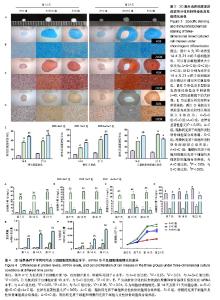
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (17): 2661-2668.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0537
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and synovial-derived mesenchymal stem cells synergistically inhibit the degeneration of inflammatory chondrocytes
Song Zhuo-yue, Wang Yang, Lian Xiao-lei, Ding Kang, Li Guang-heng
- Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2018-03-22Online:2018-06-18Published:2018-06-18 -
Contact:Li Guang-heng, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Song Zhuo-yue, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81472136
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Zhuo-yue, Wang Yang, Lian Xiao-lei, Ding Kang, Li Guang-heng. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and synovial-derived mesenchymal stem cells synergistically inhibit the degeneration of inflammatory chondrocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(17): 2661-2668.
share this article
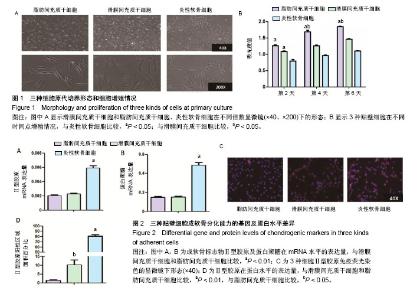
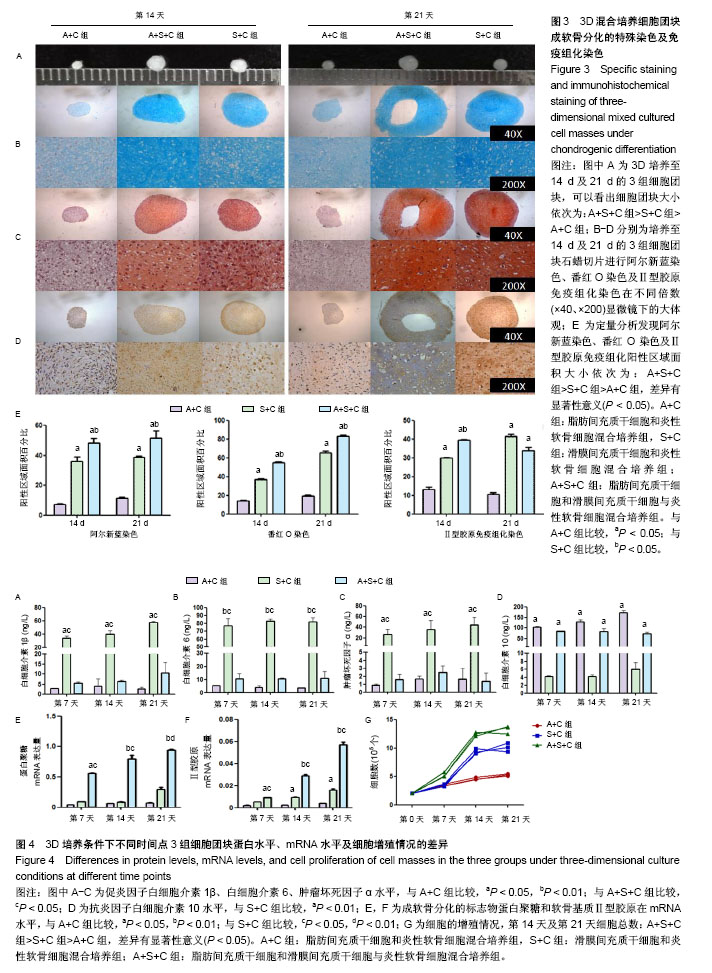
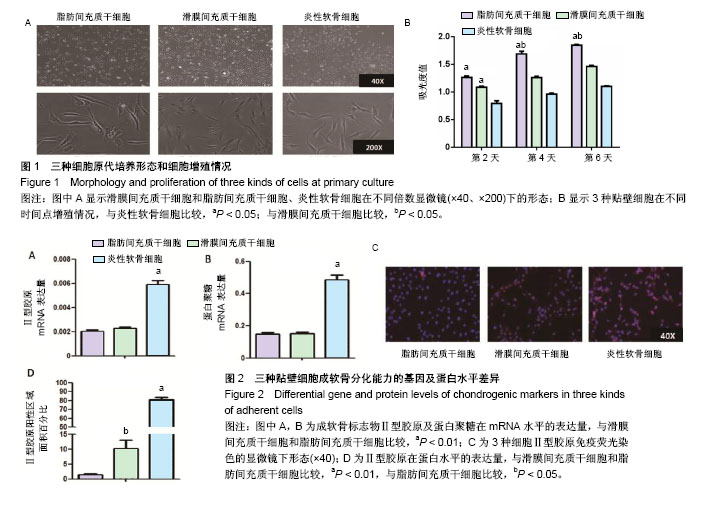
2.1 原代细胞培养及细胞增殖情况 图1A为原代培养的3种细胞即ADMSCs、SDMSCs、炎性软骨细胞,均表现出类成纤维细胞的形态即细胞均呈现梭形,少数表现为多角形。软骨细胞呈现短梭形多分支,而另外2种细胞呈现长梭形。 图1B显示3种贴壁细胞在不同时间点细胞增殖情况,通过MTS细胞增殖实验发现第2天ADMSCs和SDMSCs的增殖速率开始大于炎性软骨细胞(ADMSCs 1.3±0.2,SDMSCs 1.1±0.1,软骨细胞0.7±0.1),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),但是前两者之间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。从第4天开始ADMSCs的增殖速率开始大于SDMSCs(ADMSCs 1.65±0.1,SDMSCs 1.3±0.2,软骨细胞1.0±0.1),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而SDMSCs和软骨细胞的增殖速率差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.2 贴壁细胞成软骨分化能力的基因及蛋白水平差异 图2A及2B显示炎性软骨细胞的成软骨标志物Ⅱ型胶原蛋白及蛋白聚糖在mRNA水平的表达量要高于ADMSCs、SDMSCs,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),而ADMSCs与SDMSCs的成软骨能力在mRNA水平上差异无显著性意义。图2C为3种细胞Ⅱ型胶原免疫荧光染色的显微镜下形态,通过图2D的定量分析显示炎性软骨细胞在蛋白水平表达的Ⅱ型胶原明显高于ADMSCs、SDMSCs,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),SDMSCsⅡ型胶原蛋白水平高于ADMSCs,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.3 3D混合培养细胞团块成软骨分化的特殊染色及免疫组化染色 图3A是3D培养至14 d及21 d的3组细胞团块,可以看出培养至14,21 d的细胞团块大小依次为:A+S+C组>S+C组>A+C组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。图3B-D分别为培养至14 d及21 d的3组细胞团块石蜡切片进行阿尔新蓝染色、番红O染色及Ⅱ型胶原免疫组化染色在不同倍数(×40、×200)显微镜下的大体观,图3E为定量分析发现阿尔新蓝染色、番红O染色及Ⅱ型胶原免疫组化阳性区域面积大小依次为:A+S+C组>S+C组>A+C组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.4 3D培养条件下不同时间点3组细胞团块蛋白水平、mRNA水平及细胞增殖情况的差异 为了进一步证明联合应用ADMSCs和SDMSCs对炎性软骨细胞退变的协同抑制作用,通过蛋白、基因及细胞增殖3方面进行解释。图4A-C分别显示在3个不同时间点S+C组分泌的促炎因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平均较A+C组及A+S+C组高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。而A+C组和A+S+C组在第7,14,21天分泌的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。图4D显示不同时间点A+C组和A+S+C组分泌的抗炎因子白细胞介素10水平明显高于S+C组,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。图4E显示7,14,21 d成软骨分化的标志物蛋白聚糖在mRNA水平A+S+C组明显高于A+C组和S+C组,且第21天S+C组表达量高于A+C组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。图4F显示7,14,21 d软骨基质Ⅱ型胶原在mRNA水平A+S+C组明显高于A+C组和S+C组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。第14,21天 S+C组表达量高于A+C组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。图4G显示不同时间点3组细胞的增殖情况,在0,7 d 3组细胞个数差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),而第14天及第21天,细胞总数:A+S+C组>S+C组>A+C组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] Craft AM, Ahmed N, Rockel JS, et al. Specification of chondrocytes and cartilage tissues from embryonic stem cells. Development. 2013;140(12):2597-2610.[2] Akkiraju H, Nohe A. Role of Chondrocytes in Cartilage Formation, Progression of Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Regeneration. J Dev Biol. 2015;3(4):177-192.[3] Koh YG, Choi YJ, Kwon SK, et al. Clinical results and second-look arthroscopic findings after treatment with adipose-derived stem cells for knee osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(5):1308-1316.[4] Marupanthorn K, Tantrawatpan C, Tantikanlayaporn D, et al. The Effects of TNF-α on Osteogenic Differentiation of Umbilical Cord Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015;98 Suppl 3:S34-40.[5] Latief N, Raza FA, Bhatti FU, et al. Adipose stem cells differentiated chondrocytes regenerate damaged cartilage in rat model of osteoarthritis. Cell Biol Int. 2016;40(5):579-588.[6] Freitag J, Ford J, Bates D, et al. Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the treatment of isolated knee chondral lesions: design of a randomised controlled pilot study comparing arthroscopic microfracture versus arthroscopic microfracture combined with postoperative mesenchymal stem cell injections. BMJ Open. 2015;5(12):e009332.[7] English A, Jones EA, Corscadden D, et al. A comparative assessment of cartilage and joint fat pad as a potential source of cells for autologous therapy development in knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46(11):1676-1683.[8] Chang YH, Liu HW, Wu KC, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Clinical Applications in Osteoarthritis. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(5):937-950.[9] Salyutin RV, Zapohlska KM, Palyanytsya SS, et al. Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells of adipose tissue. Klin Khir. 2015;(3):61-64.[10] Kessler MW, Ackerman G, Dines JS, et al. Emerging technologies and fourth generation issues in cartilage repair. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2008;16(4):246-254.[11] Zheng B, Li G, Chen WC, et al. Human myogenic endothelial cells exhibit chondrogenic and osteogenic potentials at the clonal level. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(7): 1089-1095.[12] Beane OS, Fonseca VC, Cooper LL, et al. Impact of aging on the regenerative properties of bone marrow-, muscle-, and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115963.[13] Matsumoto T, Cooper GM, Gharaibeh B, et al. Cartilage repair in a rat model of osteoarthritis through intraarticular transplantation of muscle-derived stem cells expressing bone morphogenetic protein 4 and soluble Flt-1. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(5):1390-1405.[14] Koga H, Muneta T, Nagase T, et al. Comparison of mesenchymal tissues-derived stem cells for in vivo chondrogenesis: suitable conditions for cell therapy of cartilage defects in rabbit. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;333(2): 207-215.[15] Yoshimura H, Muneta T, Nimura A, et al. Comparison of rat mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, synovium, periosteum, adipose tissue, and muscle. Cell Tissue Res. 2007;327(3):449-462.[16] Jo CH, Lee YG, Shin WH, et al. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a proof-of-concept clinical trial. Stem Cells. 2014;32(5):1254-1266.[17] Sekiya I, Muneta T, Horie M, et al. Arthroscopic Transplantation of Synovial Stem Cells Improves Clinical Outcomes in Knees With Cartilage Defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(7):2316-2326.[18] Henrotin Y, Clutterbuck AL, Allaway D, et al. Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(2):141-149.[19] Campbell DD, Pei M. Surface markers for chondrogenic determination: a highlight of synovium-derived stem cells. Cells. 2012;1(4):1107-1120.[20] Jones BA, Pei M. Synovium-derived stem cells: a tissue-specific stem cell for cartilage engineering and regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18(4):301-311.[21] Campbell DD, Pei M. Surface markers for chondrogenic determination: a highlight of synovium-derived stem cells. Cells. 2012;1(4):1107-1120.[22] Vilar JM, Morales M, Santana A, et al. Controlled, blinded force platform analysis of the effect of intraarticular injection of autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells associated to PRGF-Endoret in osteoarthritic dogs. BMC Vet Res. 2013;9:131.[23] Musumeci G, Mobasheri A, Trovato FM, et al. Biosynthesis of collagen I, II, RUNX2 and lubricin at different time points of chondrogenic differentiation in a 3D in vitro model of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue. Acta Histochem. 2014;116(8):1407-1417.[24] Platas J, Guillén MI, del Caz MD, et al. Conditioned media from adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells downregulate degradative mediators induced by interleukin-1β in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:357014.[25] Skalska U, Kontny E. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from infrapatellar fat pad of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis have comparable immunomodulatory properties. Autoimmunity. 2016;49(2): 124-131.[26] Mei L, Shen B, Ling P, et al. Culture-expanded allogenic adipose tissue-derived stem cells attenuate cartilage degeneration in an experimental rat osteoarthritis model. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0176107.[27] Pagani S, Borsari V, Veronesi F, et al. Increased Chondrogenic Potential of Mesenchymal Cells From Adipose Tissue Versus Bone Marrow-Derived Cells in Osteoarthritic In Vitro Models. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(6): 1478-1488.[28] Manferdini C, Maumus M, Gabusi E, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells exert antiinflammatory effects on chondrocytes and synoviocytes from osteoarthritis patients through prostaglandin E2. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(5): 1271-1281.[29] Ivanova-Todorova E, Bochev I, Dimitrov R, et al. Conditioned medium from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells induces CD4+FOXP3+ cells and increases IL-10 secretion. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012: 295167.[30] Park MJ, Kwok SK, Lee SH, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce expansion of interleukin-10-producing regulatory B cells and ameliorate autoimmunity in a murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(11):2367-2377.[31] Nava MM, Zandrini T, Cerullo G, et al. 3D Stem Cell Niche Engineering via Two-Photon Laser Polymerization. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1612:253-266.[32] Payr S, Tichy B, Atteneder C, et al. Redifferentiation of aged human articular chondrocytes by combining bone morphogenetic protein-2 and melanoma inhibitory activity protein in 3D-culture. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0179729.[33] Sieber S, Wirth L, Cavak N, et al. Bone marrow-on-a-chip: Long-term culture of human haematopoietic stem cells in a three-dimensional microfluidic environment. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):479-489. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [5] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [6] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [7] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [8] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [9] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [10] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [11] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [12] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [13] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [14] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [15] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||