Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4125-4136.doi: 10.12307/2026.685
Previous Articles Next Articles
A Transformer-based convolutional neural network fusion approach for single inertial recognition of lumbar rehabilitation exercises
Yu Shenghan1, 2, Cheng Xiankai1, 2, Zheng Yue1, 2, Yang Ying2, 3
- 1School of Biomedical Engineering (Suzhou), University of Science and Technology of China, Suzhou 215163, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215163, Jiangsu Province, China; 3The People’s Hospital of Suzhou New District, Suzhou 215129, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2025-07-01Accepted:2025-08-22Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-27 -
Contact:Cheng Xiankai, MS, Associate researcher, School of Biomedical Engineering (Suzhou), University of Science and Technology of China, Suzhou 215163, Jiangsu Province, China; Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215163, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Yu Shenghan, MS candidate, School of Biomedical Engineering (Suzhou), University of Science and Technology of China, Suzhou 215163, Jiangsu Province, China; Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215163, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. 2023YFC3604804; Key Research and Development Program Project of Jiangsu Province, No. BE2022064-2 (to CXK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Shenghan, Cheng Xiankai, Zheng Yue, Yang Ying. A Transformer-based convolutional neural network fusion approach for single inertial recognition of lumbar rehabilitation exercises[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4125-4136.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
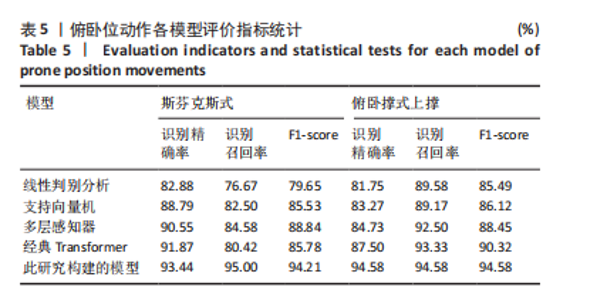
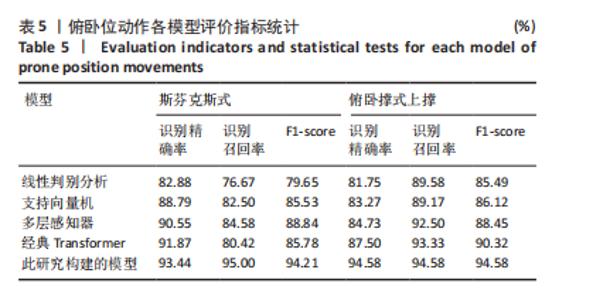
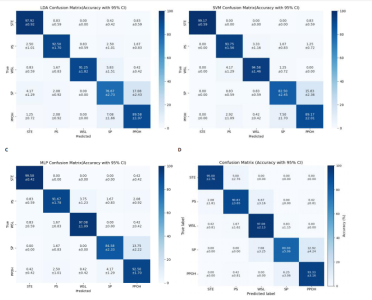
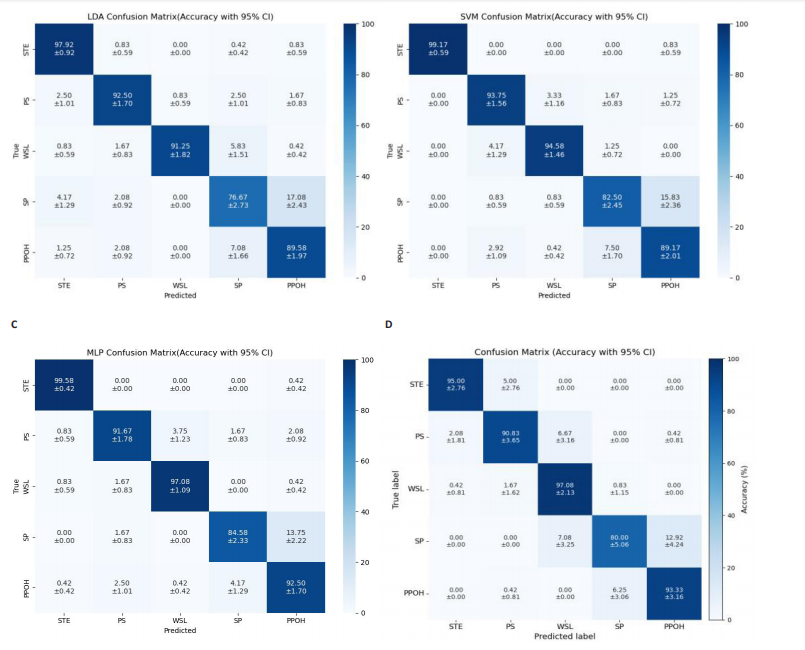
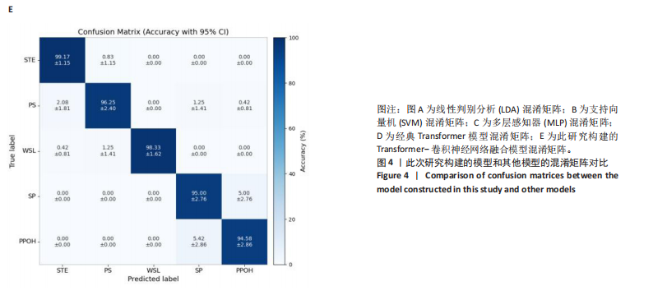
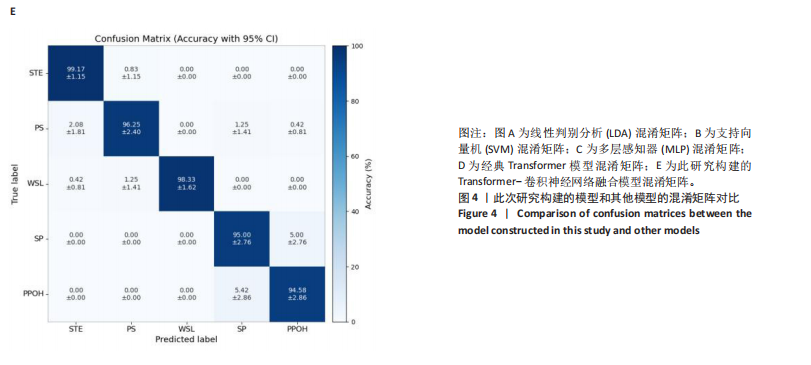
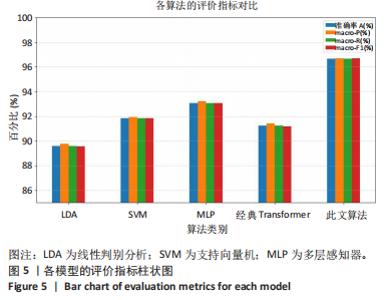
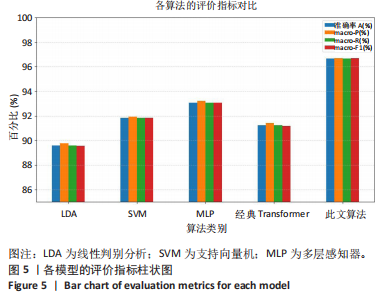
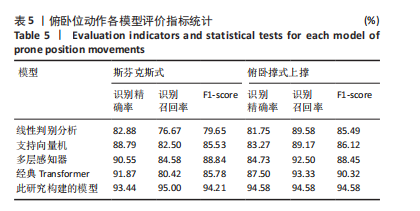
2.1 混淆矩阵对比 为验证模型先进性,设置3类基线模型,传统机器学习方法线性判别分析、支持向量机、浅层神经网络多层感知器(64-32隐藏层)以及单模态深度学习经典Transformer模型。比较CNN-Transformer模型和经典Transformer模型与传统机器学习模型在留一法交叉验证得到的混淆矩阵(95%置信区间),结果如图4所示。由图4可发现,CNN-Transformer模型的混淆矩阵的对角元素值多数比经典 Transformer模型的对角元素值大,尤其是在分辨普拉提锯式和斯芬克斯式2种动作时,改进Transformer模型具有明显更优异的分类精度。另外,改进 Transformer模型的混淆矩阵非对角线上比经典Transformer模型具有更少的误分类,尤其是对于容易混淆的普拉提锯式和斯芬克斯式2个动作。因此,改进Transformer模型可以有效提高识别准确率并减小误分类概率,相对于经典Transformer模型在分类准确性和鲁棒性方面有明显提升。 2.2 分类性能对比 表3列出了在测试集中,5种动作的识别精确率、召回率以及 F1-score。测试集总样本量为1 200个,包括:站立腰部伸展(20%)、普拉提锯式(20%)、单腿风车(20%)、斯芬克斯式(20%)、俯卧撑式上撑(20%)其中斯芬克斯式、俯卧撑式上撑的F1-score相对较低,主要是因为二者都有一个躯干上抬的动作,是一个波动的过程,当人体重心较低时,斯芬克斯式会与俯卧撑式上撑动作产生部分重叠。而不同的人运动习惯不同,甚至同一个人重复做同一动作时也不会一成不变,从而导致运动时重心出现变化,当重心都较低时,则易导致算法将斯芬克斯式和俯卧撑式上撑混淆。 由表4和图5可见,此研究构建的模型各类评价指标优于现有的传统线性判别分析与支持向量机模型,识别准确率分别比二者提高了7.09%和4.84%。相较浅层神经网络多层感知器,此次研究"
| [1] 李鑫,王楚怀.慢性腰痛的物理治疗新进展[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2021,36(6):738-742. [2] 胡玉彩.虚拟现实技术在慢性腰痛病人恐动症管理中的应用进展[J].全科护理,2024,22(16):3019-3022. [3] ROREN A, DASTE C, COLEMAN M, et al. Physical activity and low back pain: A critical narrative review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2023;66(2): 101650. [4] MAHER CG. Effective physical treatment for chronic low back pain. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004;35(1):57-64. [5] LIU Y, NIE L, LIU L, et al.From action to activity:sensor-based activity recognition. Neurocomputing. 2016;18:108-115. [6] 郭毅博,孟文化,范一鸣,等.基于可穿戴传感器数据的人体行为识别数据特征提取方法[J].计算机辅助设计与图形学学报,2021, 33(8):1246-1253. [7] SUN Z, KE Q, RAHMANI H, et al.Human action recognition from various data modalities:A review. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2022; 45(3):3200-3225. [8] GU M, CHEN Z, CHEN K, et al. RMPCT-Net: a multi-channel parallel CNN and transformer network model applied to HAR using FMCW radar. Signal Image Video Process. 2024;18(3):2219-2229. [9] BAVAN L, SURMACZ K, BEARD D, et al. Adherence monitoring of rehabilitation exercise with inertial sensors: A clinical validation study.Gait Posture. 2019;70:211-217. [10] LEE K, KIM J H, HONG H, et al. Deep learning model for classifying shoulder pain rehabilitation exercises using IMU sensor.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2024;21(1):42. [11] KÁRASON H, RITROVATO P, MAFFULLI N, et al. Wearable approaches for non-invasive monitoring of tendons: A scoping review. Internet Things. 2024:101199. [12] FOURNIOL M, VAUCHÉ R, RAO G, et al. Elbow Joint Angle Estimation Using a Low-Cost and Low-Power Single Inertial Device for Daily Home-Based Self-Rehabilitation. J Low Power Electron Appl. 2025;15(2):33. [13] BAILO G, SAIBENE FL, BANDINI V, et al. Characterization of walking in mild Parkinson’s disease: Reliability, validity and discriminant ability of the six-minute walk test instrumented with a single inertial sensor. Sensors. 2024;24(2):662. [14] PAN H, WANG H, LI D, et al. Automated, IMU-based spine angle estimation and IMU location identification for telerehabilitation. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2024;21(1):96. [15] PARK CH, BEOM J, CHUNG CK, et al. Long-term effects of lumbar flexion versus extension exercises for chronic axial low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):2714. [16] GORDON R, BLOXHAM S. A systematic review of the effects of exercise and physical activity on non-specific chronic low back pain. Healthcare. 2016;4(2):22. [17] DOTTI G, CARUSO M, FORTUNATO D, et al. A Statistical Approach for Functional Reach-to-Grasp Segmentation Using a Single Inertial Measurement Unit. Sensors. 2024;24(18):6119. [18] REPNIK E, PUH U, GOLJAR N, et al. Using inertial measurement units and electromyography to quantify movement during action research arm test execution. Sensors. 2018;8(9):2767. [19] CUI JW, LI ZG, DU H, et al. Recognition of upper limb action intention based on IMU. Sensors. 2022;22(5):1954. [20] BONNET V, JOUKOV V, KULIĆ D, et al. Monitoring of hip and knee joint angles using a single inertial measurement unit during lower limb rehabilitation. IEEE Sens J. 2015;16(6):1557-1564. [21] SIVULA T, MAGNUSSON M, MATAMOROS AA, et al. Uncertainty in Bayesian leave-one-out cross-validation based model comparison. arXiv. 2022;2008:10296. [22] BOTONIS OK, HARARI Y, EMBRY KR, et al. Wearable airbag technology and machine learned models to mitigate falls after stroke. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2022;19(1):60. [23] NAIR S, DHINESH R, SRICHARAN V, et al. A Hybrid Approach to Estimate Vertical Oscillation Using a Chest-Worn Accelerometer Device//2024 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA). IEEE. 2024:1-6. [24] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2017:30. [25] SHAVIT Y, KLEIN I.Boosting inertial-based human activity recognition with transformers. IEEE Access. 2021;9:53540-53547. [26] WALUGEMBE H, PHILLIPS C, REQUENA-CARRIÓN J, et al. Gesture Recognition in Leap Motion Using LDA and SVM, IEEE International Conference on Computing, Electronics & Communications Engineering (iCCECE). IEEE. 2019:56-61. [27] SHIN D, LEE S, HWANG S. Locomotion mode recognition algorithm based on Gaussian mixture model using IMU sensors. Sensors. 2021; 21(8):2785. [28] 龚海军.多模融合的手势识别关键技术研究[D].北京:北京邮电大学,2020. [29] ZHENG J, PENG M, HUANG L, et al. A CNN–SVM model using IMU for locomotion mode recognition IN lower extremity exoskeleton. J Mech Med Biol. 2022;22(6):2250043. [30] 夏迪.稀疏惯性三维人体姿态估计研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2023. [31] 何依.基于CNN和Transformer的医学图像分割方法研究[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江科技大学,2024. [32] CHEN W, FENG L, LU J, et al. An extended spatial transformer convolutional neural network for gesture recognition and self-calibration based on sparse sEMG electrodes. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2022;16(6):1204-1215. [33] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2015;28. [34] 陈从平,郁春明,闫焕章,等.基于改进Transformer的三维人体姿态估计[J].传感器与微系统,2024,43(6):117-121. [35] 张澳平.基于卷积神经网络和Transformer的医学图像分割算法研究[D].镇江:江苏科技大学,2024. [36] 毛琦.基于滑动窗口Transformer的运动想象脑电识别算法研究[D].西安:西安理工大学,2024. [37] 李成建.基于Transformer的睡眠呼吸暂停综合征检测方法研究[D].西安:西安理工大学,2024. [38] FEIGL T, KRAM S, WOLLER P, et al. A bidirectional LSTM for estimating dynamic human velocities from a single IMU//2019 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN). IEEE. 2019:1-8. [39] LEE CJ, LEE JK. IMU-Based Energy Expenditure Estimation for Various Walking Conditions Using a Hybrid CNN–LSTM Model. Sensors. 2024; 24(2):414. [40] HOU C. A study on IMU-based human activity recognition using deep learning and traditional machine learning//2020 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS). IEEE. 2020:225-234. [41] 史立宇,孙杨帆,谢溢翀,等.基于无阈值递归图和CNN-LSTM的人体活动识别算法[J].传感器与微系统,2025,44(3):130-133. [42] SHEN R, SHE Q, SUN G, et al. Max-Pooling Based Self-Attention with Transformer for Speaker Verification[C]//2023 7th International Conference on Machine Vision and Information Technology (CMVIT). IEEE. 2023:12-16. [43] GARG M, GHOSH D, PRADHAN PM. Gestformer: Multiscale wavelet pooling transformer network for dynamic hand gesture recognition//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024:2473-2483. [44] CHEN Z, XIE L, NIU J, et al. Visformer: The vision-friendly transformer//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2021:589-598. [45] GIRDHAR R, RAMANAN D. Attentional pooling for action recognition.//Advances in neural information processing systems. 2017:30. [46] GHOLAMALINEZHAD H, KHOSRAVI H. Pooling methods in deep neural networks, a review. arXiv preprint arXiv. 2020;2009.07485. [47] ZHANG D, HONG M, ZOU L, et al. Attention pooling-based bidirectional gated recurrent units model for sentimental classification. Int J Comput Intell Syst. 2019;12(2):723-732. [48] CHEN Y, MA G, YUAN C, et al. Graph convolutional network with structure pooling and joint-wise channel attention for action recognition. Pattern Recognition. 2020;103:107321. [49] ER MJ, ZHANG Y, WANG N, et al. Attention pooling-based convolutional neural network for sentence modelling. Information Sciences. 2016; 373:388-403. [50] TRUJILLO-GUERRERO MF, ROMÁN-NIEMES S, JAÉN-VARGAS M, et al. Accuracy comparison of CNN, LSTM, and transformer for activity recognition using IMU and visual markers. IEEE Access. 2023;11: 106650-106669. [51] SHAIKH MB, CHAI D, ISLAM SMS, et al. From CNNs to transformers in multimodal human action recognition: A survey. ACM Trans Multim Comput Commun Appl. 2024;20(8):1-24. |
| [1] | Zhou Jian, Zhang Tao, Zhou Weili, Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Shen Jie, Qian Li, Lu Ming. Effects of resistance training on quadriceps mass and knee joint function in patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [2] | Yang Chong, Wu Yuci, Yang Han, Wang Meiting, Liu Lei. Promoting effect of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training on the reconstruction of damaged neurological function in rats with cerebral infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4347-4356. |
| [3] | Hou Bing, Zhao Hongfei, Che Pengcheng, Wang Ziyi, Gao Zan, Chen Linyu, Wang Jinzhi, Dou Na. Analysis of upper limb motor function and brain function immediately and 3 weeks after transcranial direct current stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3066-3074. |
| [4] | Ma Shanxin, Zheng Jianling, Cheng Jian, Lin Xi, Li Qiuyuan, Wang Li, Zeng Yangkang, Song Luping. Early intelligent active assistance in walking for hemiplegic patients under suspension protection: #br# a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3075-3082. |
| [5] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [6] | Fang Ying, Zhang Yanwei, Li Xi, Yan Peidong, Bi Miao. Improvements in automatic diagnosis methods for knee osteoarthritis based on deep learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7511-7518. |
| [7] | Wang Simin, Zhang Dezhou, Zhao Jing, Wang Chaoqun, Li Kun, Chen Jie, Bai Xue, Zhao Hailong, Zhang Shaojie, Ma Yuan, Hao Yunteng, Yang Yang, Li Zhijun, Shi Jun, Wang Xing. Artificial intelligence and cervical spine image recognition: application prospects and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7231-7240. |
| [8] | Song Haoran, Zhang Yuqiang, Gu Na, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Visualization analysis of artificial intelligence in bone trauma research based on Citespace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 493-502. |
| [9] | Zhang Ziyu, Chen Longhao, Sheng Wei, Lyu Hanzhe, Shen Ying, Wang Binghao, Lyu Zhizhen, Lyu Lijiang. Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation: evolution towards standardization, efficiency, and precision of diagnosis and treatment methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6269-6276. |
| [10] | Cao Haijie, Song Huijie, Sun Yalu, Zhang Guangyou, Li Xiang. A wearable exoskeleton with posture feedback improves abnormal gait in patients with stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5127-5133. |
| [11] | Wei Mengli, Zhong Yaping, Gui Huixian, Zhou Yiwen, Guan Yeming, Yu Shaohua. Sports injury prediction model based on machine learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 409-418. |
| [12] | Zhang Dakuan, Li Yongjie, Han Libao, Liu Hongju, Liu Mengling, Fu Shenyu . Blood flow restriction training in the prevention and rehabilitation of foot and ankle injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2553-2559. |
| [13] | Yang Yuxuan, Tan Jingyi, Zhou Lili, Bian Zirui, Chen Yifan, Wu Yanmin. Application of deep learning in oral imaging analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2385-2393. |
| [14] | Tan Xin, Zhang Hongyue, Zhao Yuchan, Qin Chun, Xu Shuogui. Application of shape memory alloys in assistive devices and rehabilitation equipment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2113-2123. |
| [15] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||