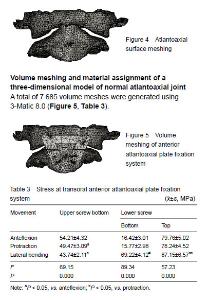
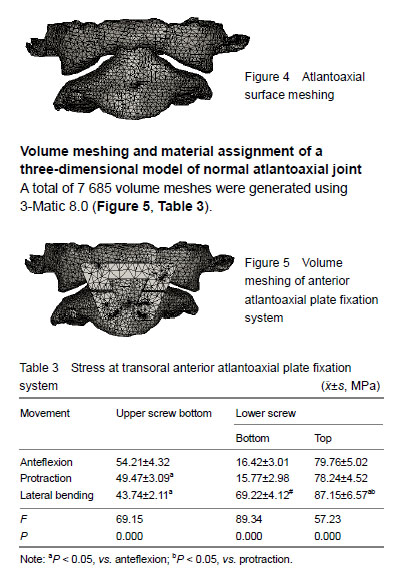
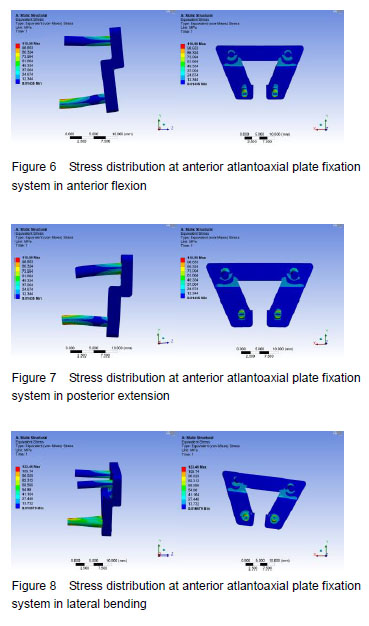
| [1]I?ik HS, Sandal E, Ça?li S. Clinical Outcomes of Posterior C1 and C2 Screw-Rod Fixation for Atlantoaxial Instability. Turk Neurosurg. 2017. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20525-17.1. [Epub ahead of print][2]Zheng Y, Hao D, Wang B, et al. Clinical outcome of posterior C1-C2 pedicle screw fixation and fusion for atlantoaxial instability: A retrospective study of 86 patients. J Clin Neurosci. 2016;32:47-50. [3]Rajinda P, Towiwat S, Chirappapha P. Comparison of outcomes after atlantoaxial fusion with C1 lateral mass-C2 pedicle screws and C1-C2 transarticular screws. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(4):1064-1072. [4]Du S, Ni B, Lu X, et al. Application of unilateral C2 translaminar screw in the treatment for atlantoaxial instability as an alternative or salvage of pedicle screw fixation. World Neurosurg. 2017;97:86-92. [5]Tauchi R, Imagama S, Ito Z, et al. Complications and outcomes of posterior fusion in children with atlantoaxial instability. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(7):1346-1352. [6]Ai F, Yin Q, Wang Z, et al. Applied anatomy of transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate internal fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(2):128-132. [7]Xia H, Yin Q, Ai F, et al. Treatment of basilar invagination with atlantoaxial dislocation: atlantoaxial joint distraction and fixation with transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate (TARP) without odontoidectomy. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(8):1648-1655. [8]Ai Fuzhi. The research of transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate (TARP) and biomechanics. Guangzhou: Sourthern Medical University, 2003.[9]Yang J, Ma X, Xia H, et al. Transoral anterior revision surgeries for basilar invagination with irreducible atlantoaxial dislocation after posterior decompression: a retrospective study of 30 cases. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(5):1099-1108.[10]Ai FZ, Yin QS, Xu DC, et al. Transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate internal fixation with transoral transpedicular or articular mass screw of c2 for the treatment of irreducible atlantoaxial dislocation: two case reports. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(8):E556-562. [11]Martins C, Cardoso AC, Alencastro LF, et al. Endoscopic-assisted lateral transatlantal approach to craniovertebral junction. World Neurosurg. 2010;74(2-3):351-358. [12]Yin QS, Ai FZ, Zhang K, et al. Transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate internal fixation for the treatment of irreducible atlantoaxial dislocation: a 2- to 4-year follow-up. Orthop Surg. 2010;2(2):149-155.[13]Wu Z, Xu J, Wang Z, et al. Transoral approach for revision surgery of os odontoideum with atlantoaxial dislocation. Orthopedics. 2014;37(9):e851-855. [14]Yuan YX, Wan L, Yin QS, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of finite element model of the cervical motion segment according to Chinese Digital Human CT data. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(26):4915-4917.[15]Hussain M, Nassr A, Natarajan RN, et al. Biomechanical effects of anterior, posterior, and combined anterior-posterior instrumentation techniques on the stability of a multilevel cervical corpectomy construct: a finite element model analysis. Spine J. 2011;11(4):324-330. [16]Okawa A, Sakai K, Hirai T, et al. Risk factors for early reconstruction failure of multilevel cervical corpectomy with dynamic plate fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(9):E582-587. [17]Zhang HN. The experimental study of anterior atlantoaxial joint fusion device. Guangzhou: Sourthern Medical University, 2014.[18]Shi L. The third generation of TARP system and posterior pedicle screw rod system biomechanical comparison. Guangzhou: Sourthern Medical University, 2014.[19]Zhang HN, Yin QS, Liu GY, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of stability of implantation of transoralatlantoaxial lateral mass fusion cage. Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepou Xue Zazhi. 2014;32(3):348-350.[20]Xu JJ, Wu ZH, Xia H, et al. Curative effect of transoropharyngeal edentulous technique for treatment of skull base depression with atlantoaxial dislocation. Guangdong Yixue. 2007;24(27):3809-3811,3815.[21]Keskil S, Göksel M, Yüksel U. Transoral screw and wire fixation for unstable anterior ½ atlas fracture. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2017;8(4):364-368. [22]Huang X, Yin Q, Wang Z, et al. Implantation of the anterior atlantoaxial lateral mass intervertebral cage using the transoral approach. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(4):630-634.[23]Wang Q, Mao K, Wang C, et al. Transoral atlantoaxial release and posterior reduction by occipitocervical plate fixation for the treatment of basilar invagination with irreducible atlantoaxial dislocation. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2017;78(4):313-320. [24]Yin QS, Li XS, Bai ZH, et al. An 11-year review of the TARP procedure in the treatment of atlantoaxial dislocation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(19):E1151-1158. [25]Wei G, Wang Z, Ai F, et al. Treatment of basilar invagination with Klippel-Feil syndrome: atlantoaxial joint distraction and fixation with transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate. Neurosurgery. 2016;78(4):492-498. [26]Zhang B, Liu H, Cai X, et al. Biomechanical comparison of modified TARP technique versus modified Goel technique for the treatment of basilar invagination: a finite element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(8):E459-466. |