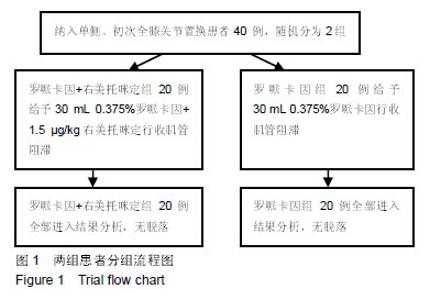
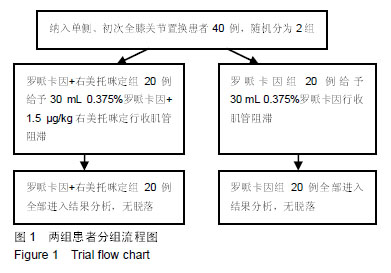
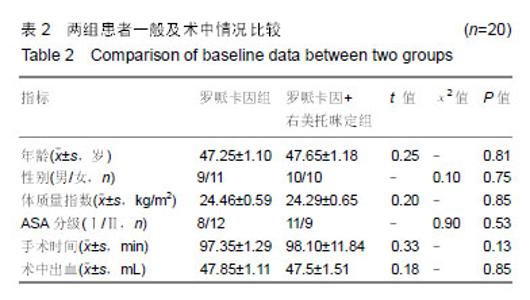
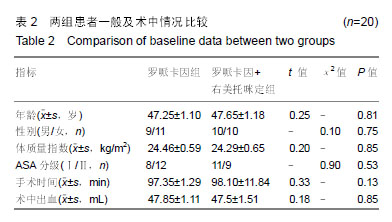
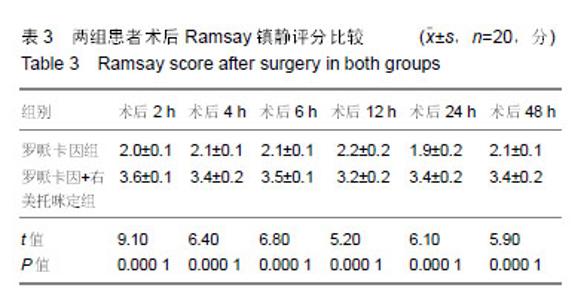
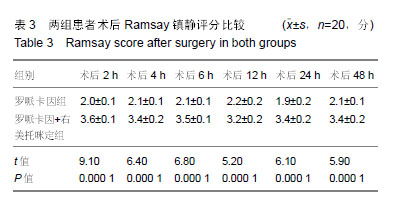
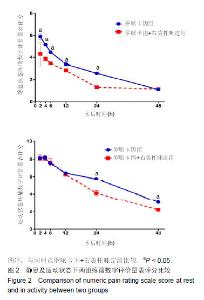
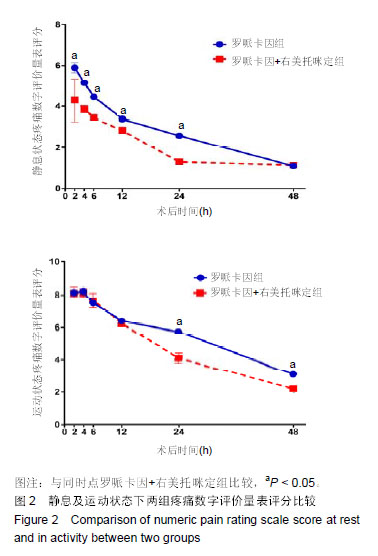
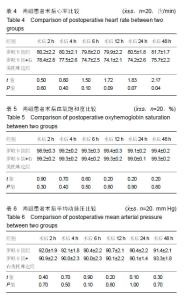
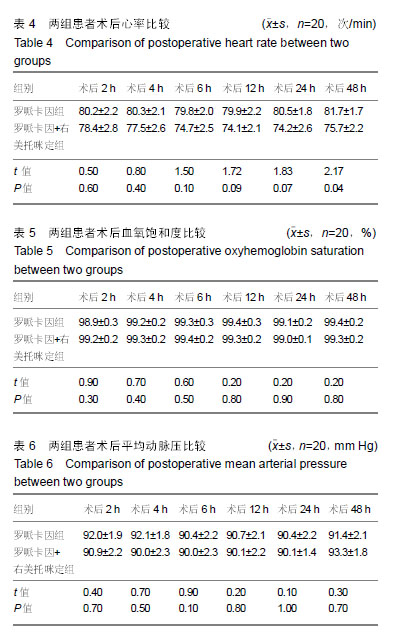
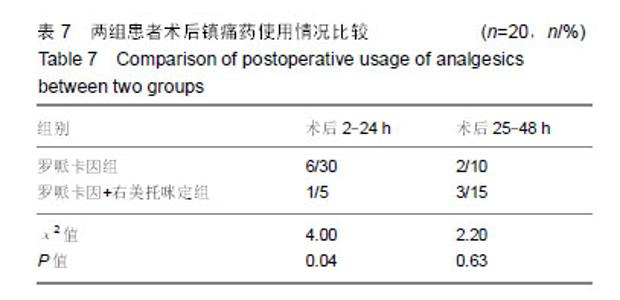
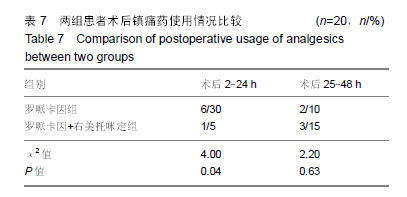
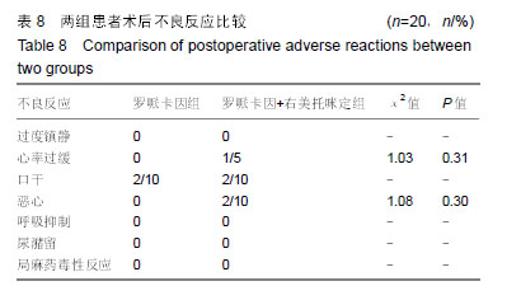
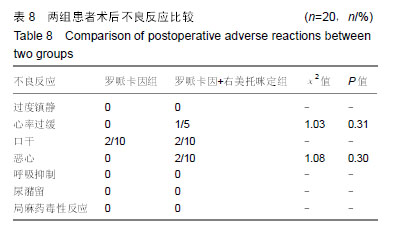
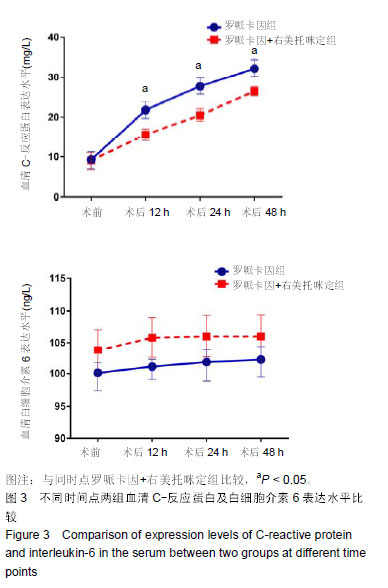
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (24): 3798-3804.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1289
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analgesia efficacy of dexmedetomidine combined with ropivacaine for adductor canal block after total knee arthroplasty
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, 2Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2019-08-28Published:2019-08-28 -
Contact:Liu Xianbao, Associate chief physician, Department of Anesthesiology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Tan Zhengling, Master, Attending physician, Department of Anesthesiology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2017A030313137 (to WL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tan Zhengling, Chen Junxing, Su Zhiyuan, Liu Xianbao, Lu Xiaoqin, Wang Le.
share this article
| [1]Hebl JR, Dilger JA, Byer DE, et al. A pre-emptive multimodal pathway featuring peripheral nerve block improves perioperative outcomes after major orthopedic surgery. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2008;33(6): 510-517.[2]王春光. 收肌管内隐神经阻滞用于全膝关节置换术后镇痛的临床研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2017.[3]Danninger T, Opperer M, Memtsoudis SG. Perioperative pain control after total knee arthroplasty: An evidence based review of the role of peripheral nerve blocks. World J Orthop. 2014;5(3): 225-232.[4]Moucha CS, Weiser MC, Levin EJ. Current Strategies in Anesthesia and Analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(2): 60-73.[5]Paul JE, Arya A, Hurlburt L, et al. Femoral nerve block improves analgesia outcomes after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(5): 1144-1162.[6]王海兰. 术前股神经阻滞对全麻下全膝关节置换术老年患者的超前镇痛效果分析[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2016, 31(4):563-565.[7]Feibel RJ, Dervin GF, Kim PR, et al. Major complications associated with femoral nerve catheters for knee arthroplasty: a word of caution. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6 Suppl): 132-137.[8]Sharma S, Iorio R, Specht LM, et al. Complications of femoral nerve block for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010;468(1): 135-140.[9]金姬延,姜伟,许蕊凤,等. 连续股神经阻滞的安全隐患分析及护理[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2015, 15(10): 958-960.[10][Jaeger P, Nielsen ZJ, Henningsen MH, et al. Adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block and quadriceps strength: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study in healthy volunteers. Anesthesiology. 2013;118(2): 409-415.[11]Krishnan C, Williams GN. Evoked tetanic torque and activation level explain strength differences by side. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009; 106(5): 769-774.[12]Abdulatif M, Fawzy M, Nassar H et al. The effects of perineural dexmedetomidine on the pharmacodynamic profile of femoral nerve block: a dose-finding randomised, controlled, double-blind study. Anaesthesia. 2016;71(10):1177-1185.[13]Rancourt MP, Albert NT, Côté M, et al. Posterior tibial nerve sensory blockade duration prolonged by adding dexmedetomidine to ropivacaine. Anesth Analg. 2012;115(4) :958-962.[14]Brummett CM, Hong EK, Janda AM, et al. Perineural dexmedetomidine added to ropivacaine for sciatic nerve block in rats prolongs the duration of analgesia by blocking the hyperpolarization-activated cation current. Anesthesiology. 2011; 115(4): 836-843.[15]杨淼,方华,章放香, 等.七氟醚麻醉下右美托咪定复合罗哌卡因行髂腹下/髂腹股沟神经阻滞的效果[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2017,33(9): 872-874.[16]Weerink M, Struys MM, Hannivoort LN, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56(8): 893-913.[17]Li A, Yuen VM, Goulay-Dufay S, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42(12): 1917-1927.[18]Reuben SS. Preventing the development of complex regional pain syndrome after surgery. Anesthesiology. 2004;101(5): 1215-1224.[19]Fowler SJ, Symons J, Sabato S, et al. Epidural analgesia compared with peripheral nerve blockade after major knee surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Br J Anaesth. 2008;100(2): 154-164.[20]Kent ML, Hackworth RJ, Riffenburgh RH, et al. A comparison of ultrasound-guided and landmark-based approaches to saphenous nerve blockade: a prospective, controlled, blinded, crossover trial. Anesth Analg. 2013;117(1): 265-270.[21]Yao Y, Yu C, Zhang X, et al. Caudal and intravenous dexmedetomidine similarly prolong the duration of caudal analgesia in children: A randomized controlled trial. Paediatr Anaesth. 2018; 28(10): 888-896.[22]Brummett CM, Padda AK, Amodeo FS, et al. Perineural dexmedetomidine added to ropivacaine causes a dose-dependent increase in the duration of thermal antinociception in sciatic nerve block in rat. Anesthesiology. 2009; 111(5): 1111-1119.[23]Mangal V, Mistry T, Sharma G, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to ropivacaine in ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus Block: A prospective, randomized, double-blind study. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2018;34(3): 357-361.[24]Chen BS, Peng H, Wu SN. Dexmedetomidine, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist, inhibits neuronal delayed-rectifier potassium current and sodium current. Br J Anaesth.2009;103(2): 244-254.[25]Maruta T, Nemoto T, Satoh S, et al. Dexmedetomidine and clonidine inhibit the function of Na(v)1.7 independent of alpha(2)- adrenoceptor in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Anesth. 2011; 25(4): 549-557.[26]Kosugi T, Mizuta K, Fujita T, et al. High concentrations of dexmedetomidine inhibit compound action potentials in frog sciatic nerves without alpha(2) adrenoceptor activation. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;160(7):1662-1676.[27]Elliott D, Aitken LM, Bucknall TK, et al. Patient comfort in the intensive care unit: a multicentre, binational point prevalence study of analgesia, sedation and delirium management. Crit Care Resusc. 2013;15(3):213-219.[28]Wan Z, Wang J, Cao H, et al. Effects of different doses of dexmedetomidine on analgesic efficacy and inflammatory cytokines in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 16(3):1743-1746.[29]Wang L, Zhang A, Liu W, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative stress response, inflammation and immune function in patients with different degrees of liver cirrhosis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(5): 3869-3874.[30]Kong L, Lu XH. Effect of dexmedetomidine on perioperative inflammatory response and cellular immune in patients undergoing radical operation of thoracoscopic lung cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018; 98(36): 2929-2932. |
| [1] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [2] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [3] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [4] | Mieralimu•Muertizha, Ainiwaerjiang•Damaola, Lin Haishan, Wang Li . Relationship between tibio-femoral mechanical axis deviation on coronal plane and early joint function recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3300-3304. |
| [5] | Deng Zhibo, Li Zhi, Wu Yahong, Mu Yuan, Mu Yuexi, Yin Liangjun. Local infiltration anesthesia versus femoral nerve block for pain control and safety after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3401-3408. |
| [6] | Huang Chenyu, Tang Cheng, Wei Bo, Li Jiayi, Li Xuxiang, Zhang Huikang, Xu Yan, Yao Qingqiang, Wang Liming. Application of three-dimensional printing guide plate in total knee arthroplasty for patients with varus and valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2789-2793. |
| [7] | Li Shangzhi, Zheng Dezhi, Liu Jun. Early analgesia of cocktail therapy after total knee arthroplasty with enhanced recovery after surgery program [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2794-2798. |
| [8] | Liu Jinlei, Yin Li, Zhang Yi, Wang Haitao, Li Zhuangyan, Xia Peige, Qiao Renqiu. Effects of intravenous tranexamic acid combined with periarticular multipoint injection of tranexamic acid cocktail on blood loss and pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2833-2839. |
| [9] | Xu Hui, Kang Bingxin, Gao Chenxin, Zhao Chi, Xu Xirui, Sun Songtao, Xie Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Effectiveness of Tuina in the treatment of pain after total knee arthroplasty in patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2840-2845. |
| [10] | Deng Bo, Hong Hainan, Fan Yongyong, Cai Guoping, Feng Xingbing, Hong Zhenghua. Efficacy and safety of tourniquet application in total knee arthroplasty and only at the time of cementing: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2908-2914. |
| [11] | Liu Kun, Xu Hao, Wang Yingzhen, Zhang Haining, Fang Yuan, Xiang Shuai, Lü Chengyu. Direct repair of medial collateral ligament injury combined with brace in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2352-2357. |
| [12] | Wang Feng, Ju Xiaocong, Wang Bing, Sun Haining. Lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty for treating lateral single compartment knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1836-1841. |
| [13] | Lin Yi, Feng Jierong, Luo Xingwen. Mobilization with movement facilitates early functional recovery after fixed-bearing posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1842-1846. |
| [14] | Pei Tianlong, Wang Yongkang, Wu Wenjie, Zhao Hong, Wang Longsheng . Anatomical and morphological characteristics of knee joint in hemophilic arthritis patients with three-dimensional CT and X-ray films [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1886-1890. |
| [15] |
Yin Jiandong, Wang Xinling, Zuo Biao, Li Nongyi.
Relationship of extrusion and elevation of blood-expelling methods during
total knee arthroplasty with postoperative complications |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||