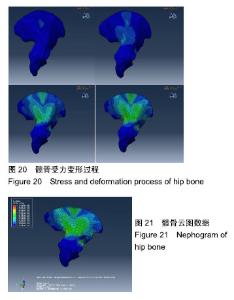
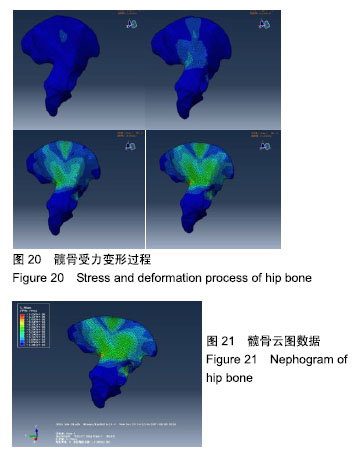
| [1]Mellon SJ,Grammatopoulos G,Andersen MS,et al.Optimal acetabular component orientation estimated using edge-loading and impingement risk in patients with metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty.J Biomech.2015|48(2):318-323.[2]Pierrepont JW,Stambouzou CZ,Miles BP,et al.Patient Specific Component Alignment in Total Hip Arthroplasty.JISRF.2016; 6(4):1-8.[3]Bergmann G,Bender A,Dymke J,et al.Standardized Loads Acting in Hip Implants. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0155612. [4]Patil S,Garbuz DS,Greidanus NV,et al.Quality of life outcomes in revision vs primary total hip arthroplasty. A prospective cohort study.J Arthroplasty.2008;23(4):550-553.[5]唐通鸣,邓佳文,张政,等.基于逆向工程和快速成型技术的髋骨三维实体模型个性化重建[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(26): 4253-4257.[6]李兴,王洪福,罗伟,等.基于术后髋骨CT数据重建个性化骨肌多体动力学模型及步态仿真[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(35): 5685-5690.[7]丁欣.上颈椎三维有限元模型的建立与分析[D].厦门:厦门大学,2014.[8]Stops A,Wilcox R,Jin Z.Computational modelling of the natural hip: a review of finite element and multibody simulations.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin.2012;15:963-979.[9]Eschweiler J,Fieten L,Dell’Anna J,et al.Application and evaluation of biomechanical models and scores for the planning of total hip arthroplasty.Proc Inst Mech Eng H.2012;226(12): 955-967.[10]Kinney AL,Besier TF,D'Lima DD,,et al.Update on grand challenge competition to predict in vivo knee loads.J Biomech Eng. 2013; 135(2):021012.[11]Hicks JL,Uchida TK,Seth A,et al.Is my model good enough? Best practices for verification and validation of musculoskeletal models and simulations of movement.J Biomech Eng.2015;137(2): 20905.[12]黄金玮,章建波,黄长林,等.CT图像的三维实体重建技术研究[J].计算机应用研究,2004,21(10):112-115.[13]罗伟.髋骨的三维重建技术与生物力学仿真研究[D].太原:中北大学, 2017.[14]聂涌,马俊,康鹏德,等.正常步态周期中髋臼周围区域的应力分布及其在THA髋臼重建中的指导[J].医用生物力学, 2014,29(1):31-37.[15]荣国灿.桥型重建锁定钢板治疗骨盆环骨折的数值模拟研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2014. |