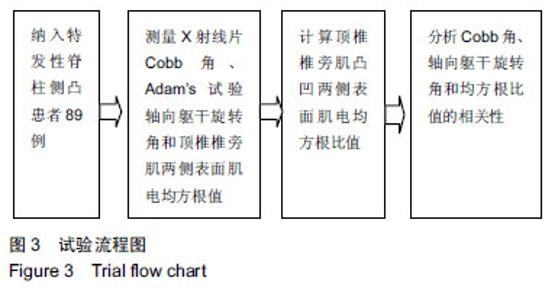
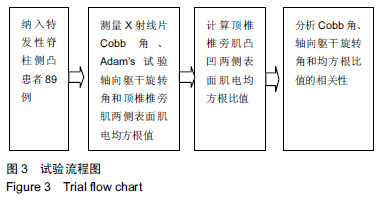
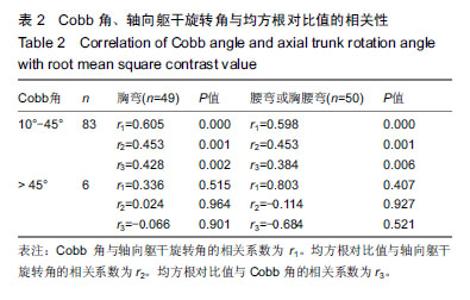
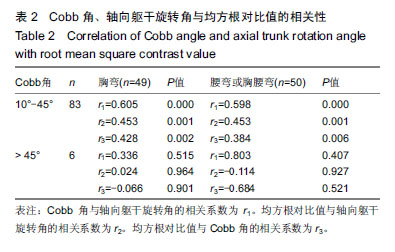
| [1]Horne JP, Flannery R, Usman S. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89(3):193-198.[2]Asher MA, Burton DC. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis:natural history and long term treatment effects. Scoliosis. 2006;1:2.[3]Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JCY, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet. 2008;371:1527-1537.[4]Zhang H, Guo C, Tang M, et al. Prevalence of scoliosis among primary and middle school students in mainland china: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(1):41-49. [5]Hengwei F, Zifang H, Qifei W, et al. Epidemiology prevalence of idiopathic scoliosis in chinese schoolchildren: a large, population-based study. Spine.2016;(2):259-264.[6]Teixeira FA, Carvalho GA. Reliability and validity of thoracic kyphosis measurements using flexicurve method. Rev Bras Fisioter. 2007;11(3):199-204. [7]Ng JK, Kippers V, Richardson CA, et al. Range of motion and lordosis of the lumbar spine: reliability of measurement and normative values. Spine. 2011;26(1):53-60. [8]Doody MM, Lonstein JE, Stovali M, et al. Breast Cancer Mortality After Diagnostic Radiography. Findings From the U.S. Scoliosis Cohort Study. Spine.2000;25:2052-2011.[9]Nash CL,Gregg EC, Brown RH, et al. Risks of exposure to X-rays in patients undergoing long term treatment for scoliosis.J Bone Joint Surg.1979;61:371-374.[10]Rao PS, Gregg EC.A revised estimate of the risk of carcinogenesis from X-rays to scoliosis patients. Invest Radiol. 1984;19:58-60.[11]Qiao J, Xu L, Zhu Z, et al. Inter- and intraobserver reliability assessment of the axial trunk rotation: manual versus smartphone-aided measurement tools. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15(1):343.[12]Döhnert MB, Tomasi E. Validity of computed photogrammetry for detecting idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents. Rev Bras Fisioter. 2008;12:290-296.[13]Murrel GAC, Coonrad RW, Moorman CT, et al. An Assesment of the Reliability of the Scoliometer. Spine.1993;18:709-703.[14]Bonagamba GH, Coelho DM, Oliveira AS. Inter and intra-raterreliability of the scoliometer. Rev Bras Fisioter. 2010;14:432-438.[15]Coelho DM, Bonagamba GH, Oliveira AS. Scoliometer measurements of patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Braz J Phys Ther. 2013;17(2):179-184.[16]Carlson BB, Burton DC, Asher MA. Comparison of trunk and spine deformity in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis. 2013;8(1):2.[17]Criswell E. Cram’s introduction to Surface Electromyography. MA: Jonesand Bartlett, 2009:3.[18]Odermatt D, Mathieu PA, Beausejour M, et al. Electromyography of scoliotic patients treated with a brace. J Orthop Res. 2003;21:931-936.[19]Cheung J, Veldhuizen AG, Halberts JP, et al. Geometric and electromyographic assessments in the evaluation of curve progression in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2006;31:322-329.[20]Zoabli G, Mathieu PA, Aubin CE. Back muscles biometry in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J. 2007;(7): 338-344.[21]Mannion AF, Meier M, Grob D. Paraspinal muscle fibre type alterations associated with scoliosis: an old problem revisited with new evidence. Eur Spine J. 1998;(7):289-293.[22]Kwok G, Yip J, Cheung MC, et al. Evaluation of myoelectric activity of paraspinal muscles in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis during habitual standing and sitting. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:958. [23]Nestoriuc Y, Martin A, Rief W, et al. Biofeedback treatment for headache disorders: a comprehensive efficacy review. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2008;33(3):125-140.[24]Ahmed MU, Begum S, Funk P, et al. A multi-module case-based biofeedback system for stress treatment. Artif Intell Med. 2011;51(2):107-115. [25]Kappes B. Biofeedback therapy: training or treatment. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2008;33:173-179.[26]DeVries HA. Efficiency of electrical activity" as a physiological measure of the functional state of muscle tissue. Am J Phys Med. 1968; 47(1):10-22.[27]Christenstensen H, Lo Monaco M, Dahl K, et al. Progressing of electrical activity in human muscle during a gradual increase in force. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1984;58(3):230-239.[28]de Oliveira AS, Gianini PE, Camarini PM, et al. Electromyographic analysis of paravertebral muscles in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2011;36(5):E334-339. [29]Kwok G, Yip J, Cheung MC, et al. Evaluation of myoelectric activity of paraspinal muscles in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis during habitual standing and sitting. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015: 958450.[30]Cheung J, Veldhuizen AG, Halberts JP, et al. Geometric and electromyographic assessments in the evaluation of curve progression in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006 ;31(3):322-329. [31]Mannion AF, Meier M, Grob D, et al. Paraspinal musclefibre type alterations associated with scoliosis: An old problemrevisited with new evidence. Eur Spine J. 1998; 7(4):289-293.[32]Bylund P, Jansson E, Dahlberg E, et al. Muscle fiber types inthoracic erector spinae muscles fiber types in idiopathicand other fo RMS of scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(214): 222-228. |