骨盆倾斜修正参数、矢状面垂直轴修正参数和骨盆入射角减去腰椎前凸角修正参数。弯曲类型分为:①T型弯曲:仅冠状位影像上胸椎主弯Cobb角>30°(T9椎体顶端及以上节段);②L型弯曲:仅冠状位影像上腰椎或胸腰椎主弯 Cobb角>30°(T10椎体顶端及以下节段);③D型弯曲:冠状位影像上出现双主弯且每个主弯 Cobb角>30°;④S型弯曲:冠状位影像上未见 Cobb角>30°的弯曲但伴有矢状位影像上的畸形。研究发现,健康相关生活质量与弯曲类型和3个矢状位修正参数密切相关。L型弯曲和原发性矢状面畸形患者比T型弯曲或D型弯曲患者残疾更大,健康状况更差。矢状面修正等级较高的患者更有可能接受脊椎截骨矫形手术、髂内固定或减压手术。这一分类反映了疾病的严重程度,并提出了治疗指南。但目前还没有关于畸形融合程度等具体治疗方法的建议,手术方法的确立应个性化。 2.3 临床表现 2.3.1 腰痛 退变性脊柱侧凸最常见的症状是腰背痛,通常表现在脊柱弯曲的凸侧。腰背痛进展较快,药物不易缓解,活动时腰痛加剧,且症状持续时间长,反复发作,逐年加重。退变性脊柱侧凸引起的腰背痛具有晨轻暮重的特点,即腰痛在早起时较轻,随着白天的活动,渐渐觉得腰痛加重。背痛的患病率各不相同,但一般占成人脊柱侧凸的60%-80%[15-16]。腰背痛主要由于椎间盘和关节突关节退行性改变引起,由脊柱不平衡引起的肌肉疲劳也会引起背痛。疼痛与侧凸大小没有直接关系,然而椎体的旋转脱位和矢状位不平衡可能加重腰背疼痛[17-18]。 2.3.2 根性症状和间歇性跛行 腿痛表现为间歇性跛行或腰椎管狭窄引起的放射痛。只有31%的成人特发性脊柱侧凸患者存在椎管狭窄,而90%的退行性脊柱侧凸患者存在椎管狭窄。椎管狭窄表现为椎间孔狭窄多于中央管狭窄,凹侧狭窄多于凸侧狭窄。小关节过度增生肥大和横向半脱位与椎间孔狭窄密切相关[19]。行走根的迂曲受压可引起凹侧放射痛,行走根的机械牵拉了引起凸侧的放射痛。此外,椎间高度的丢失可使上位椎体椎弓根下沉,引起双侧椎间孔狭窄,导致双侧神经根受压症状。 2.3.3 畸形 初期脊柱侧弯是由于患者为缓解腰背疼痛而采取的保护性姿势改变,支点位X射线检查一般并无显著畸形改变,Bending位X射线脊柱柔韧性尚可。后期随着腰背痛加重、关节突关节异常增生、骨化,脊柱活动度明显下降。畸形也是青少年脊柱侧凸的主要症状,而下腰痛或神经系统症状是成人退行性脊柱侧凸的主要症状。除了脊柱侧凸,成人退行性脊柱侧凸还经常出现矢状面和冠状面失衡,导致姿势不当及下腰痛[18]。 2.4 治疗 2.4.1 保守治疗 对于症状较轻的患者可选择保守治疗,其主要适应证为:腰背疼痛可以耐受;没有或者较轻的下肢疼痛及间歇性跛行;影像学检查提示脊柱矢状面及冠状面基本保持平衡。治疗方法主要有非类固醇抗炎药、肌松药应用,加强腰背肌功能训练,局部药物封闭注射。此外,预防骨质疏松对减缓侧凸的加重也有一定的作用。作者不推荐外固定支具的使用,急性期可短期使用,长期使用支具可引起一侧要被肌肉失用性萎缩,加剧侧凸程度,不建议长期使用。另外,济宁市第一人民医院开展的腰椎硬膜外药物注射技术,在保守治疗成人脊柱侧凸根性症状方面取得了较好的疗效。对于不能耐受全麻手术或者定位阶段不清者,可选择此技术。 2.4.2 手术治疗 成人退行性脊柱侧凸手术的主要指征是腰背痛和间歇性跛行呈进行性加重;单侧或双侧下肢放射痛伴肢体麻木;脊柱侧凸进行性加重伴脊柱失稳(Cobb角每年增加大于5°),或合并冠状面及矢状面失平衡[20]。仅用于缓解腰痛的手术很少被提及。此外,手术前应充分考虑患者是否合并有其他基础疾病;是否有骨质疏松症;矫正后脊柱曲线的刚度;冠状位和矢状位是否平衡,术后矢状位不平衡常导致手术效果不佳,因此恢复不平衡比纠正脊柱侧凸本身更为关键[18]。由于术后不平衡恶化的病例较多,因此在选择合适的手术方案时应慎重考虑这一因素[21-22]。 退行性脊柱侧凸引起放射痛的主要原因是椎间孔狭窄,而不是中央管狭窄。此外,椎间盘间隙在凹陷侧挤压神经根、椎体半脱位、关节突小关节肥大增生也是重要因素。单纯减压可引起椎体半脱位的进展和恶化。因此,恢复椎间盘间隙,纠正关节突关节半脱位,更有助于减轻放射痛。脊柱融合可改善伴有退行性改变的下腰痛。恢复脊柱冠状位及矢状位的平衡可以缓解肌肉疲劳引起的慢性腰背疼痛。 手术的目的是缓解腰背痛,改善放射痛和跛行,纠正脊柱畸形[23-24]。为了实现这些目标,可以进行多种手术选择,包括减压、复位和/或畸形矫正。包括畸形矫正在内的高水平脊柱融合可能会导致失血过多和手术时间延长,导致更多的术后并发症。如果预期会出现这种并发症,可以根据患者的年龄和一般医疗状况选择有限的手术。当选择有限的手术时,疼痛通常会复发,并且在未融合区可能发生新的退行性改变,最终导致邻椎病。 手术方式的选择包括:单纯减压术、减压加短节段固定融合术、减压加长节段矫形融合固定术。选择手术时应充分了解症状的原因,同时考虑每一种手术选择的优点、缺点、适应证及并发症[25]。 (1)单纯减压术:虽然大多数患者需要减压手术来缓解下肢放射痛,但成人退行性脊柱侧凸通常不建议单纯减压。目前各种开放性的减压手术,对脊柱的稳定性均有一定的破坏。椎板和关节突小关节面切除后,可导致畸形和脊柱不稳进一步恶化,导致脊柱侧凸复发并加重[26]。但该方法适用于病情较差、围术期并发症发生率较高的老年患者。术前通过影像学资料及专科查体,明确责任间隙后,通过有限单纯减压松解受压神经根,对缓解下肢放射痛有不错的疗效。此外,随着各种腔镜技术的发展,腔镜下的手术不仅可摘除突出的椎间盘,在神经根减压方面亦有一定作用,这在一定程度上也为单纯减压术提供了可更多的选择。作者认为,如非患者不能耐受手术外,单纯减压手术长期疗效有待长期随访研究,不做推荐。 (2)减压加短节段固定融合术:减压加短节段椎体融合是成人脊柱侧凸手术治疗的另一个选择,可防止单纯减压带来的脊柱不稳,维持减压效果。该术式的关键在于有限减压和短节段融合固定,其减压范围仅仅为侧凸的某一个区域,不能改善侧凸畸形和纠正脊柱在冠状位及矢状位的失平衡。因此,该技术是中度脊柱侧凸和轻度腰椎半脱位的良好选择,见图2。由于患者自身情况及经济条件,这种术式也是最常采用的方法。邻椎病是该术式最常见的并发症。当融合在畸形内停止时,融合外退行性 改变可能会加速。因此,融合固定不应停止在侧凸的顶点,应在顶点以上或以下终止。"

近端融合水平是否应该延伸至T10椎体或止于腰椎仍有争议。在L1椎体处停止融合可能导致胸腰椎近端邻近节段病变。为了防止这种情况的发生,建议融合到T10椎体,因为T10椎体上有真正的肋骨附着,比T11和T12椎体更稳定。然而,一些外科医生认为,这不能从根本上预防邻椎病[29]。相反,由于融合时间的延长和手术时间的延长,T10椎体以下的融合可能会导致围术期并发症。Cho等[30]的报道,当上固定椎体位于上端椎体上方时,T11或T12椎体融合是可以接受的。 远端融合水平是否应在L5椎体停止或延伸至骶骨应根据具体情况分析。由于脊柱侧凸的尖端位于L2-4椎体,且L4-5椎间盘有退行性改变,因此远端融合通常发生在L5椎体。对于L5-S1层面存在椎管狭窄、椎体滑脱、严重退行性改变等病理情况的患者,行骶骨融合是毫无疑问的。然而,当L5-S1节段看起来健康时,融合是止于L5椎体还是延伸至骶骨仍存在争议[31-32]。 与S1椎体相比,融合止于L5椎体的手术被认为是相对较小的,然而这可能导致随后的L5-S1加速退变。Edwards等[33]报道,61%的L5椎体固定术患者表现为退行性改变加重,导致矢状面不稳,增加再次手术的风险。因此,矢状位失稳患者更倾向于与S1椎体融合,因为融合止于L5椎体极有可能在L5-S1节段引起退行性变,甚至在术前即退行性改变。 骶骨融合比L5融合能更好地纠正矢状面不平衡。但骶骨融合率偏低,假关节形成是L5-S1节段融合最常见的并发症,42%的骶骨融合患者出现假关节,但4%的L5椎体融合患者出现假关节。为了防止假关节形成,强烈推荐椎体间融合联合髂内固定。骶骨融合后矢状位失代偿并不少见,因此恢复腰椎前凸是实现矢状位平衡的关键。 2.4.3 术后并发症 过度失血在成人脊柱畸形手术中并不少见,这与硬膜外血肿、肺栓塞、呼吸衰竭等围术期并发症密切相关。融合节段的增加和手术时间的延长与失血量的增加有关。此外,低剂量阿司匹林由于具有预防心血管疾病的潜力而越来越流行,这使术中更加难以控制出血。尽管手术前7 d没有服用阿司匹林,但是经常服用阿司匹林的患者的失血量仍然比不服用阿司匹林的患者高。减少围术期并发症需要减少出血量,可尝试术前自体献血、术中自体血回输、抗纤溶性给药和异体输血等。 为减少围术期并发症,成人退行性脊柱侧凸已引入微创技术。侧向腰椎椎间融合术与开放矫形手术相比,出血量少,发病率低。但也有文献报道侧向椎体间融合技术的局限性[34-35],L5-S1节段的手术不能通过侧向入路进行,因为髂嵴阻碍了手术入路;术中神经信息监测并不能完全预防与手术入路相关的并发症,如大腿区域感觉缺损等。晚期并发症包括邻椎病、假关节形成和内固定失败。邻椎病表现为椎管狭窄和近端交界性后 凸[36]。邻椎病的主要危险因素为矢状面不平衡、小关节损伤和老年患者。 与骶骨融合时,假关节形成最常见于L5-S1椎间隙[37],但它也常发生在胸腰交接段。假关节形成的发病率在老年、腰椎后凸>20°及腰椎前凸减少的患者中较高。矢状位不平衡是假关节形成的另一个危险因素。 内固定器械失效最长见于最远端和/或近端螺钉的松动和拔出[38]。螺钉松脱常发生在矢状位不平衡的患者中,尤其是在长节段融合的患者中,近端螺钉加骨水泥有助于减少螺钉松动。为防止器械远端部分固定失败,建议增加髂骨螺钉固定。由于L5螺钉松脱常见于矢状位不平衡患者,因此建议将此融合延伸至骶骨[39-40]。 成人退行性脊柱侧凸常伴有矢状面不平衡。虽然矢状位失稳的恢复对于改善临床疗效至关重要,但一些患者在使用内固定器械融合固定后仍存留矢状位失稳[41-42]。较高的骨盆内凹和较大的骨盆倾斜可能与矢状位失代偿纠正不足有关,在这些患者中,需要对腰椎前凸进行更高程度的矫正。内固定后椎间盘间隙矫正的缺失也可能导致腰椎前凸矫正效果不佳。带支架的前柱支撑有助于防止椎间盘间隙矫正的丢失。"

| [1]Carter OD, Haynes SG. Prevalence rates for scoliosis in US adults: results from the first National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Int J Epidemiol.1987;16(4):537-544.[2]Schwab F, Dubey A, Gamez L, et al. Adult scoliosis: prevalence, SF-36, and nutritional parameters in an elderly volunteer population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(9):1082-1085.[3]Hong JY, Suh SW, Modi HN, et al. The prevalence and radiological findings in 1347 elderly patients with scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(7):980-983.[4]Graham RB, Sugrue PA, Koski TR. Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(3):95-107.[5]Garcia-Ramos CL, Obil-Chavarria CA, Zarate-Kalfopulos B, et al. Degenerative adult scoliosis. Acta Ortop Mex. 2015;29(2):127-138.[6]Dehnokhalaji M, Golbakhsh M R, Siavashi B, et al. Evaluation of the Degenerative Changes of the Distal Intervertebral Discs after Internal Fixation Surgery in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Asian Spine J. 2018;12(6):1060-1068.[7]Akazawa T, Watanabe K, Matsumoto M, et al. Modic changes and disc degeneration in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients who reach middle age without surgery: Can residual deformity cause lumbar spine degeneration? J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(6):884-888.[8]Tome-Bermejo F, Pinera AR, Alvarez-Galovich L. Osteoporosis and the Management of Spinal Degenerative Disease (I). Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2017;5(5):272-282.[9]Lowe T, Berven SH, Schwab FJ, et al. The SRS classification for adult spinal deformity: building on the King/Moe and Lenke classification systems. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19 Suppl):S119-S125.[10]Aebi M. The adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2005;14(10):925-948.[11]Schwab F, Farcy JP, Bridwell K, et al. A clinical impact classification of scoliosis in the adult. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2109-2114.[12]Schwab F, Lafage V, Farcy JP, et al. Surgical rates and operative outcome analysis in thoracolumbar and lumbar major adult scoliosis: application of the new adult deformity classification. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(24):2723-2730.[13]Sengupta DK. Re: Schwab F, Ungar B, Blondel B, et al. Scoliosis research society-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification--a validation study. Spine 2012; 37:1077-82. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(20):1790.[14]York PJ, Kim HJ. Degenerative Scoliosis. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017;10(4):547-558.[15]Daffner SD, Vaccaro AR. Adult degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ).2003;32(2):77-82, 82.[16]Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Suh PB. Results of surgical treatment of painful adult scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1994;19(14):1619-1627.[17]Cheng JC, Castelein RM, Chu WC, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15030.[18]Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, et al. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(18):2024-2029.[19]Simmons ED. Surgical treatment of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis with associated scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(384): 45-53.[20]Putzier M, Pumberger M, Halm H, et al. [Surgical treatment of de-novo scoliosis]. Orthopade. 2016;45(9):744-754.[21]Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S, et al. Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a prospective multicenter analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(13): E803-E812.[22]Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, et al. Risk factors of sagittal decompensation after long posterior instrumentation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(17):1595-1601.[23]Bradford DS, Tay BK, Hu SS. Adult scoliosis: surgical indications, operative management, complications, and outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(24):2617-2629.[24]Marchesi DG, Aebi M. Pedicle fixation devices in the treatment of adult lumbar scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1992;17(8 Suppl):S304-S309.[25]Akbarnia BA, Ogilvie JW, Hammerberg KW. Debate: degenerative scoliosis: to operate or not to operate. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006; 31(19 Suppl):S195-S201.[26]Vaccaro AR, Ball ST. Indications for instrumentation in degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. Orthopedics. 2000;23(3):260-271, 272-273.[27]Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, et al. Short fusion versus long fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(5):650-656.[28]Bradford DS, Tribus CB. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of rigid coronal decompensation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976),1997;22(14): 1590-1599.[29]Shufflebarger H, Suk S I, Mardjetko S. Debate: determining the upper instrumented vertebra in the management of adult degenerative scoliosis: stopping at T10 versus L1. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31 (19 Suppl):S185-S194.[30]Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, et al. Selection of proximal fusion level for adult degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(2):394-401.[31]Bridwell KH, Edwards CN, Lenke LG. The pros and cons to saving the L5-S1 motion segment in a long scoliosis fusion construct. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(20):S234-S242.[32]Polly DJ, Hamill CL, Bridwell KH. Debate: to fuse or not to fuse to the sacrum, the fate of the L5-S1 disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19 Suppl):S179-S184.[33]Edwards CN, Bridwell KH, Patel A, et al. Thoracolumbar deformity arthrodesis to L5 in adults: the fate of the L5-S1 disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(18):2122-2131.[34]Dakwar E, Cardona RF, Smith DA, et al. Early outcomes and safety of the minimally invasive, lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach for adult degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28(3):E8.[35]Isaacs RE, Hyde J, Goodrich JA, et al. A prospective, nonrandomized, multicenter evaluation of extreme lateral interbody fusion for the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis: perioperative outcomes and complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(26 Suppl): S322-S330.[36]Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Sagittal thoracic decompensation following long adult lumbar spinal instrumentation and fusion to L5 or S1: causes, prevalence, and risk factor analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(20):2359-2366.[37]Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Pseudarthrosis in adult spinal deformity following multisegmental instrumentation and arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(4):721-728.[38]Emami A, Deviren V, Berven S, et al. Outcome and complications of long fusions to the sacrum in adult spine deformity: luque-galveston, combined iliac and sacral screws, and sacral fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(7):776-786.[39]Pateder DB, Kebaish KM, Cascio BM, et al. Posterior only versus combined anterior and posterior approaches to lumbar scoliosis in adults: a radiographic analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(14): 1551-1554.[40]Tsuchiya K, Bridwell KH, Kuklo TR, et al. Minimum 5-year analysis of L5-S1 fusion using sacropelvic fixation (bilateral S1 and iliac screws) for spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006;31(3):303-308.[41]Cho KJ, Kim KT, Kim WJ, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy in elderly patients with degenerative sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2013;38(24):E1561-E1566.[42]Schwab FJ, Patel A, Shaffrey CI, et al. Sagittal realignment failures following pedicle subtraction osteotomy surgery: are we doing enough?: Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(6):539-546. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| [4] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [5] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [8] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [9] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [10] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [11] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [12] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [13] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [14] | Yuan Xinping, Shao Yanbo, Wu Chao, Wang Jianling, Tong Liangcheng, Li Ying. Accuracy of target bone segments in personalized differential modeling and simulation of CT scanning parameters at fracture end [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 912-916. |
| [15] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||