Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 2968-2973.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0281
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation of intraoperative ligament stability with functional outcomes following total knee arthroplasty
Liu Qing-kuan, Wang Guo-dong, Wang Cheng-qun, Kong Ying, Niu Shuai-shuai, Ma Long-fei
- Department of Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining 272029, Shandong Province, China
-
Online:2018-07-08Published:2018-07-08 -
Contact:Wang Guo-dong, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining 272029, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Qing-kuan, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining 272029, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Qing-kuan, Wang Guo-dong, Wang Cheng-qun, Kong Ying, Niu Shuai-shuai, Ma Long-fei. Correlation of intraoperative ligament stability with functional outcomes following total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 2968-2973.
share this article
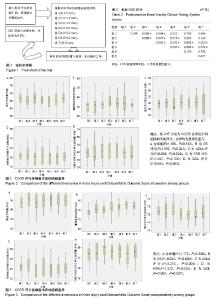
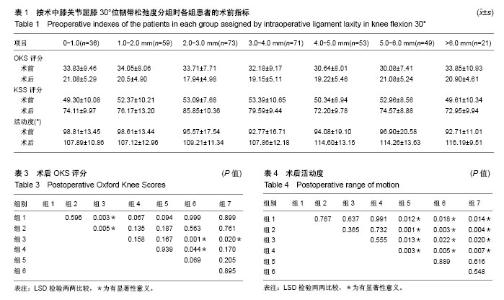
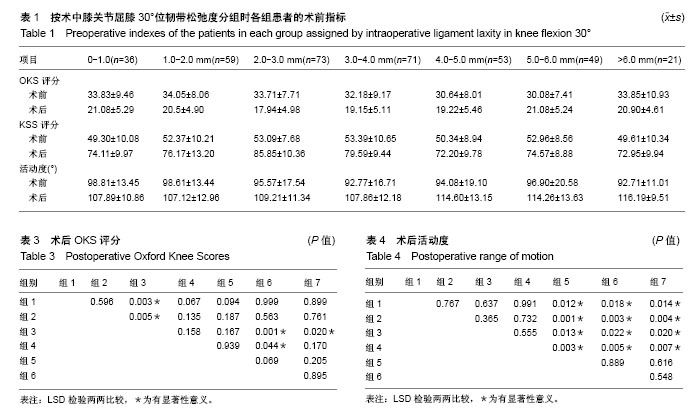
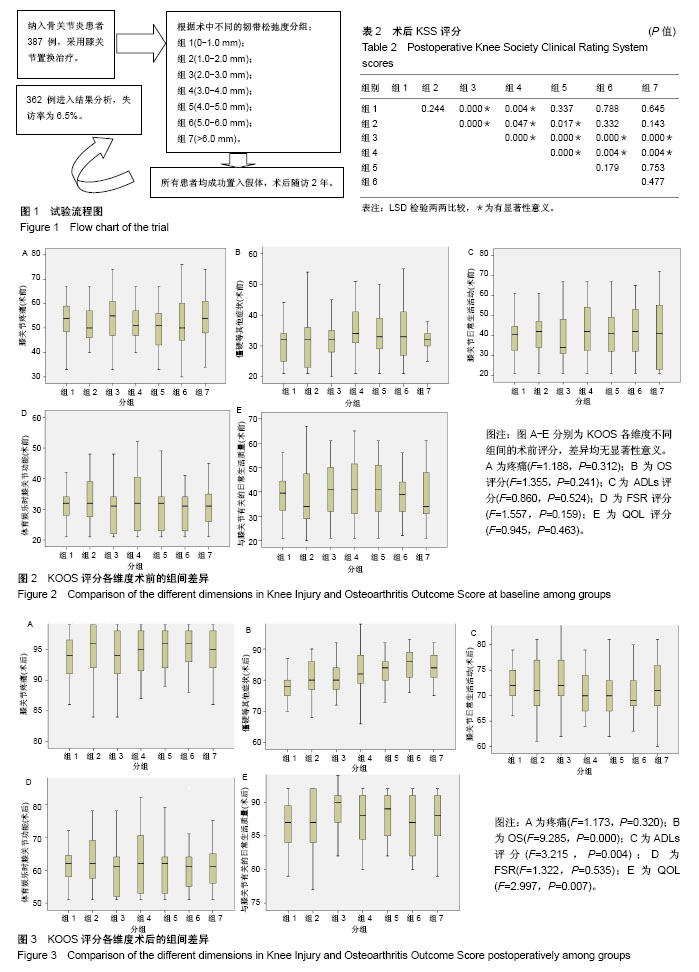
2.1 参与者数量分析 387例患者符合纳入标准,随访时间为2年,最终获得随访的患者有362例,失访率为6.5%,失访原因包括迁移去外地(12例)、因合并症治疗(8例)及联系不到(5例)等,见图1。 2.2 术前各组功能评分 根据术中韧带松弛度分组,回溯术前各组患者的KSS评分(F=1.507,P=0.175)、OKS评分(F=1.926,P=0.076),各组间差异无显著性意义;术前各组患者的活动度各组间差异无显著性意义(F=1.092,P=0.366),见表1;术前KOOS评分不同维度下各组间差异无显著性意义(图2)。 2.3 术后各组功能评分 术后患者的膝关节功能评分(KSS及OKS评分)均较术前有明显改善(表1)。术后KSS评分各组间差异有显著性意义(F=16.273,P=0.000),LSD检验两两比较见表2,评分最高的2组为组3(2.0-3.0 mm)和组4(3.0-4.0 mm),分别为85.85±10.36 和79.59±9.44;术后OKS评分,各组间差异有显著性意义(F=3.103,P=0.006),LSD检验两两比较见表3,评分最低的组3(2.0-3.0mm)为17.94±4.98,其余各组差异不大;术后膝关节活动度,各组间差异有显著性意义(F=4.227,P=0.000),LSD检验两两比较见表4,活动度最大的是组6和组7,分别为(114.26±13.63)°和(116.19±9.51)°,这2组间差异无显著性意义。 2.4 术后KOOS评分 术后患者的KOOS评分各维度均较术前明显改善(图3)。术后KOOS疼痛及体育娱乐时膝关节功能评分各组间差异无显著性意义;僵硬等其他症状,AVONA显示各组间差异有显著性意义(F=9.285,P=0.000),LSD两两比较,评分最低的是组1(0-1.0 mm),为77.47±4.39,与其他各组间差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);评分最高的是组6和组7,分别为84.87±4.89和83.95±3.76,与其他各组间差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);膝关节的日常生活活动评分,AVONA显示各组间差异有显著性意义(F=3.215,P=0.004),LSD两两比较,评分最高的是组3(2.0-3.0 mm),为73.05±4.74,与组4-7之间的差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 膝关节有关的日常生活质量评分,AVONA显示各组间差异有显著性意义(F=2.997,P=0.007),LSD两两比较,评分最高的是组3(2.0-3.0 mm),为89.00±3.10,与其余各组之间的差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] Parratte S, Pagnano MW. Instability after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:184. [2] Mihalko WM, Krackow KA. Flexion and extension gap balancing in revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;446: 121-126.[3] Takeda M, Ishii Y, Noguchi H, et al. Changes in varus-valgus laxity after total knee arthroplasty over time. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20:1988-1993.[4] Matsumoto T, Muratsu H, Tsumura N, et al. Soft tissue balance measurement in posterior- stabilized total knee arthroplasty with a navigation system. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:358-364. [5] Warren PJ, Olanlokun TK, Cobb AG, et al. Laxity and function in knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;305:200. [6] Edwards E, Miller J, Chan KH. The effect of post-operative collateral ligament laxity ?in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;236:44. [7] Paxton EW, Furnes O, Namba RS, et al. Comparison of the Norwegian knee arthroplasty register and a United States arthroplasty registry. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 2011;93(Suppl 3):20-30.[8] Asano H, Muneta T, Sekiya I.Soft tissue tension in extension in total knee arthroplasty affects postoperative knee extension and stability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16:999-1003.[9] Kuster MS, Bitschnau B, Votruba T. Influence of collateral ligament laxity on patient satisfaction after total knee arthro- plasty: a comparative bilateral study. Arch OrthopTrauma Surg. 2004;124: 415-417. [10] Mihalko WM, Whiteside LA, Krackow KA. Comparison of ligament-balancing techniques during total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 2003;85-A(Suppl 4):132-135. [11] Whiteside LA. Selective ligament release in total knee arthroplasty of the knee in valgus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;367:130-140.[12] Whiteside LA, Saeki K, Mihalko WM. Functional medial ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; 380:45–57.[13] Collins NJ, Roos EM. Patient-reported outcomes for total hip and knee arthroplasty: commonly used instruments and attributes of a ‘‘good’’ measure. Clin Geriatr Med. 2012;28:367-394.[14] Roos EM, Lohmander LS. The Knee injury and Osteoar- thritis Outcome Score (KOOS): from joint injury to osteoarthritis. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2003;1:64.[15] Jenny JY, Louis P, Diesinger Y . High activity arthroplasty score has a lower ceiling effect than standard scores after knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2014;29:719-721. [16] Vince KG, Abdeen A, Sugimori T. The unstable total knee arthroplasty: causes and?cures. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(4 Suppl. 1):44. [17] Kim J, Nelson CL, Lotke PA. Stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. Prevalence of the complication and outcomes of revision. J Bone Joint Surg(Am).2004;86:1479.[18] Seah RB, Pang HN, Lo NN, et al.Evaluation of the relationship between anteroposterior translation of a posterior cruciate ligament-retaining total knee replacement and functional outcome. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2012;94:1362-1365.[19] Heesterbeek PJ, Verdonschot N, Wymenga AB.In vivo knee laxity in flexion and extension: a radiographic study in 30 older healthy subjects. Knee. 2008;15:45-49.[20] Bellemans J, Vandenneucker H, Van LJ, et al. A new surgical technique for medial collateral ligament balancing: multiple needle puncturing. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25:1151-1156.[21] Aunan E, Kibsgard T, Clarke-Jenssen J, et al. A new method to measure ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty: laxity measurements in 100 knees. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132: 1173-1181.[22] Whitehouse SL, Blom AW, Taylor AH, et al. The Oxford Knee Score: problems and pitfalls. Knee. 2005;12(4): 287.[23] Kleeblad LJ, Borus TA, Coon TM, et al. Midterm survivorship and patient satisfaction of robotic-arm-assisted medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: A Multicenter Study. J Arthroplasty. 2018; S0883-5403(18):30074-30083.[24] Park BJ, Cho HM, An KY, et al. Acute arterial occlusion following primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2018;30(1): 84-88.[25] Malik AT, Azmat SK, Ali A, et al. Seasonal influence on postoperative complications after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2018;30(1):42-49.[26] Palsis JA, Brehmer TS, Pellegrini VD, et al. The cost of joint replacement: comparing two approaches to evaluating costs of total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(4): 326-333.[27] Namba RS, Inacio MCS, Pratt NL, et al. Persistent opioid use following total knee arthroplasty: a signal for close surveillance. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):331-336.[28] Wilson CJ, Theodoulou A, Damarell RA, et al. Knee instability as the primary cause of failure following Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA): A systematic review on the patient, surgical and implant characteristics of revised TKA patients. Knee. 2017;24(6):1271-1281.[29] Lim JBT, Chong HC, Pang HN, et al. Revision total knee arthroplasty for failed high tibial osteotomy and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty have similar patient-reported outcome measures in a two-year follow-up study. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(10):1329-1334.[30] Cancienne JM, Granadillo VA, Patel KJ, et al. Risk factors for repeat debridement, spacer retention, amputation, arthrodesis, and mortality after removal of an infected total knee arthroplasty with spacer placement. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):515-520.[31] Koh YG, Son J, Kwon SK,et al. Preservation of kinematics with posterior cruciate-, bicruciate- and patient-specific bicruciate-retaining prostheses in total knee arthroplasty by using computational simulation with normal knee model. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(9):557-565. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [4] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [5] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [6] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [7] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [11] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [12] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [13] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [14] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [15] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||